Reservoir characteristics and development control factors of Benxi Formation bauxite in the Linxing area of Ordos Basin
-
摘要:
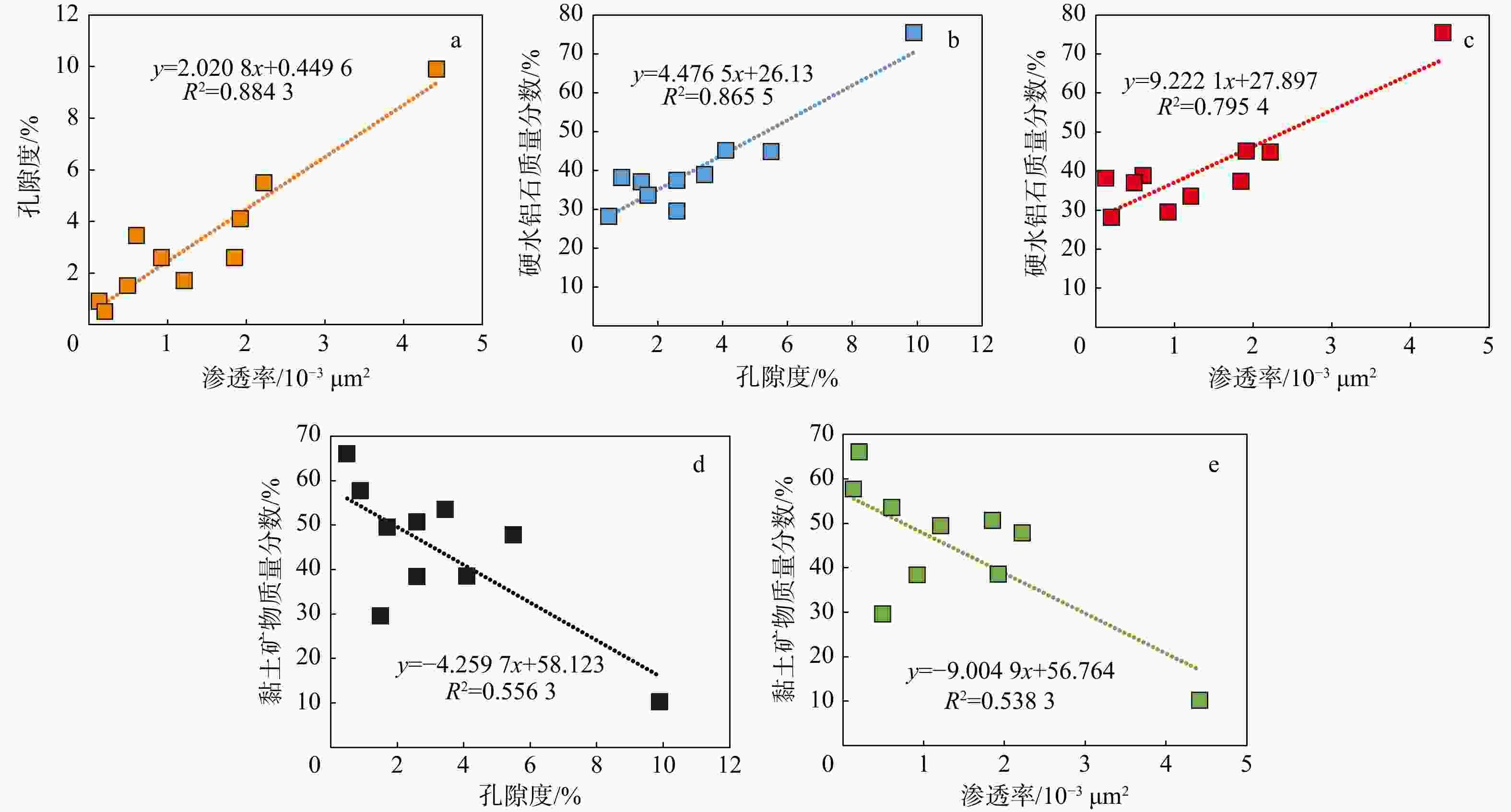
近年来,鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区太原组铝土岩气勘探取得了重大突破,吸引了国内外的广泛关注。同期,临兴地区本溪组铝土岩气也取得了一定进展,但对于该区铝土岩储层特征及其发育控制因素认识不清,制约了勘探进程。为了明确临兴地区本溪组铝土岩的储层特征与控制因素,通过开展全岩 X 射线衍射(X-ray diffraction,简称 XRD)、铸体薄片、扫描电镜、高压压汞、氮气吸附、二氧化碳吸附、常规孔渗检测等分析手段,对铝土岩储层的矿物组成、孔隙结构、储层物性等进行了精细表征,并结合地震测井等资料对铝土岩储层发育的控制因素进行了探讨。研究表明:临兴地区本溪组铝土岩中含铝矿物主要为硬水铝石,孔隙类型主要为粒内溶孔、粒间溶孔、基质溶孔、晶间孔以及微裂隙,偶见有机质孔。此外,铝土岩孔隙体积主要由介孔和宏孔提供,孔峰分布范围主要为30~70,80~130,
4000 ~13000 nm。再次,铝土岩储层物性条件一般,孔隙度平均为3.28%,渗透率平均为1.398×10−3 μm2,但底部硬水铝石含量较高层段仍具有较好的物性条件。最后,临兴地区铝土岩储层发育受控于古地貌形态、古沉积环境和成岩作用,其中,洼地和沟槽的古地貌形态和封闭−半封闭的间歇沼泽和泻湖沉积环境控制了铝土岩的富集和分布,成岩作用则是在沉积环境基础上控制了铝土岩储层储集空间类型和物性条件。研究成果可为铝土岩气勘探提供理论参考。Abstract:In recent years, the bauxite gas exploration of the Taiyuan Formation in the Longdong area of Ordos Basin has made a breakthrough, which has attracted wide attention at home and abroad. During the same period, the bauxite rock gas of the Benxi Formation in the Linxing area has also made some progress; however, the characteristics and controlling factors of the bauxite reservoir in this area remain unclear, which restricts the exploration process.
Objective To identify the reservoir characteristics and influencing factors of Benxi Formation bauxite in the Linxing area,
Methods the paper carried out X-ray diffraction (XRD), cast sheet imaging, scanning electron microscope-energy-dispersive spectrometer (SEM-EDS), mercury intrusion porosimetry, nitrogen and carbon dioxide adsorption, and routine porosity measurements, coupled with seismic logging data, to characterize the mineral composition, pore structure, and physical properties of the bauxite reservoir and to discuss the controls on its development.
Result The results show that the aluminum-bearing minerals in Benxi Formation bauxite in the Linxing area are dominated by diaspore. Pore types are primarily intra-granular, intergranular, matrix, and microcrack pores, with occasional organic pores. Pore volume is mainly contributed by mesopores and macropores, with pore-size peaks mainly at 30−70, 80−130,
4000 −13000 nm. The overall reservoir physical properties are modest, with an average porosity of 3.28% and an average permeability of 1.398×10−3 μm2. However, the lower part of the section, which has a higher diaspore content, exhibits relatively better properties. Finally, the development of the Linxing bauxite reservoir is controlled by palaeo-geomorphology, palaeo-sedimentary environment, and diagenesis. Specifically, accumulation and distribution of bauxite are controlled by the paleogeomorphology of depressions and troughs and by enclosed to semi-enclosed intermittent swamps and lagoons. Diagenesis determines the reservoir-space types and the resulting physical-property conditions within the sedimentary context.Conclusion The research results can provide theoretical guidance for the bauxite gas exploration.
-
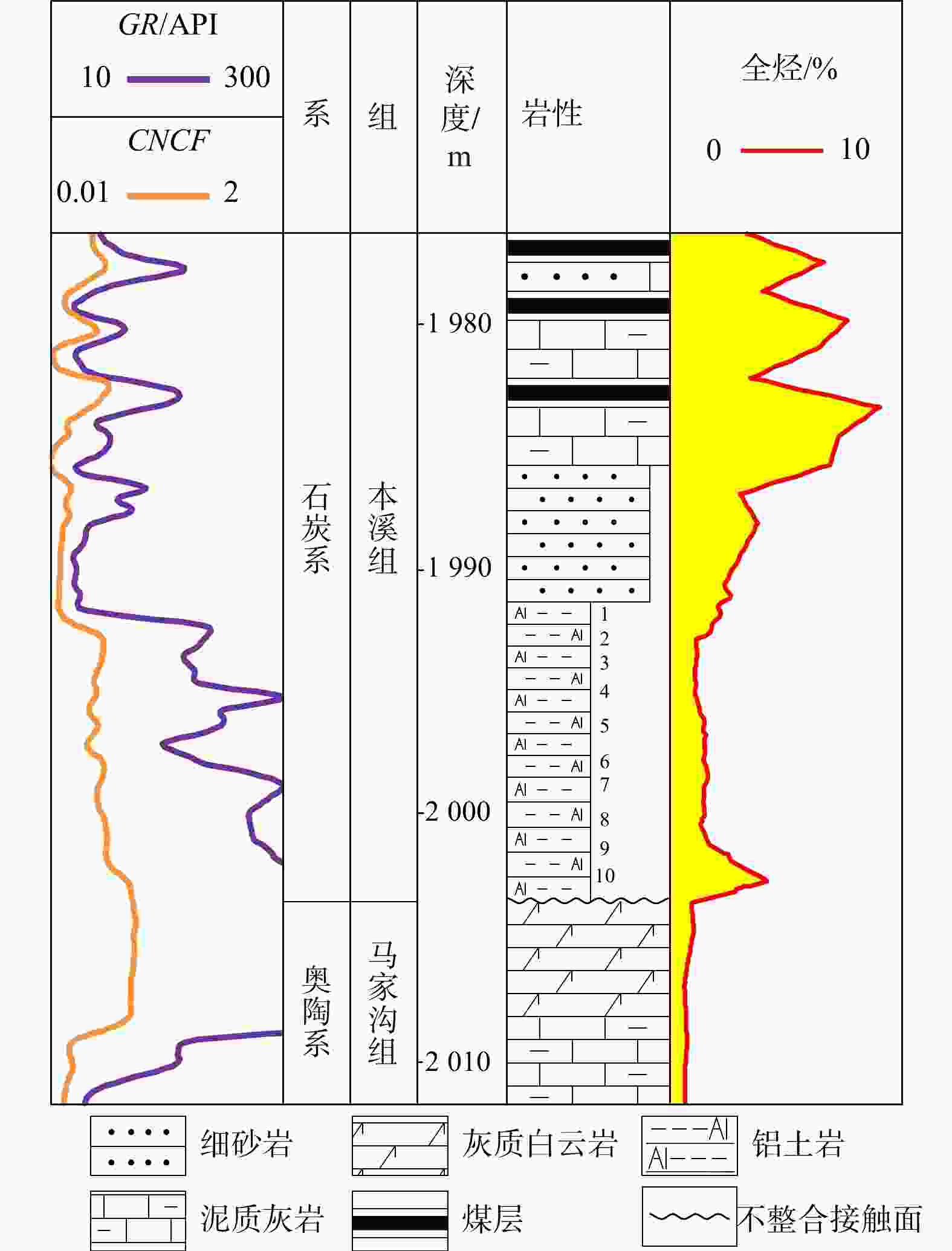
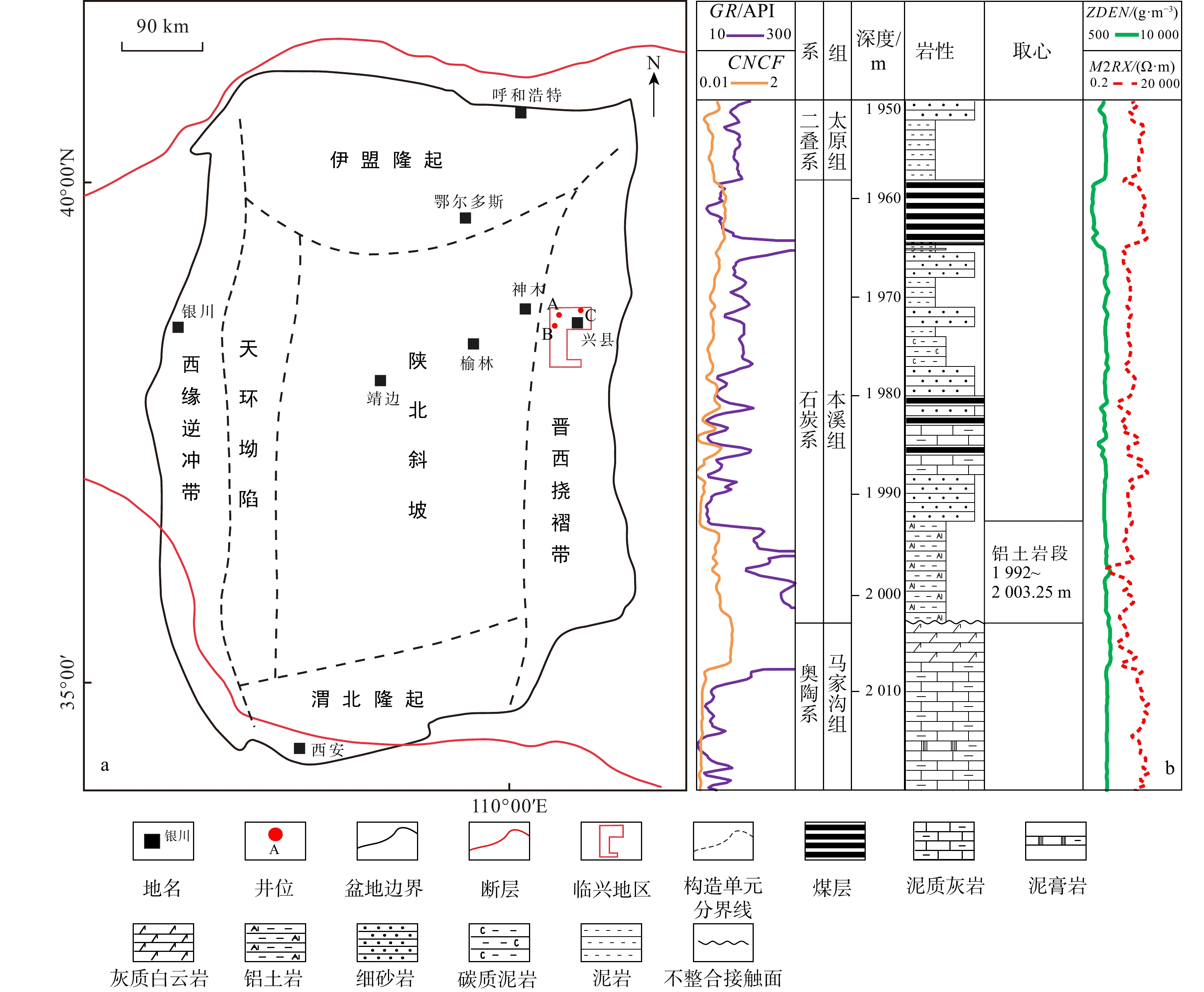
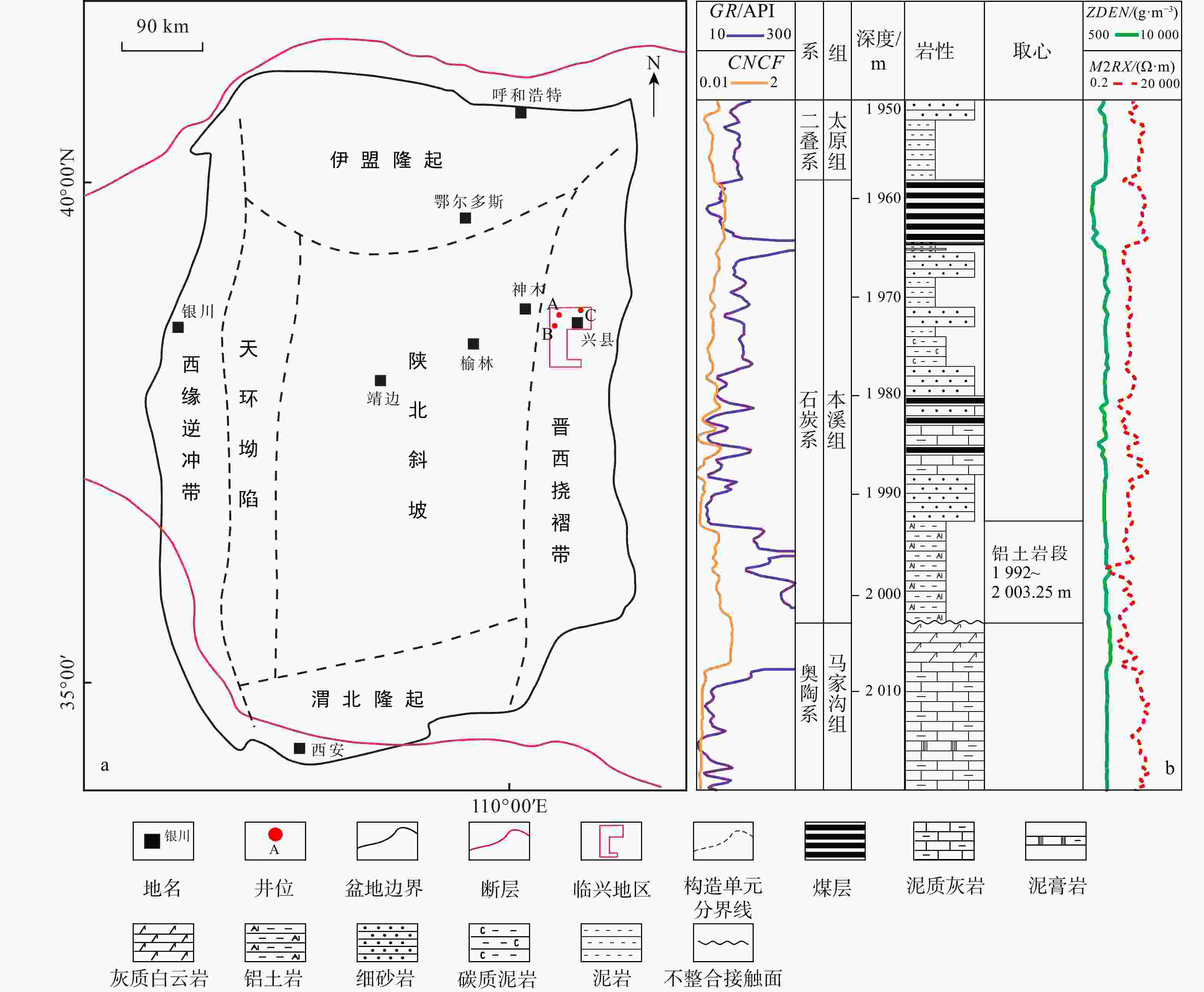
图 1 鄂尔多斯盆地临兴地区地质综合图
a. 鄂尔多斯盆地构造单元及临兴地区位置,据文献[12]修改;b. 临兴地区A井柱状图。GR. 自然伽马;CNCF. 补偿中子;ZDEN. 密度;M2RX. 高分辨感应电阻率;下同
Figure 1. Geological comprehensive map of Linxing area, Ordos Basin
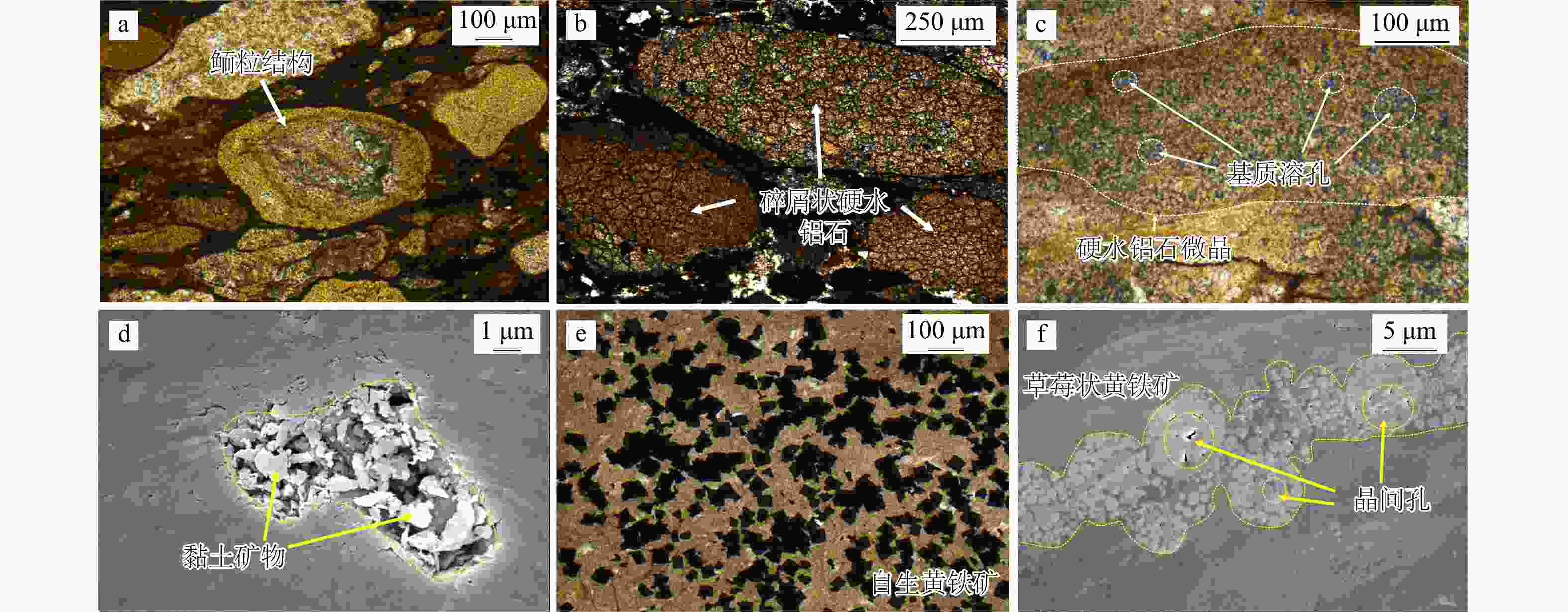
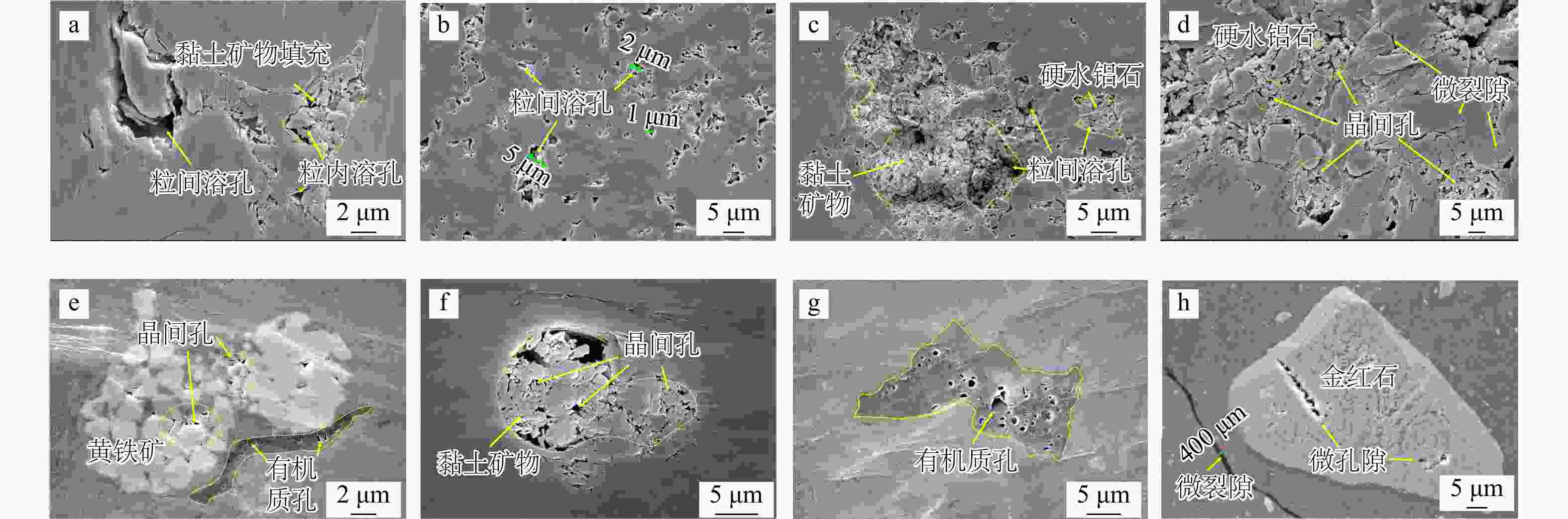
图 3 临兴地区A井本溪组铝土岩孔隙特征
a.
1996.43 m,碎屑矿物溶蚀孔被黏土矿物充填;b.2003.15 m,硬水铝石粒间溶孔;c.2003.15 m,粒间孔内充填硬水铝石和黏土矿物等;d.2003.15 m,硬水铝石晶间孔和微裂隙;e.1999.85 m,黄铁矿晶间孔和有机质孔;f.2002.31 m,黏土矿物晶间孔;g.2000.07 m,有机质孔;h.2000.07 m,金红石微孔隙以及微裂隙Figure 3. Pore characteristics in Benxi Formation bauxite rock of Well A in the Linxing area
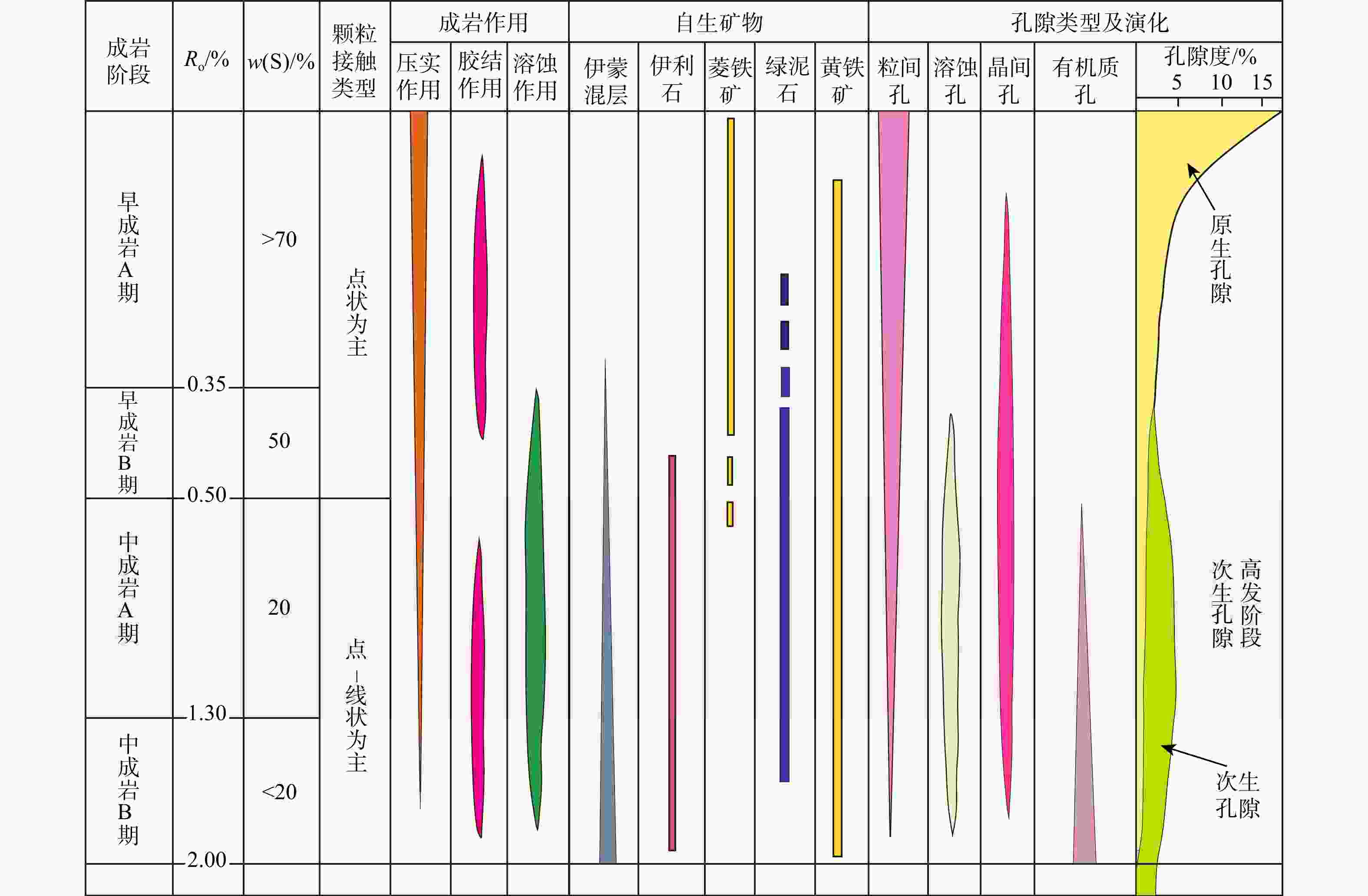
图 9 临兴地区铝土岩成岩作用阶段(据文献[33]修改;Ro. 镜质体反射率;S. 蒙脱石)
Figure 9. Diagenetic stage of bauxite rock in the Linxing area
表 1 临兴地区本溪组铝土岩XRD分析结果
Table 1. XRD analysis results of Benxi Formation bauxite rock in the Linxing area
取心井 样品编号 深度/m 石英 钛质矿物 铁质矿物 黏土矿物 铝质矿物 伊/蒙混层比(I/S) 锐钛矿 金红石 黄铁矿 赤铁矿 高岭石 伊利石 伊蒙混层 硬水铝石 wB/% A 1 1992.82 16.99 / / / / 40.13 9.33 / 33.55 / 2 1993.86 27.64 / / 5.76 / 29.58 / / 37.02 / 3 1995.09 / 2.40 / / 29.73 34.14 4.21 / 29.52 / 4 1996.43 / 3.69 / / 2.12 21.78 / 44.25 28.16 80%∶20% 5 1998.73 3.65 2.81 / / 1.21 26.54 / 26.95 38.84 80%∶20% 6 1999.85 / 14.71 / 1.68 / 37.26 1.24 / 45.11 / 7 2000.07 0.97 2.31 0.1 / 0.80 28.84 / 28.85 38.13 80%∶20% 8 2002.31 2.44 / / / 4.90 41.63 6.17 / 44.86 / 9 2002.97 / 7.11 0.1 / 4.81 45.91 4.73 / 37.34 / 10 2003.15 / / 0.1 14.34 / 10.18 / / 75.38 / B 11 2054.80 2.9 2.82 / / 3.14 53.97 / 21.70 15.47 80%∶20% 12 2059.20 2.14 4.89 / / 1.68 55.50 / / 35.79 / 13 2065.80 / 5.70 / / / 20.87 / / 73.43 / C 14 2343.30 3.39 4.23 / / 1.28 71.35 / / 19.75 / 15 2348.20 / 3.12 / / / 62.51 3.13 / 31.24 / 16 2350.80 / / / / 17.32 34.70 / / 47.98 / 平均 / 3.76 3.36 0.02 1.36 4.19 35.43 4.80 7.61 39.47 80%∶20% 表 2 临兴地区A井本溪组铝土岩储层低温气体吸附与高压压汞实验孔隙参数
Table 2. Pore parameters from low-temperature gas adsorption and mercury intrusion porosimetry experiments in Benxi Formation bauxite reservoir of Well A in the Linxing area
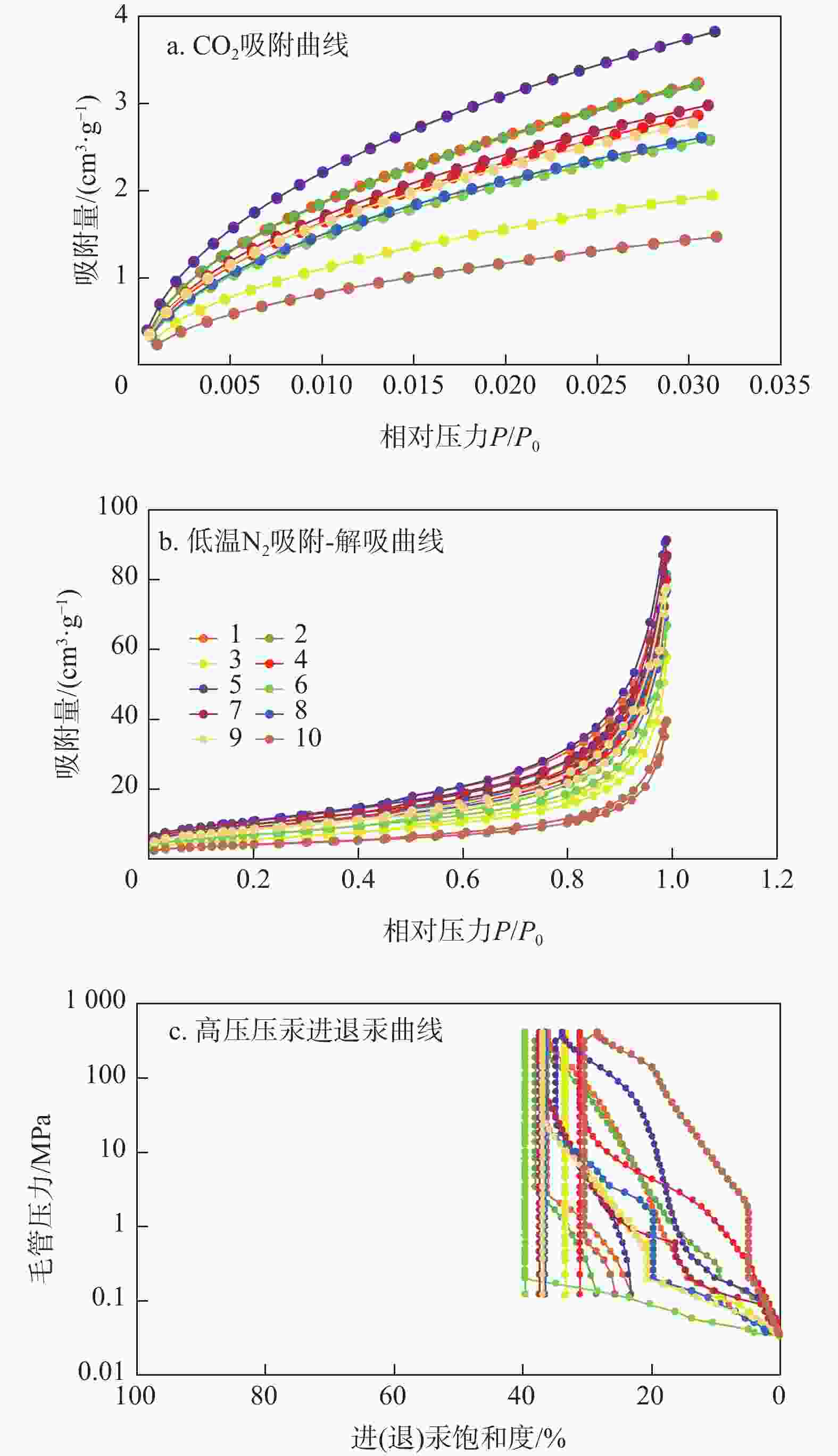
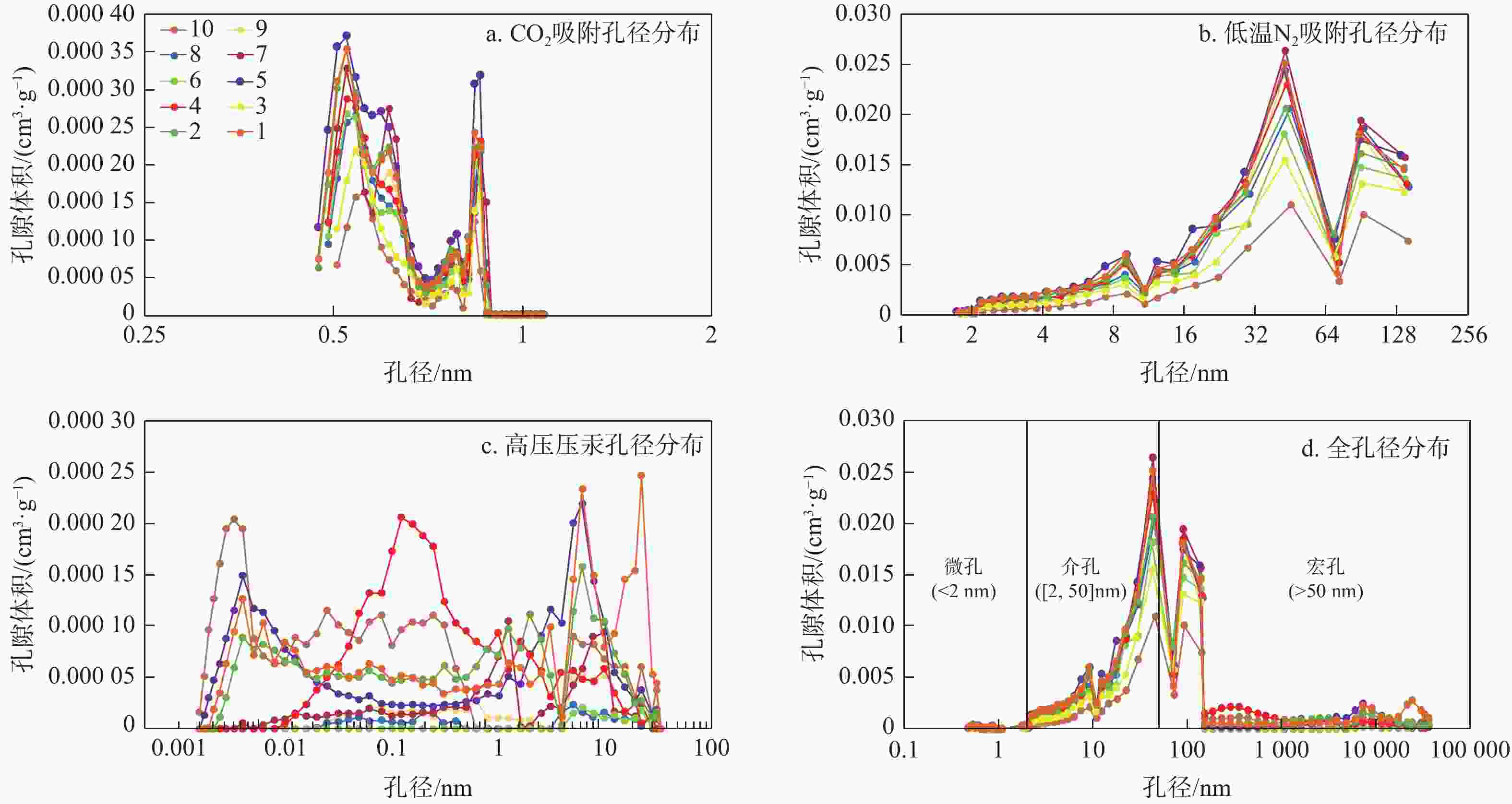
样品编号 深度/m CO2 吸附 N2 吸附 高压压汞 孔隙体积/(cm3·g−1) 比表面积/(m2·g−1) 孔径/nm 孔隙体积/(cm3·g−1) 比表面积/(m2·g−1) 孔径/nm 孔隙体积/(cm3·g−1) 比表面积/(m2·g−1) 孔径/nm 1 1992.82 0.021 25.372 0.472 0.135 38.748 12.529 0.0033 0.359 37.12 2 1993.86 0.020 25.227 0.472 0.128 35.721 12.897 0.0027 0.248 43.46 3 1995.09 0.013 15.509 0.507 0.090 20.558 14.805 / / 246.60 4 1996.43 0.018 23.122 0.489 0.125 32.730 13.549 0.0028 0.046 22.62 5 1998.73 0.022 29.597 0.472 0.143 39.550 12.751 0.0029 0.509 / 6 1999.85 0.018 20.420 0.489 0.104 25.375 14.185 0.0001 0.0001 188.60 7 2000.07 0.020 23.533 0.489 0.136 35.632 13.733 0.0010 0.021 354.29 8 2002.31 0.018 20.689 0.489 0.120 31.425 13.845 0.0002 0.003 429.94 9 2002.97 0.017 21.706 0.489 0.121 30.053 14.332 0.0007 0.006 14.56 10 2003.15 0.011 11.802 0.507 0.062 14.416 15.607 0.0035 0.955 37.12 平均 / 0.018 21.698 0.488 0.116 30.421 13.966 0.0019 0.239 246.85 表 3 临兴地区A井本溪组铝土岩储层物性参数
Table 3. Reservoir physical properties of Benxi Formation bauxite rock of Well A in the Linxing area
样品编号 深度/m 孔隙度/% 渗透率/10−3μm2 1 1992.82 1.7 1.212 2 1993.86 1.5 0.494 3 1995.09 2.6 0.922 4 1996.43 0.5 0.203 5 1998.73 3.45 0.604 6 1999.85 4.1 1.924 7 2000.07 0.9 0.128 8 2002.31 5.5 2.224 9 2002.97 2.6 1.853 10 2003.15 9.9 4.418 平均 / 3.28 1.398 陇东地区[8] / 10.65 4.040 -
[1] BARRDOSSY G, ALEVA G J J. Lateritic bauxites[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1990: 1-504. [2] DARGENIO B, MINDSZENTY A. Bauxites and related paleokarst: Tectonic and climatic event markers at regional unconformities[J]. Eclogae Geologicae Helvetiae, 1995, 88(3): 453-499. [3] 杜远生, 余文超. 沉积型铝土矿的陆表淋滤成矿作用: 兼论铝土矿床的成因分类[J]. 古地理学报, 2020, 22(5): 812-826.DU Y S, YU W C. Subaerial leaching process of sedimentary bauxite and the discussion on classifications of bauxite deposits[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2020, 22(5): 812-826.(in Chinese with English abstract [4] 孟祥化, 葛铭, 肖增起. 华北石炭纪含铝建造沉积学研究[J]. 地质学报, 1987, 22(2): 182-197.MENG X H, GE M, XIAO Z Q. Study on the sedimentology of the Carboniferous allite-bearing formation (sequence) of North China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1987, 22(2): 182-197.(in Chinese with English abstract [5] 温同想. 河南石炭纪铝土矿地质特征[J]. 华北地质矿产杂志, 1996, 11(4): 491-511.WEN T X. Geological characteristics of Carboniferous bauxite in Henan Province[J]. Journal of Geology & Mineral Resource in North China, 1996, 11(4): 491-511.(in Chinese with English abstract [6] 袁珍, 武富礼, 封蓉, 等. 鄂尔多斯延长气田铝土岩分布规律及其地质意义[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2016, 36(6): 843-848.YUAN Z, WU F L, FENG R, et al. The distribution rule and its geological significance of bauxite in Yanchang gas field of Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2016, 36(6): 843-848.(in Chinese with English abstract [7] 杨俊杰, 裴锡古. 中国天然气地质学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1996.YANG J J, PEI X G. Natural gas geology of China[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1996.(in Chinese) [8] 姚泾利, 石小虎, 杨伟伟, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区二叠系太原组铝土岩系储层特征及勘探意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2023, 41(5): 1583-1597.YAO J L, SHI X H, YANG W W, et al. Reservoir characteristics and exploration significance of the bauxite rock series of Permian Taiyuan Formation in the Longdong area of the Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2023, 41(5): 1583-1597.(in Chinese with English abstract [9] 冯娟萍, 欧阳征健, 周义军, 等. 鄂尔多斯地区中元古界“拗拉槽”的重新厘定[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 48(4): 587-592.FENG J P, OUYANG Z J, ZHOU Y J, et al. Revision of the Mesoproterozoic "Aulacogen" in Ordos area[J]. Journal of Northwest University(Natural Science Edition), 2018, 48(4): 587-592.(in Chinese with English abstract [10] 姜福杰, 贾承造, 庞雄奇, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地上古生界全油气系统成藏特征与天然气富集地质模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2023, 50(2): 250-261.JIANG F J, JIA C Z, PANG X Q, et al. Upper Paleozoic total petroleum system and geological model of natural gas enrichment in Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2023, 50(2): 250-261.(in Chinese with English abstract [11] 杨俊杰. 鄂尔多斯盆地构造演化与油气分布规律[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2002: 33-60.YANG J J. Tectonic evolution and oil-gas reservoirs distribution in Ordos Basin[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2002: 33-60.(in Chinese) [12] 李松, 马立元, 王濡岳, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地石盒子组−山西组致密储层形成主控因素与发育模式: 以彬长地区为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(2): 28-40.LI S, MA L Y, WANG R Y, et al. Main controlling factors and development model of tight reservoir in Shihezi Formation-Shanxi Formation in Ordos Basin: Taking Binchang area as an example[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(2): 28-40.(in Chinese with English abstract [13] 辛红刚, 田杨, 冯胜斌, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地典型夹层型页岩油地质特征及潜力评价: 以宁228井长7段为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(3): 114-124.XIN H G, TIAN Y, FENG S B, et al. Geological characteristics and potential evaluation of typical interlayer shale oil in the Ordos Basin: A case study of the Chang 7 Member of Well Ning228[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(3): 114-124.(in Chinese with English abstract [14] 陈晓智, 庞雄奇, 邵新荷, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地临兴A地区下石盒子组致密砂岩气成藏条件[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(1): 169-176.CHEN Z X, PANG X Q, SHAO X H, et al. Accumulation conditions of tight sandstone gas in the Lower Shihezi Formation in Linxing A area, Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(1): 33-60.(in Chinese with English abstract [15] 国家能源局. 沉积岩中黏土矿物和常见非黏土矿物X射线衍射分析方法: SY/T5163-2018[S]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2018.National Energy Administration. Analysis method for clay minerals and ordinary non-clay minerals in sedimentary rocks by the X-ray diffraction: SY/T5163-2018[S]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2018. (in Chinese) [16] 国家能源局. 岩石薄片鉴定: SY/T5368-2016[S]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2016.National Energy Administration. Identification for thin section of rocks: SY/T5368-2016[S]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2016. (in Chinese) [17] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 岩石毛管压力曲线的测定: GB/T29171-2012[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2013.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, National Standardization Administration. Rock capillary pressure measurement: GB/T29171-2012[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2013. (in Chinese) [18] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 岩心分析方法: GB/T29172-2012[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2013.General Administration of Quality Supervision,Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China. Practices for core analysis: GB/T29172-2012[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2013. (in Chinese) [19] 常丽华, 陈曼云, 金巍, 等. 透明矿物薄片鉴定手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2006: 105-199.CHANG L H, CHEN M Y, JIN W, et al. Manual for identification of transparent minerals in thin section [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2006: 105-199.(in Chinese) [20] LIU X F, WANG Q F , PENG Y B , et al. Intensified and apace bauxitization over the paleo-karstic surface linked to volcanism[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2022, 135: 1187-1205. [21] LIU X F, WANG Q F, ZHAO L H, et al. Metallogeny of the large-scale Carboniferous karstic bauxite in the Sanmenxia area, southern part of the North China Craton, China[J]. Chemical Geology, 2020, 556: 119851. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2020.119851 [22] WANG Q F, DENG J, LIU X F, et al. Provenance of Late Carboniferous bauxite deposits in the North China Craton: New constraints on marginal arc construction and accretion processes[J]. Gondwana Research, 2016, 38: 86-98. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.10.015 [23] ZHAO L H, LIU X F, YANG S J, et al. Regional multi-sources of Carboniferous karstic bauxite deposits in North China Craton: Insights from multi-proxy provenance systems[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2021, 421: 105958. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2021.105958 [24] 余文超, 杜远生, 熊国林, 等. 中国铝土矿沉积中的碎屑锆石记录: 对铝土矿物源模式与矿床分类的启示[J]. 古地理学报, 2020, 22(5): 945-964.YU W C, DU Y S, XIONG G L, et al. Detrital zircon records in bauxite deposits of China: Implication for the provenance model and ore deposits classification of bauxite[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2020, 22(5): 945-964.(in Chinese with English abstract [25] WANG Y, ZHOU L Y, LIU S F, et al. Post-cratonization deformation processes and tectonic evolution of the North China Craton[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 177: 320-365. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.11.017 [26] YU W C, YAN J X, et al. Climatic and hydrologic controls on upper Paleozoic bauxite deposits in South China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2019, 189: 159-176. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.06.014 [27] 李文厚, 张倩, 李克永, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地及周缘地区晚古生代沉积演化[J]. 古地理学报, 2021, 23(1): 39-52.LI W H, ZHANG Q, LI K Y, et al. Sedimentary evolution of the late Paleozoic in Ordos Basin and its adjacent areas[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2021, 23(1): 39-52.(in Chinese with English abstract [28] 何发岐, 王付斌, 郭利果, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地古生代原型盆地演化与构造沉积格局变迁[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(3): 373-384.HE F Q, WANG F B, GUO L G, et al. Evolution of prototype basin and change of tectonic-sedimentary pattern in Paleozoic, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(3): 373-384. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 赵振宇, 郭彦如, 王艳, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地构造演化及古地理特征研究进展[J]. 特种油气藏, 2012, 19(5): 15-20.ZHAO Z Y, GUO Y R, WANG Y, et al. Study progress in tectonic evolution and paleogeography of Ordos Basin[J]. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs, 2012, 19(5): 15-20. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] 南珺祥, 柳娜, 王邢颖, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区太原组铝土岩储层特征及形成机理[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2022, 33(2): 288-296.NAN J X, LIU N, WANG X Y, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of bauxite reservoir in Taiyuan Formation, Longdong area, Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2022, 33(2): 288-296.(in Chinese with English abstract [31] 杜佳, 朱光辉, 吴洛菲, 等. 临兴地区致密气“多层系准连续”成藏模式与大气田勘探实践[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(3): 58-71.DU J, ZHU G H, WU L F, et al. "Multi-series and quasi-continuous" tight gas accumulation pattern and giant gas field exploration practice in Linxing area[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(3): 58-71.(in Chinese with English abstract [32] 国家经济贸易委员会. 碎屑岩成岩阶段划分: SY/T5477-2003[S]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2003.National Economic and Trade Commission. The division of diagenetic stages in clastic rocks: SY/T5477-2003[S]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2003. (in Chinese) [33] 焦养泉, 吴立群, 荣辉. 聚煤盆地沉积学[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2015.JIAO Y Q, WU L Q, RONG H. Sedimentology of coal-bearing basins[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2015. (in Chinese) -




 下载:
下载: