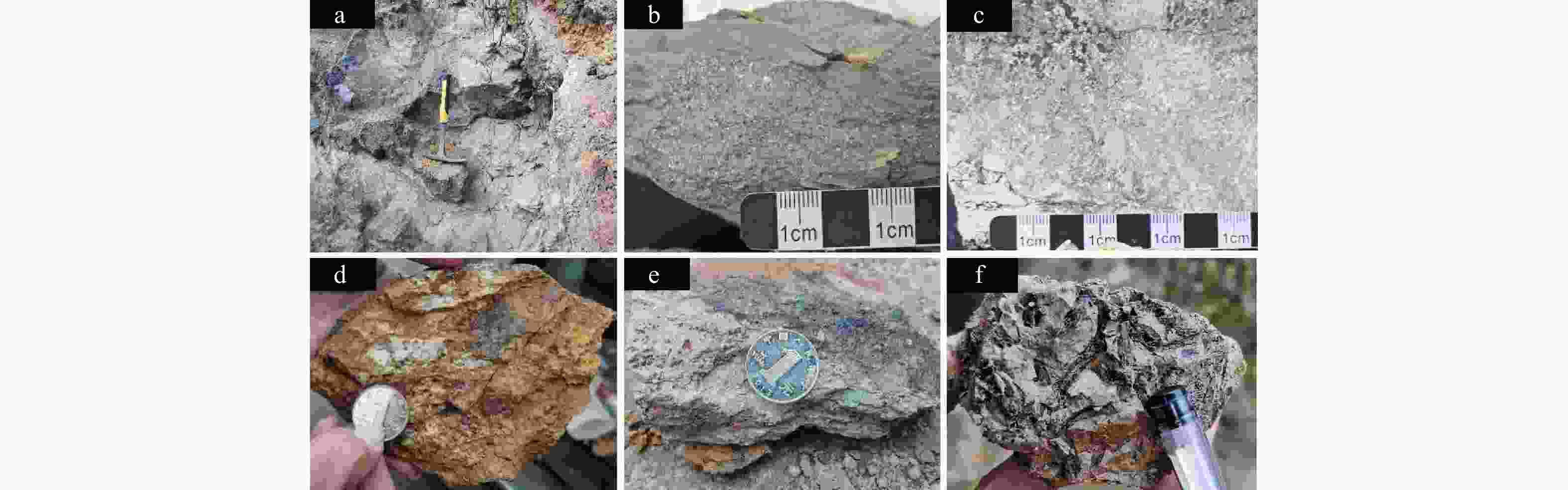
Enrichment characteristics and occurrence of Nb in clay rocks in the lower part of Upper Permian Longtan Formation in Xingwen area, southern Sichuan
-
摘要:
我国关键金属铌(Nb)资源匮乏,被“卡脖子”的风险高,为了破解这一困局,加强新类型铌矿床的研究和地质勘探迫在眉睫。以川南兴文地区上二叠统龙潭组(P3
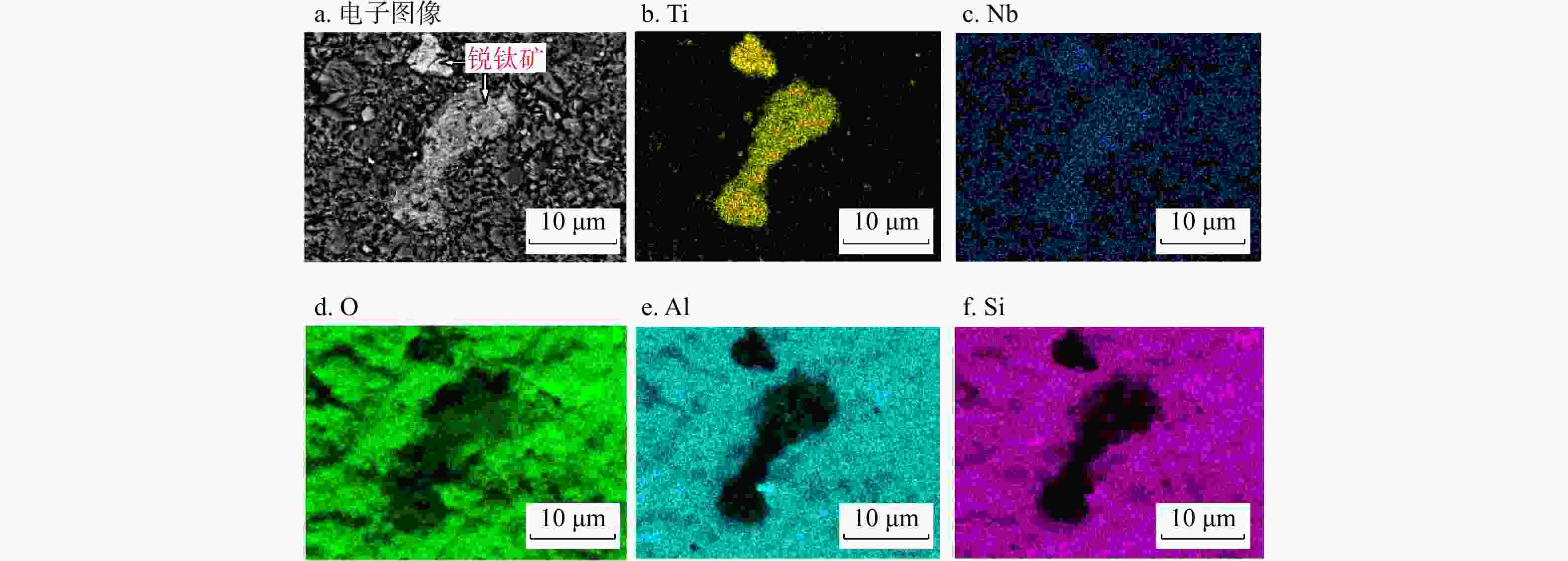
l )下部黏土岩为研究对象,在样品铌含量分析的基础上,结合粉晶X射线衍射(XRD)、扫描电镜−能谱(SEM-EDS)、电子探针(EPMA)等手段,对富Nb样品进行了矿物鉴定及定量分析。结果表明,黏土岩中Nb2O5质量分数为41×10−6~437×10−6,平均187.2×10−6,达到了风化壳型矿床的最低工业指标,Li、Ga等元素富集程度也较高,是多种关键金属的富集层,具有良好的成矿潜力和找矿前景。粉晶X射线衍射(XRD)分析显示富铌黏土岩中含有较丰富锐钛矿,电子探针(EPMA)分析表明锐钛矿中Nb2O5的质量分数为0.09%~3.40%,平均1.17%。依据锐钛矿中铌含量、扫描电镜−能谱(SEM-EDS)扫面,以及全岩样品Nb2O5的含量特征,认为铌主要以类质同象形式赋存于锐钛矿之中,还有一部分被黏土矿物所吸附。Nb主要继承自峨眉山玄武岩中榍石等矿物的风化产物,风化作用的强弱对Nb富集成矿具有重要的影响,为风化−沉积型矿床。研究成果为铌资源地质找矿、资源评价以及综合开发利用提供科学依据。Abstract:Niobium(Nb) is a critical metal, and China faces a high risk of being "strangled" due to the limited availability of niobium.
Objective To address this challenge, it is imperative to strengthen the research and geological exploration of new types of niobium deposits.
Methods This study focuses on the clay rocks in the lower part of the Upper Permian Longtan Formation (P3
l ) in Xingwen area of southern Sichuan. Based on the analysis of Nb contents in the collected samples, we combine various analytical techniques such as X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy with energy dispersive spectrometer (SEM-EDS), and electron probe micro-analyzer (EPMA) to conduct mineral identification and quantitative analysis on Nb-enriched samples.Results The results show that the content of Nb2O5 in the clay rocks ranges from 41×10−6 to 437×10−6, with an average of 187.2×10−6, reaching the lowest industrial indicator for weathering crust-type deposits. The enrichment of elements like Li, Ga, and others is also significant, making the clay layer rich in multiple critical metals and possessing considerable ore-forming potential. XRD analysis reveals a substantial presence of anatase in the Nb-rich clay rock. EPMA analysis indicates that the content of Nb2O5 in anatase ranges from 0.09% to 3.40%, with an average of 1.17%. Based on the Nb content in anatase, SEM-EDS scanning, and the Nb2O5 content of whole-rock samples, we conclude that Nb primarily exists in anatase as an isomorphous substitution, and some are adsorbed by clay minerals. Nb is predominantly inherited from the weathering products of minerals such as sphene in the Emeishan basalts, and the weathering degree has a significant impact on the enrichment and mineralization of Nb, with characteristic of weathering-sedimentary deposit.
Conclusion The research results provide a scientific basis for the geological prospecting, resource evaluation, and comprehensive development and utilization of niobium resources.
-
Key words:
- niobium(Nb) /
- critical metal /
- anatase /
- occurrence state /
- Longtan Formation /
- clay rock /
- Xingwen area, South Sichuan
-
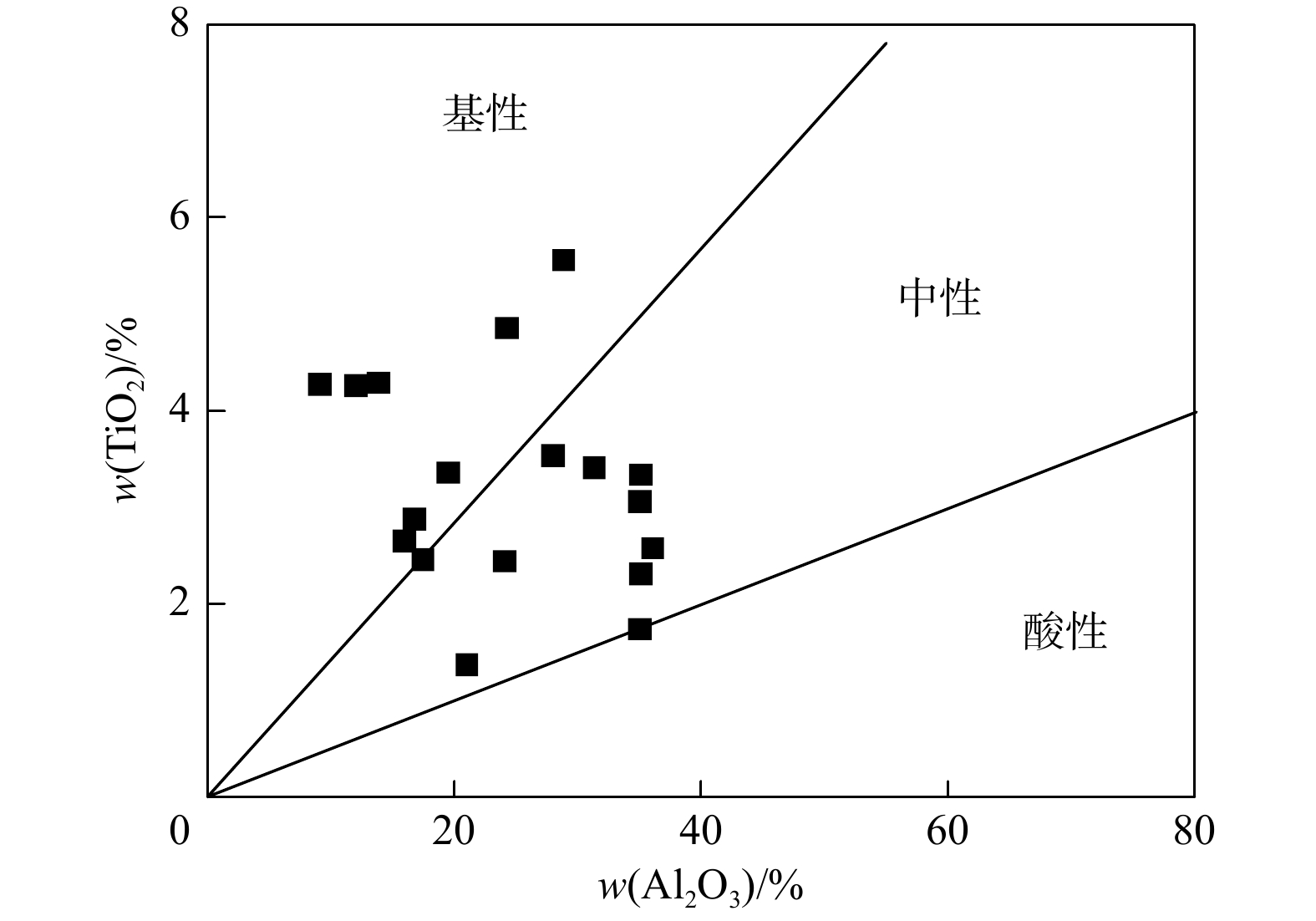
图 10 TiO2-Al2O3二元图[46]
Figure 10. Binary diagram of TiO2 vs. Al2O3
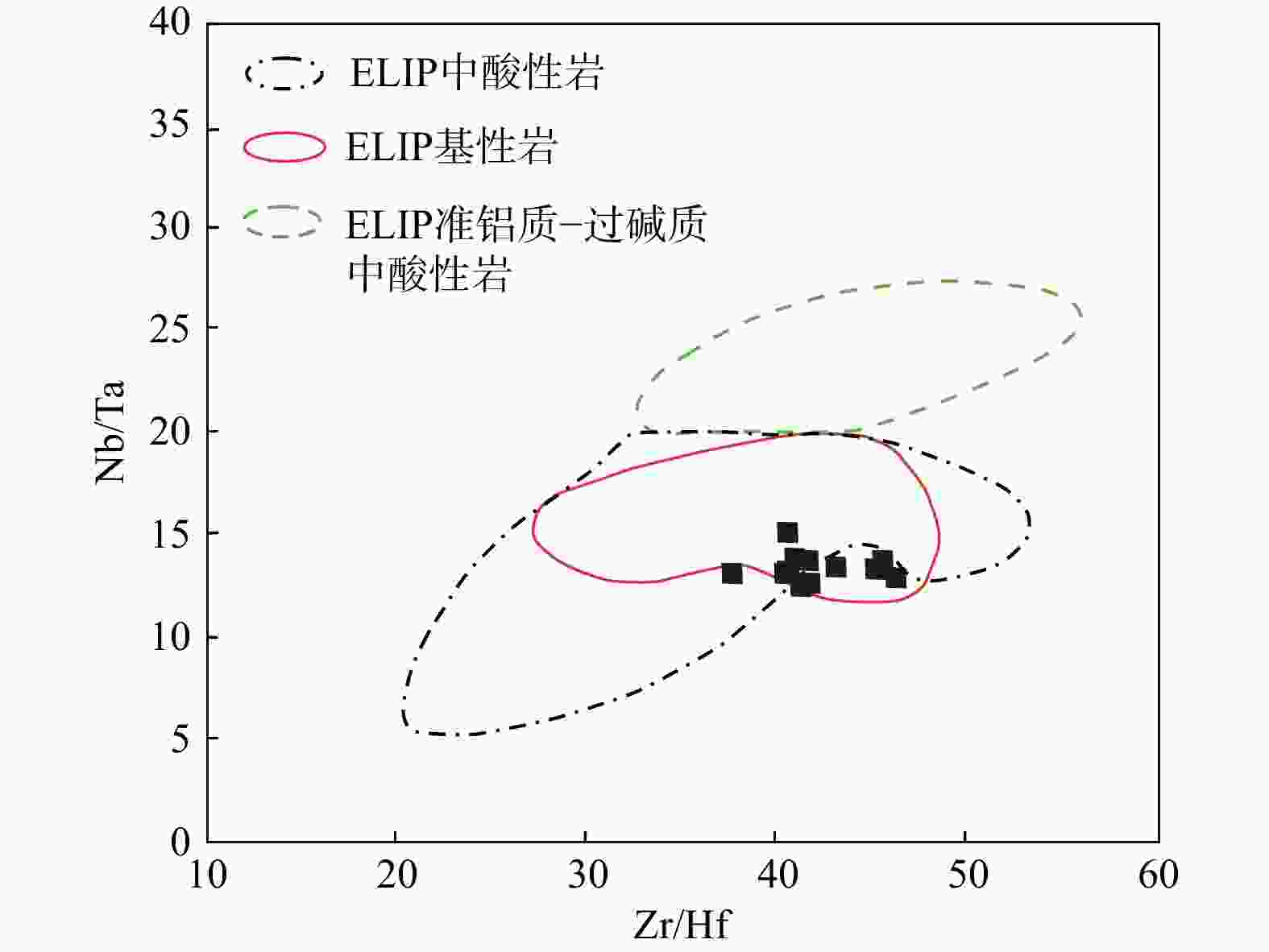
图 11 Nb/Ta-Zr/Hf二元图[32]
Figure 11. Binary diagram of Nb/Ta vs. Zr/Hf
表 1 龙潭组下部黏土岩中Nb、Li、Ga元素质量分数分析结果
Table 1. Analysis results of Nb, Li and Ga in clay rocks of lower part of Longtan Formation
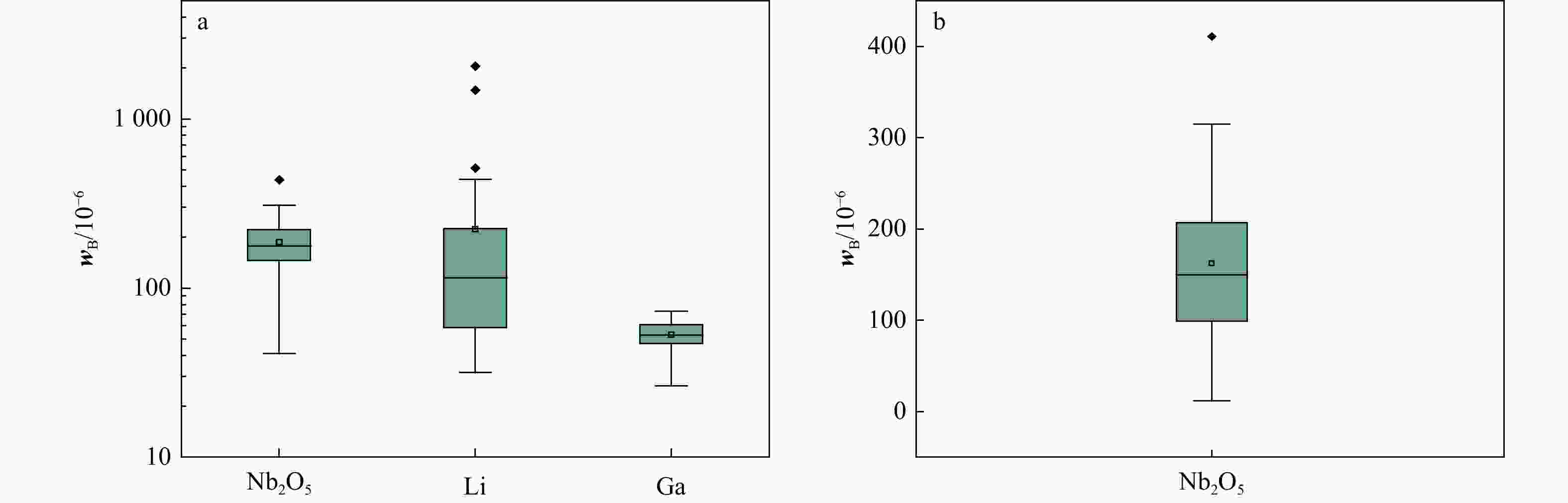
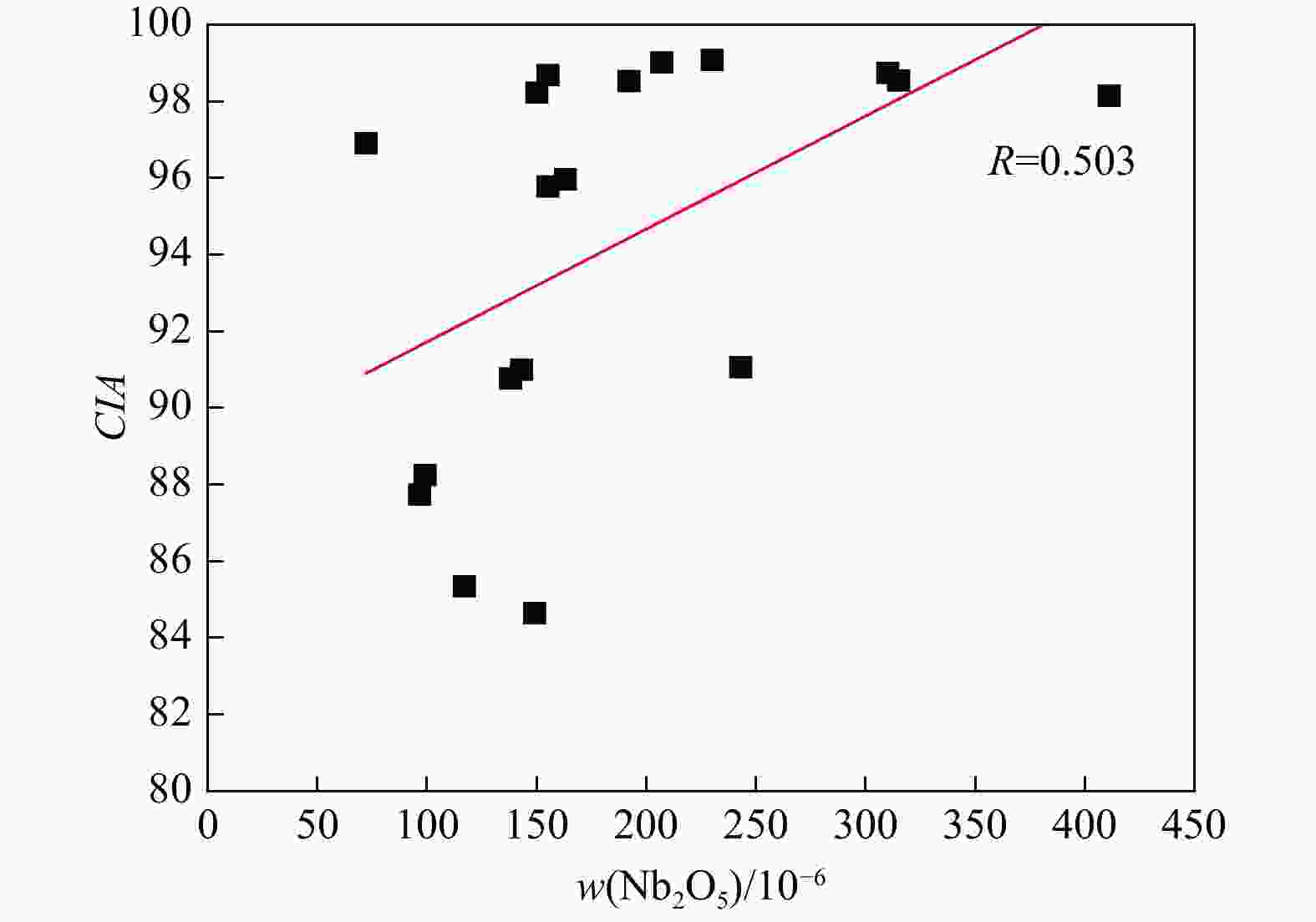
wB/10−6 样 号 Nb2O5 Li Ga 样 号 Nb2O5 Li Ga 样 号 Nb2O5 Li Ga CN01-1 309 133 64 CN11-3 226 243 63.5 CN57-2 200 266 52.8 CN02-1 222 68 60.1 CN12-1 212 107 53.3 CN58-2 172 177 60.6 CN02-3 269 143 61.6 CN13-1 139 1482 37.6 CN59-1 176 219 54.3 CN03-1 239 145 56.2 CN14-1 245 224 73 CN64-1 163 40.4 51.1 CN04-1 169 32.5 50.2 CN15-1 166 42.2 52.6 CN68-1 197 84 66.6 CN04-2 245 44.4 52.7 CN16-1 119 51.4 54.7 CN75-2 183 58.5 60.3 CN05-1 115 256 47.6 CN17-2 263 76.6 57.4 CN76-1 89 79.4 26.5 CN05-2 177 186 52.2 CN19-1 176 147 46.8 CN77-1 41 439 43.9 CN06-1 196 115 73.2 CN19-2 217 115 69.2 CN79-1 177 226 47.4 CN06-2 140 46.9 43.9 CN19-3 283 118 64.7 CN80-1 134 235 45.7 CN07-1 222 77.4 68.2 CN20-1 186 80.5 38.5 CN90-1 437 424 61 CN07-2 172 76.9 53.9 CN52-2 154 2053 34 CN08-1 146 33.8 41.5 CN53-2 146 51.3 42.3 平均值 187 223 53.1 CN09-2 93 513 27.4 CN55-2 189 165 67.3 最大值 437 2053 73.2 CN09-4 156 42.4 48.2 CN56-1 115 31.7 52.5 最小值 41 31.7 26.5 表 2 ZK03钻孔岩心样品化学分析结果
Table 2. Results of chemical analysis of ZK03 borehole
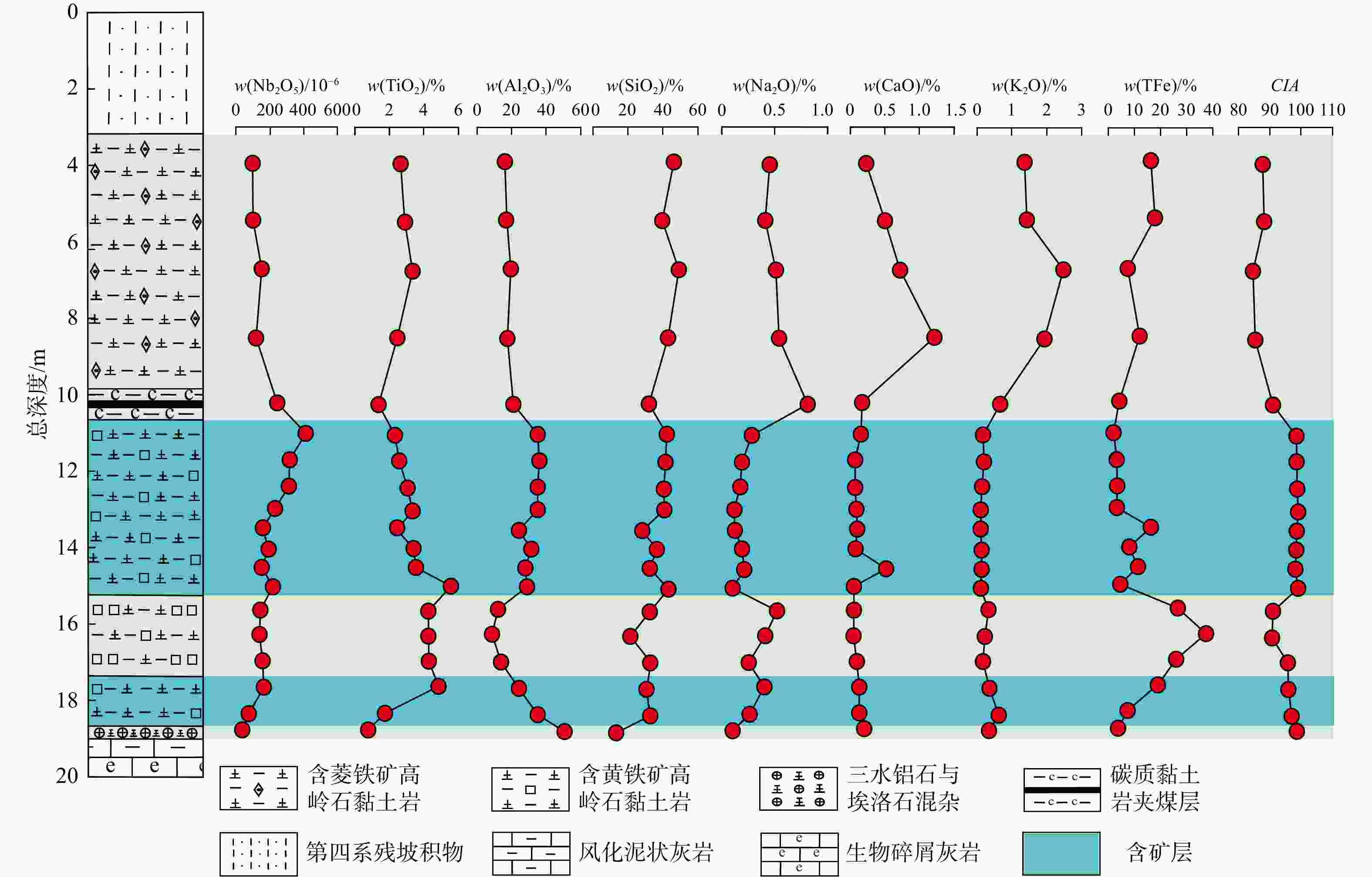
样 号 岩性 Al2O3 CaO K2O Na2O SiO2 TFe MgO MnO TiO2 Zr Hf Ta Nb Nb2O5 CIA Nb/Ta Zr/Hf Al2O3/
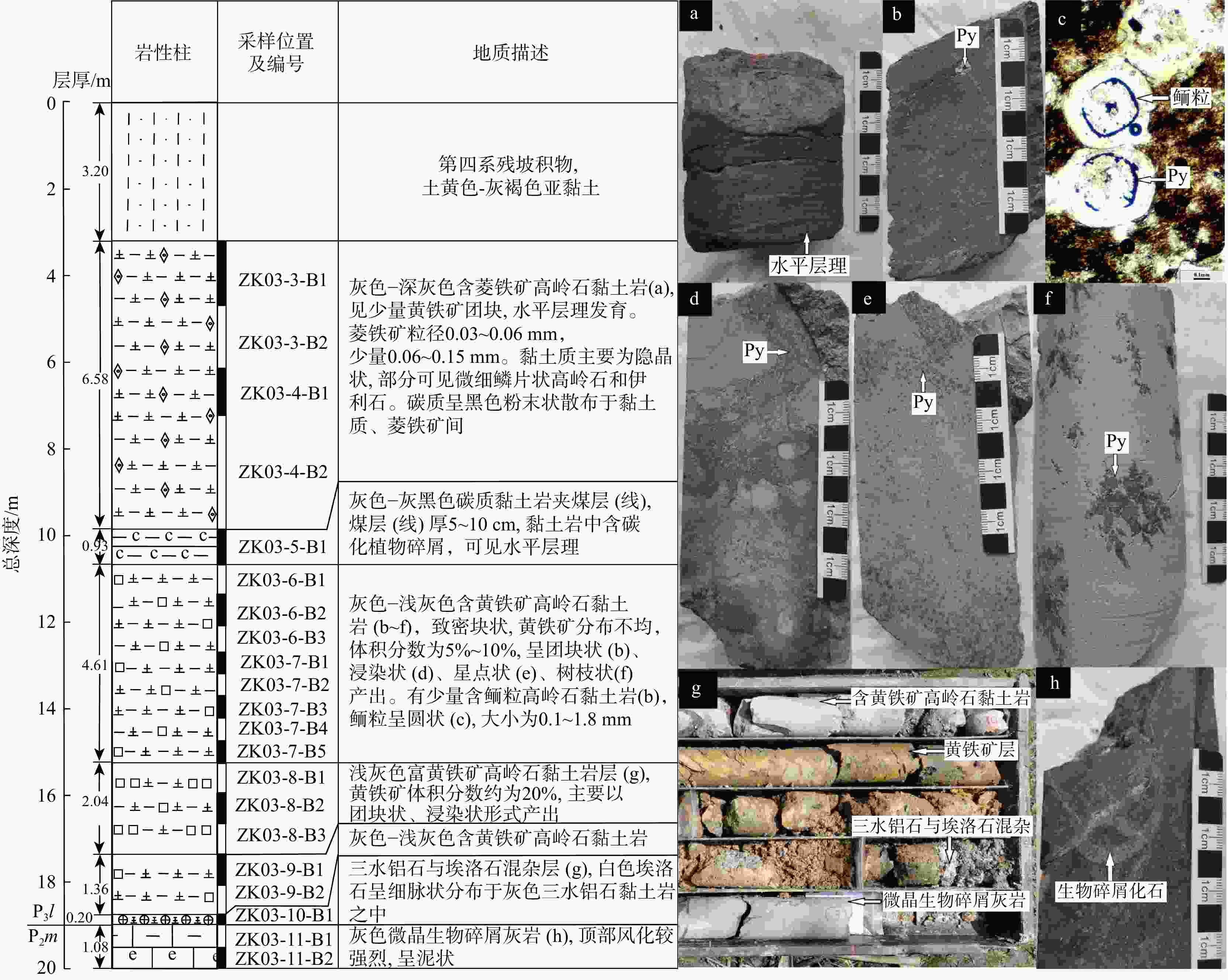
TiO2wB/% wB/10−6 ZK03-3-B1 含菱铁矿
高岭石黏土岩15.96 0.23 1.37 0.45 46.29 16.21 0.71 0.33 2.65 457 11.3 4.42 67.5 96.6 87.74 15.27 40.44 6.02 ZK03-3-B2 16.79 0.5 1.43 0.41 39.67 17.83 0.88 0.37 2.88 482 11.6 4.96 69.2 99 88.26 13.95 41.55 5.83 ZK03-4-B1 19.51 0.72 2.48 0.51 49.15 7.29 1.26 0.31 3.36 690 17.1 7.73 104 149 84.65 13.45 40.35 5.81 ZK03-4-B2 17.44 1.22 1.93 0.54 42.99 11.8 2.15 0.5 2.46 579 14.2 6.18 82.1 117 85.35 13.28 40.77 7.09 ZK03-5-B1 碳质黏土岩夹煤层 21.04 0.17 0.67 0.81 31.92 4.13 0.28 0.032 1.37 1440 34.7 13.2 170 243 91.07 12.88 41.50 15.36 ZK03-6-B1 含黄铁矿
高岭石黏土岩35.1 0.15 0.18 0.28 42.12 1.9 0.041 0.015 2.31 2372 57.8 21.6 287 411 98.15 13.29 41.04 15.19 ZK03-6-B2 36.06 0.068 0.2 0.19 41.51 3.08 0.1 0.004 2.58 1961 47.7 16.5 220 315 98.55 13.33 41.11 13.98 ZK03-6-B3 35.04 0.071 0.15 0.17 40.6 3.25 0.089 0.001 3.06 1880 45.7 17.1 217 310 98.75 12.69 41.14 11.45 ZK03-7-B1 35.08 0.087 0.117 0.117 40.71 3.11 0.15 0.003 3.34 1448 35.8 12 161 230 99.09 13.42 40.45 10.50 ZK03-7-B2 24.09 0.1 0.11 0.12 28.14 16.23 0.15 0.005 2.44 919 22.5 7.72 108 155 98.69 13.99 40.84 9.87 ZK03-7-B3 31.33 0.078 0.14 0.19 36.52 7.84 0.13 0.005 3.41 1293 31.9 10.1 134 192 98.53 13.27 40.53 9.19 ZK03-7-B4 27.98 0.5 0.14 0.21 32.4 11.28 0.11 0.001 3.54 918 22.8 7.89 105 150 98.23 13.31 40.26 7.90 ZK03-7-B5 28.85 0.05 0.11 0.1 43.17 4.81 0.089 0.004 5.56 1233 30.6 10.9 145 207 99.02 13.30 40.29 5.19 ZK03-8-B1 富黄铁矿高
岭石黏土岩12.03 0.053 0.337 0.5 32.43 26.55 0.153 0.008 4.26 800 17.6 7.2 99.8 143 91.01 13.86 45.45 2.82 ZK03-8-B2 9.1 0.048 0.23 0.41 21.25 37.34 0.18 0.008 4.27 716 15.5 7.36 96.3 138 90.77 13.08 46.19 2.13 ZK03-8-B3 13.85 0.091 0.18 0.25 32.61 25.91 0.2 0.013 4.29 843 18.7 8.02 108 155 95.79 13.47 45.08 3.23 ZK03-9-B1 含黄铁矿
高岭石黏土岩24.25 0.13 0.36 0.38 30.58 18.89 0.16 0.008 4.86 885 20.6 8.42 114 163 95.97 13.54 42.96 4.99 ZK03-9-B2 35.02 0.13 0.63 0.26 32.55 7.31 0.28 0.22 1.74 401 10.7 3.79 50.5 72.2 96.92 13.32 37.48 20.13 ZK03-10-B1 三水铝石与
埃洛石混杂层50.43 0.197 0.347 0.1 13.09 3.59 0.095 0.54 0.78 182 5.87 1.9 25.2 36.05 98.93 13.26 31.01 64.65 ZK03-11-B1 茅口组灰岩 4.08 45.74 0.08 0.052 2.73 0.75 0.34 0.13 0.19 86.2 1.93 0.998 11.5 16.45 ZK03-11-B2 1.21 50.77 0.07 0.046 1.76 0.49 0.4 0.044 0.13 54.7 1.09 0.79 8.43 12.06 注:CIA. 化学蚀变指数,CIA=[Al2O3/(Al2O3+CaO*+Na2O+K2O)],式中化学成分的含量均为摩尔数,CaO*是指存在于硅酸盐矿物中CaO。MECLENNAN等[31]认为当n(CaO)>n(Na2O)时,n(CaO*)=n(Na2O),而当n(CaO)<n(Na2O)时,则n(CaO*)=n(CaO),其中n(CaO),n(Na2O)和n(CaO*)分别为CaO,Na2O和CaO*的摩尔数;下同 表 3 锐钛矿的电子探针定量分析结果
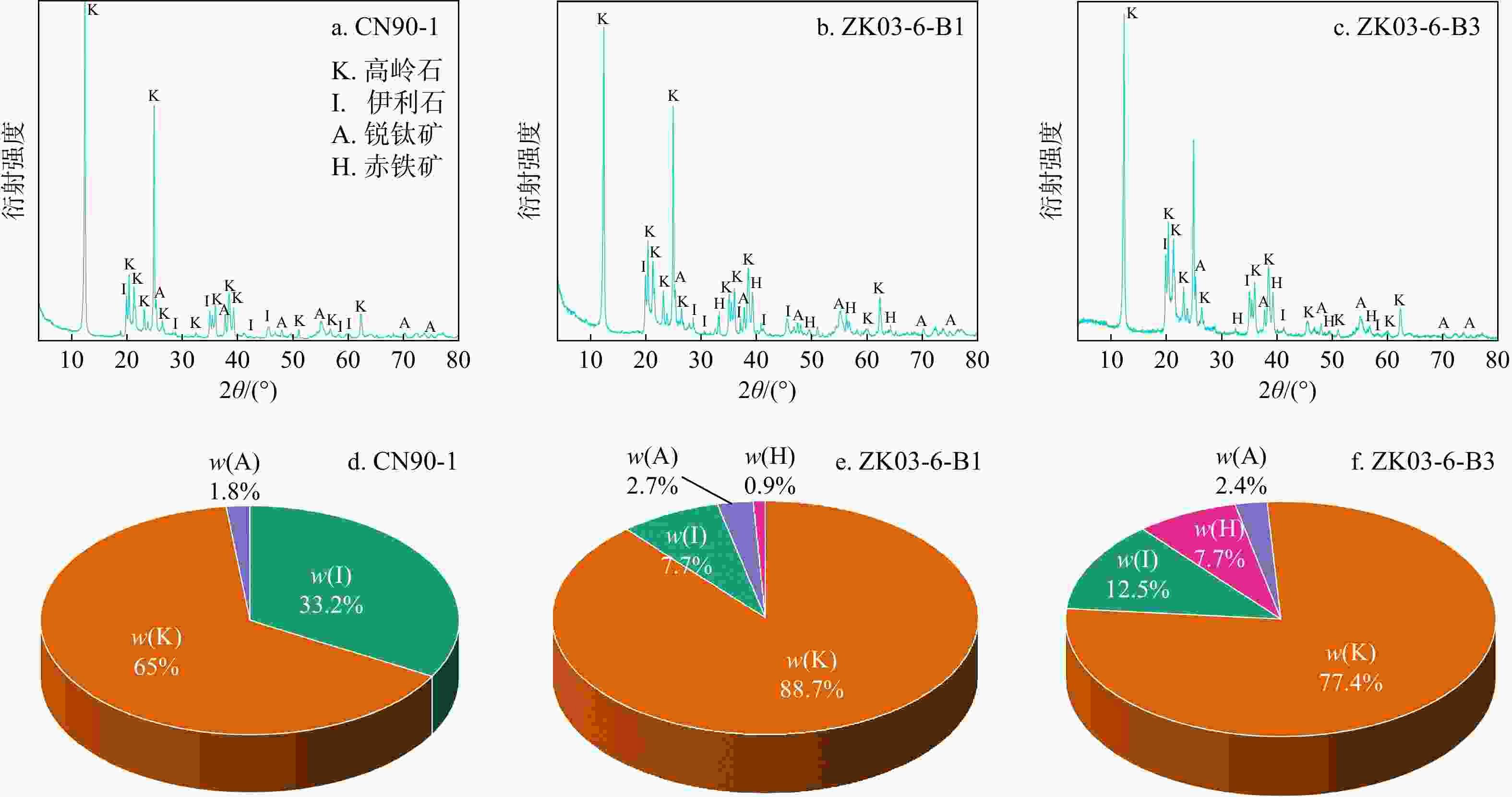
Table 3. EPMA analytical results of anatase grains
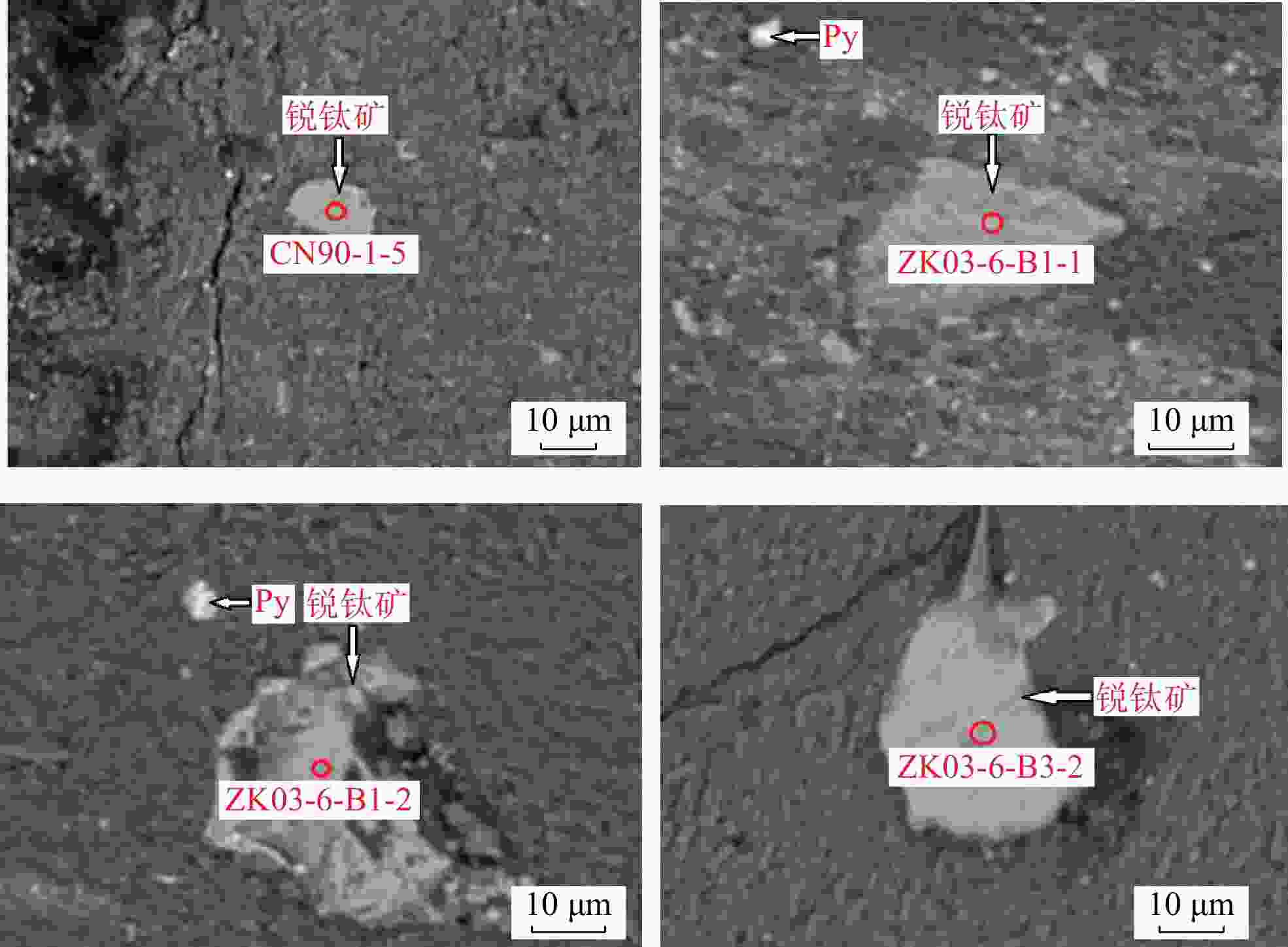
wB/% 测试点位 Nb2O5 Na2O MgO Al2O3 SiO2 CaO ZrO2 FeO Cr2O3 TiO2 Ce2O3 SO3 V2O3 总计 CN90-1-1 1.16 0.01 0.04 0.99 0.58 0.05 0.50 0.31 0.17 93.92 — 0.05 1.14 98.91 CN90-1-2 0.51 0.13 0.01 1.56 1.64 0.06 0.09 0.43 0.44 91.04 0.23 0.09 2.54 98.77 CN90-1-3 0.86 0.07 0.02 1.95 1.54 0.05 1.40 0.71 0.38 90.01 0.06 0.13 1.34 98.49 CN90-1-4 3.40 0.21 0.03 0.80 0.60 0.06 0.15 1.59 0.71 89.95 0.05 0.06 1.01 98.61 CN90-1-5 1.69 — 0.05 2.10 1.84 0.02 0.57 1.23 0.60 81.95 0.05 0.04 8.55 98.68 CN90-1-6 0.95 0.19 0.03 2.23 2.39 0.06 0.09 1.16 0.34 89.23 — 0.05 2.22 98.92 ZK03-6-B1-1 1.84 — — 0.83 0.78 0.01 0.21 1.21 1.12 90.57 0.19 0.24 2.04 99.03 ZK03-6-B1-2 0.09 0.04 — 0.18 0.03 0.01 0.22 0.83 0.14 95.81 0.04 0.06 1.51 98.94 ZK03-6-B1-3 1.71 — 0.02 0.81 0.42 0.07 1.74 0.40 0.21 92.40 — 0.15 1.21 99.13 ZK03-6-B1-4 1.30 0.08 — 0.68 0.69 0.06 1.18 0.84 0.91 91.09 0.01 0.21 1.52 98.57 ZK03-6-B1-5 1.50 0.04 0.02 1.03 0.86 0.04 0.31 1.27 1.17 89.93 0.17 0.39 2.48 99.22 ZK03-6-B3-1 0.94 0.23 0.05 2.45 2.85 0.06 0.89 0.44 0.50 89.06 — 0.17 1.30 98.92 ZK03-6-B3-2 0.69 0.09 0.02 0.83 0.62 0.05 1.63 0.49 0.45 92.47 — 0.02 1.42 98.78 ZK03-6-B3-3 0.44 — — 0.67 0.71 0.06 0.51 0.39 0.24 94.93 — 0.07 1.15 99.18 ZK03-6-B3-4 0.39 — — 2.24 1.80 0.08 0.73 0.26 0.25 91.59 0.07 — 1.10 98.50 平均 1.17 0.07 0.02 1.29 1.16 0.05 0.68 0.77 0.51 90.93 0.06 0.11 2.04 98.84 注:“—”表示测试数据低于检测限 -
[1] NICO C, MONTEIRO T, GRAÇA M P F. Niobium oxides and niobates physical properties: Review and prospects[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2016, 80: 1-37. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2016.02.001 [2] 何海洋, 何敏, 李建武. 我国铌矿资源供需形势分析[J]. 中国矿业, 2018, 27(11): 1-5. doi: 10.12075/j.issn.1004-4051.2018.11.016HE H Y, HE M, LI J W. Analysis of the niobium resources supply and demand pattern in China[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2018, 27(11): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12075/j.issn.1004-4051.2018.11.016 [3] 陈骏. 关键金属超常富集成矿和高效利用[J]. 科技导报, 2019, 37(24): 1.CHEN J. Metallogenesis and effective utilization ofstrategic-critical metals[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2019, 37(24): 1. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 翟明国, 吴福元, 胡瑞忠, 等. 战略性关键金属矿产资源: 现状与问题[J]. 中国科学基金, 2019, 33(2): 106-111.ZHAI M G, WU F Y, HU R Z, et al. Critical metal mineral resources: Current research status and scientific issues[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2019, 33(2): 106-111. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 侯增谦, 陈骏, 翟明国. 战略性关键矿产研究现状与科学前沿[J]. 科学通报, 2020, 65(33): 3651-3652. doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-1417HOU Z Q, CHEN J, ZHAI M G. Current status and frontiers of research on critical mineral resources[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(33): 3651-3652. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-1417 [6] USGS. Mineral commodity summaries-niobium (columbium)(2014−2018)[R]. Reston, Virginia: U.S. Geological Survey, 2022. [7] 曹飞, 杨卉芃, 张亮, 等. 全球钽铌矿产资源开发利用现状及趋势[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2019, 39(5): 56-67.CAO F, YANG H P, ZHANG L, et al. Current situation and trend analysis of global tantalum and niobium mineral resources[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019, 39(5): 56-67. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 赵浩男, 邢乐才, 何洪涛, 等. 广西平果上二叠统合山组铝土矿中铌的赋存状态[J]. 矿物学报, 2022, 42(4): 453-460.ZHAO H N, XING L C, HE H T, et al. The mode of occurrence of niobium in bauxite of the Upper Permian Heshan Formation in the Pingguo area, Guangxi Autonomous Region, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2022, 42(4): 453-460. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 杜胜江, 温汉捷, 罗重光, 等. 宣威−威宁地区铌矿床的元素赋存状态及富集机制[J]. 地质学报, 2023, 97(4): 1192-1210.DU S J, WEN H J, LUO C G, et al. Nb occurrence and enrichment mechanism of niobium deposit at the Xuanwei Formation in Xuanwei-Weining area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2023, 97(4): 1192-1210. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] PAL D C, MISHRA B, BERNHARDT H J. Mineralogy and geochemistry of pegmatite-hosted Sn-, Ta-Nb-, and Zr-Hf-bearing minerals from the southeastern part of the Bastar-Malkangiri pegmatite belt, central India[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2007, 30(1): 30-55. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2005.10.004 [11] KÜSTER D. Granitoid-hosted Ta mineralization in the Arabian-Nubian shield: Ore deposit types, tectono-metallogenetic setting and petrogenetic framework[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2009, 35(1): 68-86. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2008.09.008 [12] 吴学敏, 周敏娟, 罗喜成, 等. 江西西北部锂及稀有金属成矿条件及找矿潜力分析[J]. 华东地质, 2016, 37(4): 275-283.WU X M, ZHOU M J, LUO X C, et al. The metallogenic conditions and prospecting potential of lithium and rare metals in northwestern Jiangxi[J]. East China Geology, 2016, 37(4): 275-283. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 李建康, 李鹏, 王登红, 等. 中国铌钽矿成矿规律[J]. 科学通报, 2019, 64(15): 1545-1566. doi: 10.1360/N972018-00933LI J K, LI P, WANG D H, et al. A review of niobium and tantalum metallogenic regularity in China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2019, 64(15): 1545-1566. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1360/N972018-00933 [14] ZHU J C, LI R K, LI F C, et al. Topaz-albite granites and rare-metal mineralization in the Limu District, Guangxi Province, Southeast China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2001, 36(5): 393-405. doi: 10.1007/s001260100160 [15] 冷成彪, 王守旭, 苟体忠, 等. 新疆阿尔泰可可托海3号伟晶岩脉研究[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 2007(1): 14-20.LENG C B, WANG S X, GOU T Z, et al. A review of the research on the Koktokay No. 3 granitic pegmatite dyke, Altai, Xinjiang[J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 2007(1): 14-20(in Chinese with English abstract [16] HE B, XU Y G, HUANG X L, et al. Age and duration of the Emeishan flood volcanism, SW China: Geochemistry and SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating of silicic ignimbrites, post-volcanic Xuanwei Formation and clay tuff at the Chaotian Section[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 255(3/4): 306-323. [17] DAI S F, ZHOU Y P, ZHANG M Q, et al. A new type of Nb (Ta)-Zr(Hf)-REE-Ga polymetallic deposit in the Late Permian coal-bearing strata, eastern Yunnan, southwestern China: Possible economic significance and genetic implications[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2010, 83(1): 55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2010.04.002 [18] ZHAO L X, DAI S F, GRAHAM I, et al. Clay mineralogy of coal-hosted Nb-Zr-REE-Ga mineralized beds from Late Permian strata, eastern Yunnan, SW China: Implications for paleotemperature and origin of the micro-quartz[J]. Minerals, 2016, 6(2): 45. doi: 10.3390/min6020045 [19] 杜胜江, 温汉捷, 罗重光, 等. 滇东−黔西地区峨眉山玄武岩富Nb榍石矿物学特征[J]. 矿物学报, 2019, 39(3): 253-263.DU S J, WEN H J, LUO C G, et al. Mineralogy study of Nb-rich sphene generated from the Emeishan basalts in eastern Yunnan-western Guizhou area, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2019, 39(3): 253-263. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 张七道, 肖长源, 李致伟, 等. 黔西北普宜地区富关键金属元素硫铁矿地质、地球化学和S同位素特征及其对成因的约束[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(4): 149-164.ZHANG Q D, XIAO C Y, LI Z W, et al. Geological, geochemical and sulfur isotopic characteristics of critical metal-enriched pyritic ore in the Puyi area, Northwest Guizhou Province: Constraints on the genesis of the deposit[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(4): 149-164. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 中华人民共和国国土资源部. 矿产地质勘查规范稀有金属类: DZ/T0203-2020[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2020.Ministry of Land and Resources, the People's Republic of China. Standard for geological survey of rare metals: DZ/T0203-2020[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2020. (in Chinese) [22] 文俊, 刘治成, 赵俊兴, 等. 川南沐川地区宣威组底部铌−稀土多金属富集层富集规律、沉积环境与成矿模式[J]. 地质学报, 2022, 96(2): 592-615. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.02.016WEN J, LIU Z C, ZHAO J X, et al. Enrichment regularity, sedimentary environment and metallogenic model of niobium-rare earth polymetallic enrichment layer at the bottom of the Xuanwei Formation in Muchuan area, South Sichuan[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2022, 96(2): 592-615. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.02.016 [23] YU W C, ALGEO T J, DU Y S, et al. Mixed volcanogenic-lithogenic sources for Permian bauxite deposits in southwestern Youjiang Basin, South China, and their metallogenic significance[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2016, 341: 276-288. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2016.04.016 [24] 冯增昭, 杨玉卿, 李尚武, 等. 中国南方二叠纪岩相古地理[M]. 山东东营: 石油大学出版社, 2001.FENG Z Z, YANG Y Q, LI S W, et al. Lithofacies paleogeography of the Permian of South China[M]. Dongying Shandong: Petroleum University Publishing House, 2001. (in Chinese) [25] HE B, XU Y G, CHUNG S L, et al. Sedimentary evidence for a rapid, kilometer-scale crustal doming prior to the eruption of the Emeishan flood basalts[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2003, 213(3/4): 391-405. [26] 何斌, 徐义刚, 肖龙, 等. 峨眉山大火成岩省的形成机制及空间展布: 来自沉积地层学的新证据[J]. 地质学报, 2003, 77(2): 194-202. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2003.02.007HE B, XU Y G, XIAO L, et al. Generation and spatial distribution of the Emeishan large igneous province: New evidence from stratigraphic records[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2003, 77(2): 194-202. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2003.02.007 [27] SHELLNUTT J G. The Emeishan large igneous province: A synthesis[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2014, 5(3): 369-394. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2013.07.003 [28] XU Y G, CHUNG S L, SHAO H, et al. Silicic magmas from the Emeishan large igneous province, Southwest China: Petrogenesis and their link with the end-Guadalupian biological crisis[J]. Lithos, 2010, 119(1/2): 47-60. [29] ZHAO L X, DAI S F, GRAHAM I T, et al. New insights into the Lowest Xuanwei Formation in eastern Yunnan Province, SW China: Implications for Emeishan large igneous province felsic tuff deposition and the cause of the end-Guadalupian mass extinction[J]. Lithos, 2016, 264: 375-391. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2016.08.037 [30] YANG S Y. Electron probe microanalysis in geosciences: Analytical procedures and recent advances[J]. Atomic Spectroscopy, 2022, 43(2): 186-200. [31] MCLENNAN S M. Weathering and global denudation[J]. Journal of Geology, 1993, 101: 295-303.MCLENNAN S M. Weathering and global denudation[J]. Journal of Geology, 1993, 101: 295-303. [32] 凌坤跃, 温汉捷, 张起钻, 等. 广西平果上二叠统合山组关键金属锂和铌的超常富集与成因[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2021, 51(6): 853-873. doi: 10.1360/SSTe-2020-0140LING K Y, WEN H J, ZHANG Q Z, et al. Super-enrichment of lithium and niobium in the Upper Permian Heshan Formation in Pingguo, Guangxi, China[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 2021, 51(6): 853-873. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1360/SSTe-2020-0140 [33] 魏均启, 朱丹, 桂博艺, 等. 湖北竹溪岩屋沟−青岩沟铌矿矿石物质组成及铌的赋存状态研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(6): 158-162. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.06.027WEI J Q, ZHU D, GUI B Y, et al. Research on mineral composition and niobium occurrence state of niobium ore in Yanwugou-Qingyangou, Zhuxi, Hubei[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(6): 158-162. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.06.027 [34] DA SILVA A L, HOTZA D, CASTRO R H R. Surface energy effects on the stability of anatase and rutile nanocrystals: A predictive diagram for Nb2O5-doped-TiO2[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 393: 103-109. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.09.126 [35] 秦志军, 周豹, 苌笙任, 等. 鄂西北杀熊洞铌−稀土矿床烧绿石矿物学及地球化学特征及其形成机理[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(5): 150-160.QIN Z J, ZHOU B, CHANG S R, et al, Mineralogy and geochemistry of pyrochlore from the Shaxiongdong Nb-REE deposit, northwestern Hubei Province: Implications for the niobium enrichment mechanism in carbonatites[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(5): 150-160. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] 周义平. 中国西南龙潭早期碱性火山灰蚀变的TONSTEINS[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 1999, 27(4): 5-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.1999.04.002ZHOU Y P. The synsedimentary alkalinity-volcanic ash derived tonsteins of early Longtan age in southwestern China[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 1999, 27(4): 5-9. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.1999.04.002 [37] ZHOU Y P, BOHOR B F, REN Y L. Trace element geochemistry of altered volcanic ash layers (tonsteins) in Late Permian coal-bearing formations of eastern Yunnan and western Guizhou Provinces, China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2000, 44(3/4): 305-324. [38] 代世峰, 周义平, 任德贻, 等. 重庆松藻矿区晚二叠世煤的地球化学和矿物学特征及其成因[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2007, 37(3): 353-362.DAI S F, ZHOU Y P, REN D Y, et al. Geochemical and mineralogical characteristics and genesis of Late Permian coal in Songzao mining area, Chongqing[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 2007, 37(3): 353-362. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] 王瑞江, 王登红, 李建康, 等. 稀有稀土稀散矿产资源及其开发利用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2015.WANG R J, WANG D H, LI J K, et al. Development and utilization of rare metals, rare earth and dissipated metal mineral resources[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2015. (in Chinese) [40] 邓守和. 川南晚二叠世初期沉积黄铁矿成因分析[J]. 四川地质学报, 1986, 6(1): 8-20.DENG S H. Cause analysis of early Late Permian sedimentary pyrite in southern Sichuan[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 1986, 6(1): 8-20. (in Chinese with English abstract [41] 陈聪, 林良彪, 余瑜, 等. 四川盆地南部CLD1井龙潭组地球化学特征及古环境意义[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 49(2): 225-238.CHEN C, LIN L B, YU Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics and paleo-environmental significance of Longtan Formation in Well CLD1 in southern Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2022, 49(2): 225-238. (in Chinese with English abstract [42] ZHONG Y T, HE B, XU Y G. Mineralogy and geochemistry of claystones from the Guadalupian-Lopingian boundary at Penglaitan, South China: Insights into the pre-Lopingian geological events[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 62: 438-462. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.10.028 [43] DAI S F, LI T, SEREDIN V V, et al. Origin of minerals and elements in the Late Permian coals, tonsteins, and host rocks of the Xinde mine, Xuanwei, eastern Yunnan, China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2014, 121: 53-78. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2013.11.001 [44] ZHANG Z W, ZHENG G D, TAKAHASHI Y, et al. Extreme enrichment of rare earth elements in hard clay rocks and its potential as a resource[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 72: 191-212. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.07.018 [45] HAYASHI K I, FUJISAWA H, HOLLAND H D, et al. Geochemistry of ~1.9 Ga sedimentary rocks from northeastern Labrador, Canada[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1997, 61(19): 4115-4137. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00214-7 [46] WINCHESTER J A, FLOYD P A. Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements[J]. Chemical Geology, 1977, 20: 325-343. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(77)90057-2 [47] YANG J H, CAWOOD P A, DU Y S. Voluminous silicic eruptions during Late Permian Emeishan igneous province and link to climate cooling[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 432: 166-175. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2015.09.050 [48] 杨瑞东, 鲍淼, 廖琍, 等. 贵州西部中、上二叠统界线附近风化壳类型及成矿作用[J]. 矿物学报, 2007, 27(1): 41-48. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2007.01.007YANG R D, BAO M, LIAO L, et al. Ancient weathering crust and its mineralization near the Middle-Upper Permian boundary in western Guizhou Province, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2007, 27(1): 41-48. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2007.01.007 [49] 陈国勇, 范玉梅, 孟昌忠, 等. 贵州威宁−赫章二叠系乐平统含铁、铝岩系沉积环境及成矿元素富集特征分析[J]. 地质与勘探, 2017, 53(2): 237-246. doi: 10.12134/j.dzykt.2017.02.004CHEN G Y, FAN Y M, MENG C Z, et al. Sedimentary environments and mineral element concentration features of iron-aluminum-bearing rock series in the Leping series of Permian of the Weining-Hezhang area, Guizhou[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2017, 53(2): 237-246. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12134/j.dzykt.2017.02.004 [50] 张海, 郭佩佩, 杨国彬. 贵州西部峨眉山玄武岩风化壳中稀土元素赋存状态研究[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2022, 40(5): 901-908.ZHANG H, GUO P P, YANG G B. REE occurrence in the Emeishan basalt weathering crust of western Guizhou[J]. Journal of the Chinese Society of Rare Earths, 2022, 40(5): 901-908. (in Chinese with English abstract [51] HASTIE A R, MITCHELL S F, KERR A C, et al. Geochemistry of rare high-Nb basalt lavas: Are they derived from a mantle wedge metasomatised by slab melts?[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2011, 75(17): 5049-5072. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2011.06.018 [52] DEBLONDE G J, CHAGNES A, BÉLAIR S, et al. Solubility of niobium(V) and tantalum(V) under mild alkaline conditions[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2015, 156: 99-106. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2015.05.015 [53] YANG R D, WANG W, ZHANG X D, et al. A new type of rare earth elements deposit in weathering crust of Permian basalt in western Guizhou, NW China[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2008, 26(5): 753-759. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(08)60177-5 [54] 常丽华, 陈曼云, 金巍, 等. 透明矿物薄片鉴定手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2006.CHANG L H, CHEN M Y, JIN W, et al. Manual for the identification of thin sections of transparent minerals[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2006. (in Chinese) [55] JACKSON J C, HORTON J W, CHOU I M, et al. A shock-induced polymorph of anatase and rutile from the Chesapeake Bay impact structure, Virginia, U. S. A. [J]. American Mineralogist, 2006, 91(4): 604-608. doi: 10.2138/am.2006.2061 [56] HENRIK F, CASEY WILLIAM H. Niobium is highly mobile As a polyoxometalate ion during natural weathering[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 2018, 56(6): 905-912. doi: 10.3749/canmin.1800058 [57] 王秀平, 王启宇, 安显银. 川南地区二叠系沉积环境及其演化特征: 以四川古蔺芭蕉村剖面为例[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2022, 42(3): 398-412.WANG X P, WANG Q Y, AN X Y. Characteristics of sedimentary environment and evolution of Permian in southern Sichuan Basin: An example from the profile of Gulin Bajiaocun in Sichuan Province[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2022, 42(3): 398-412. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: