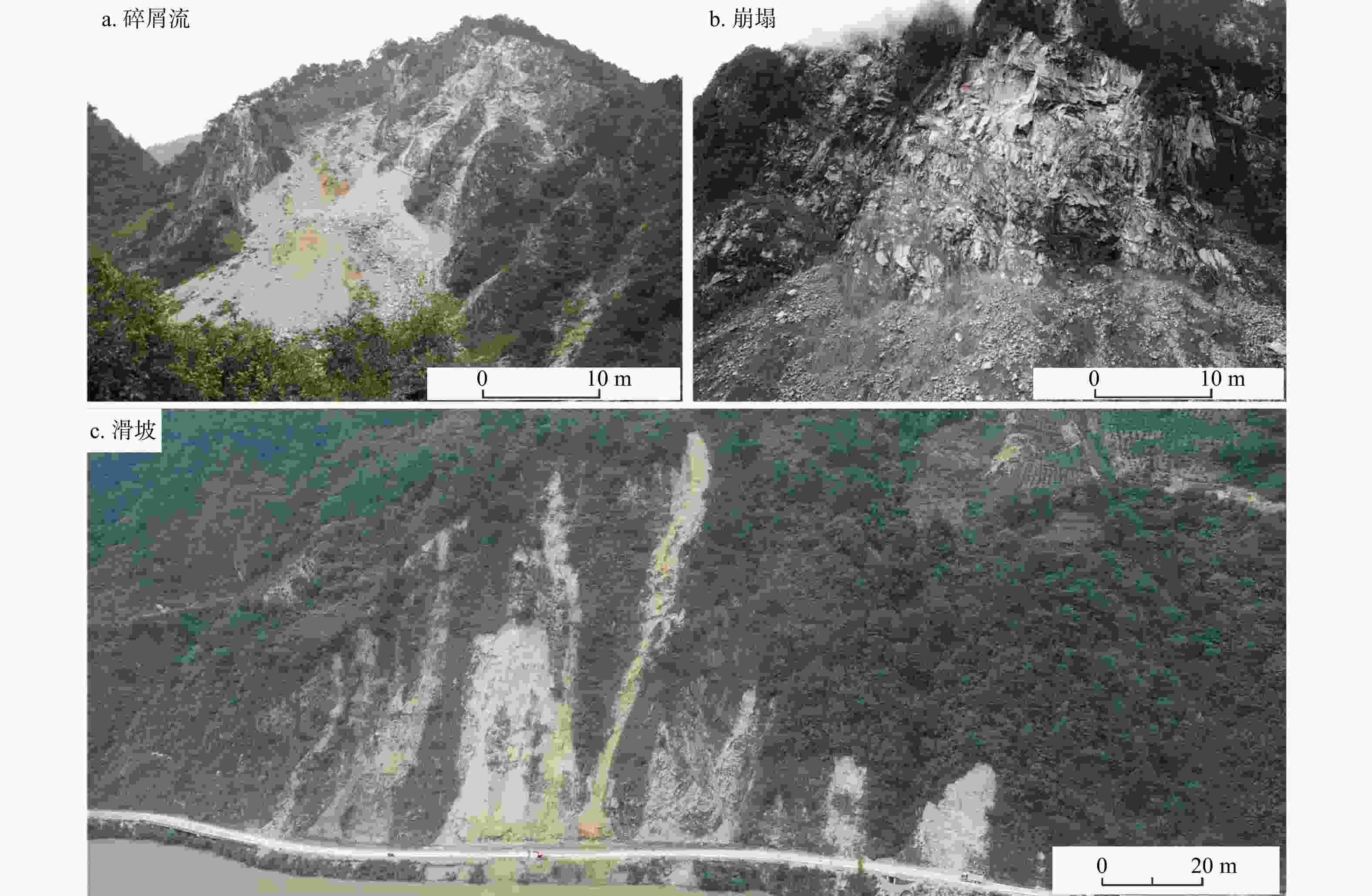
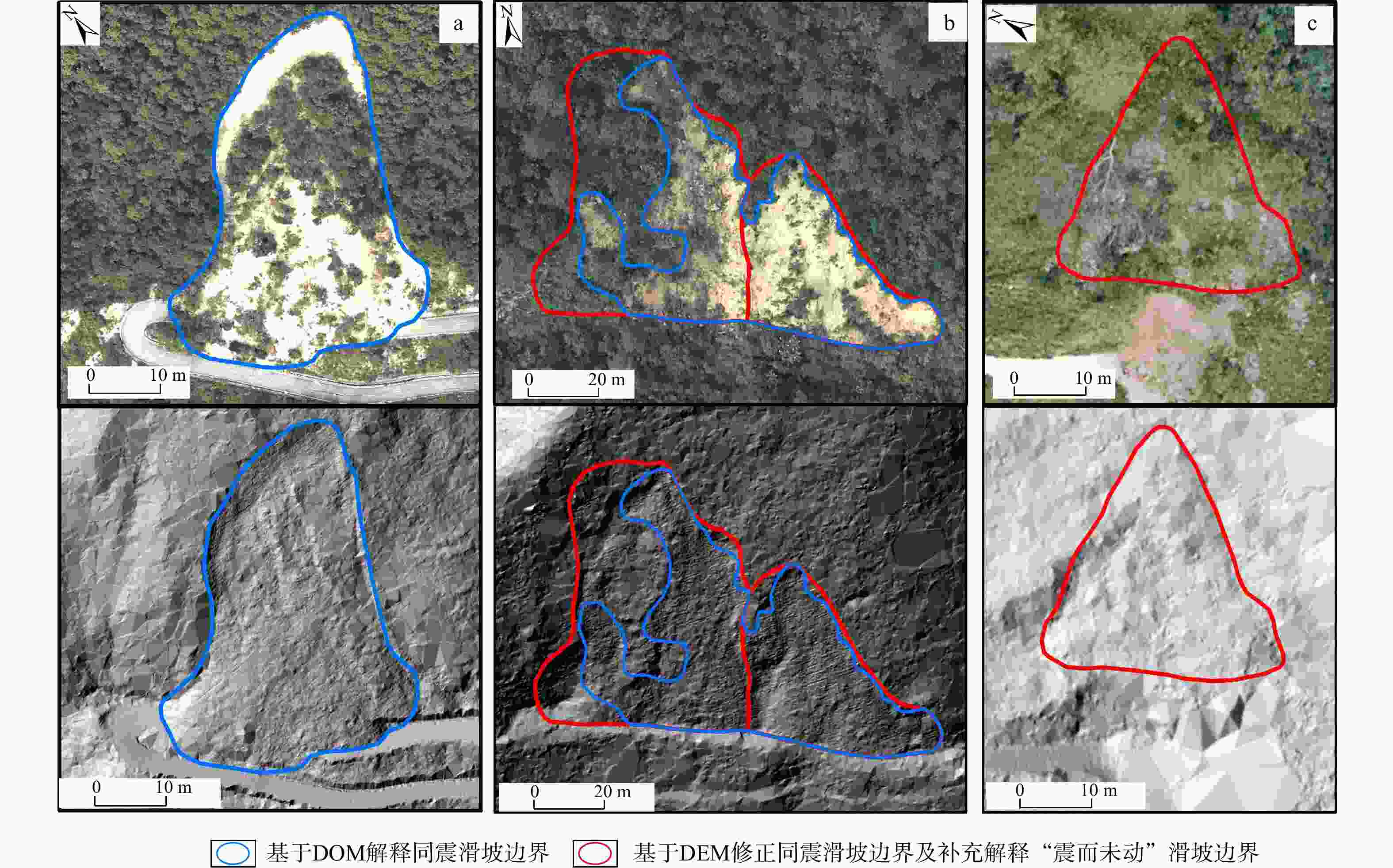
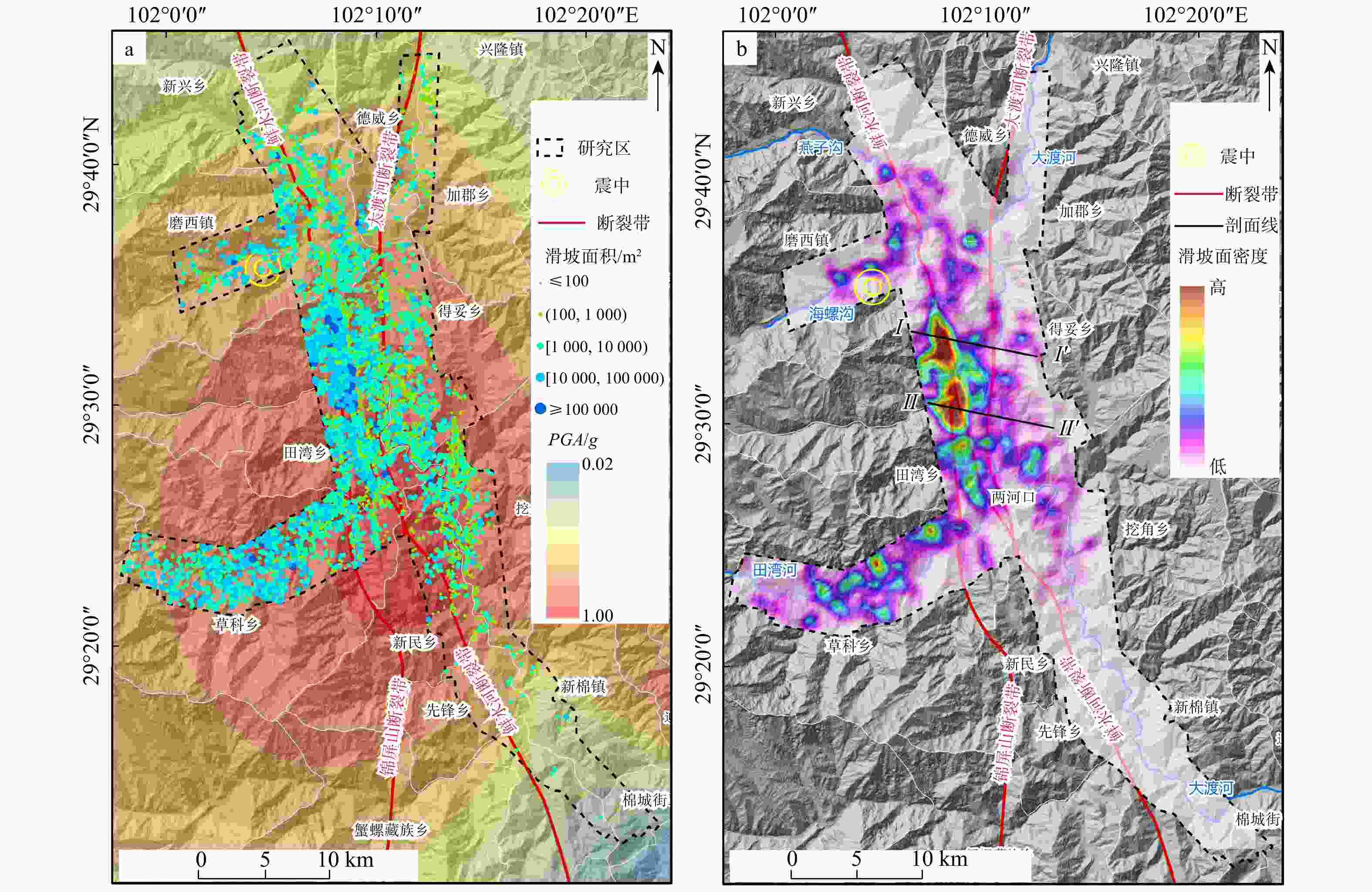
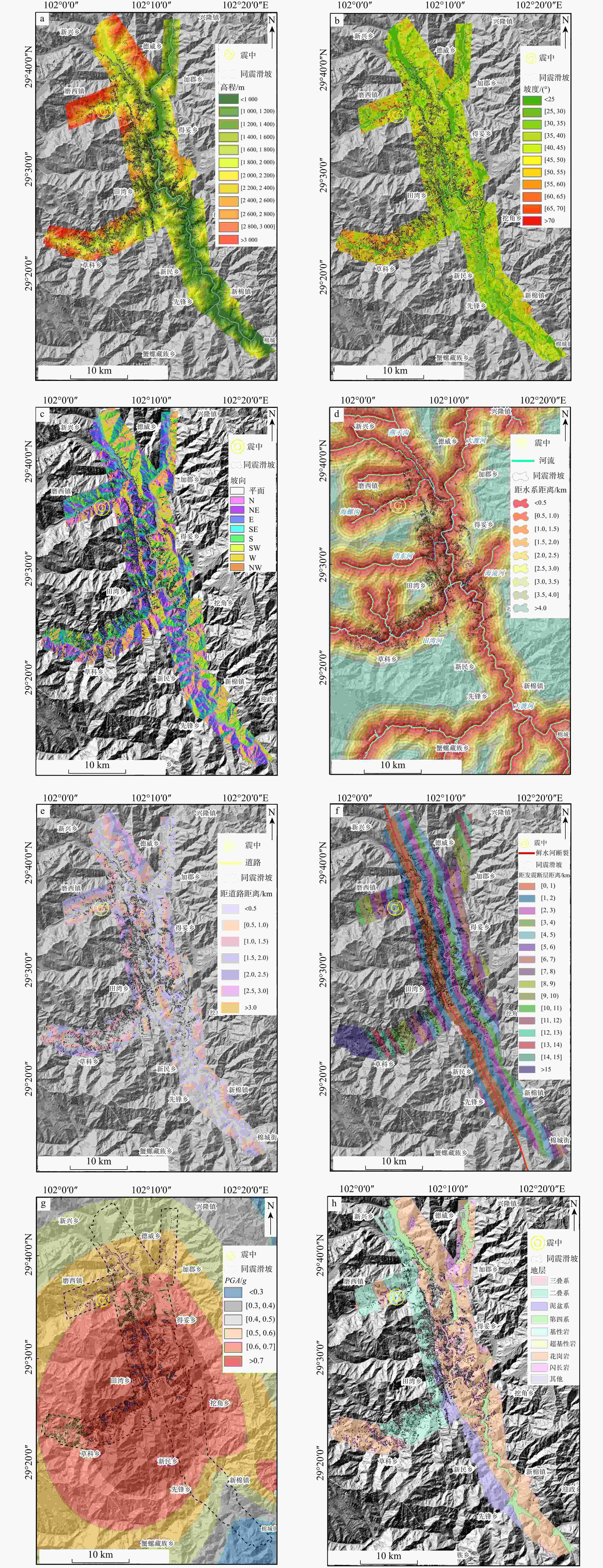
Spatial distribution of earthquake-induced landslide in densely populated area of the Luding 9·5 earthquake
-
摘要:
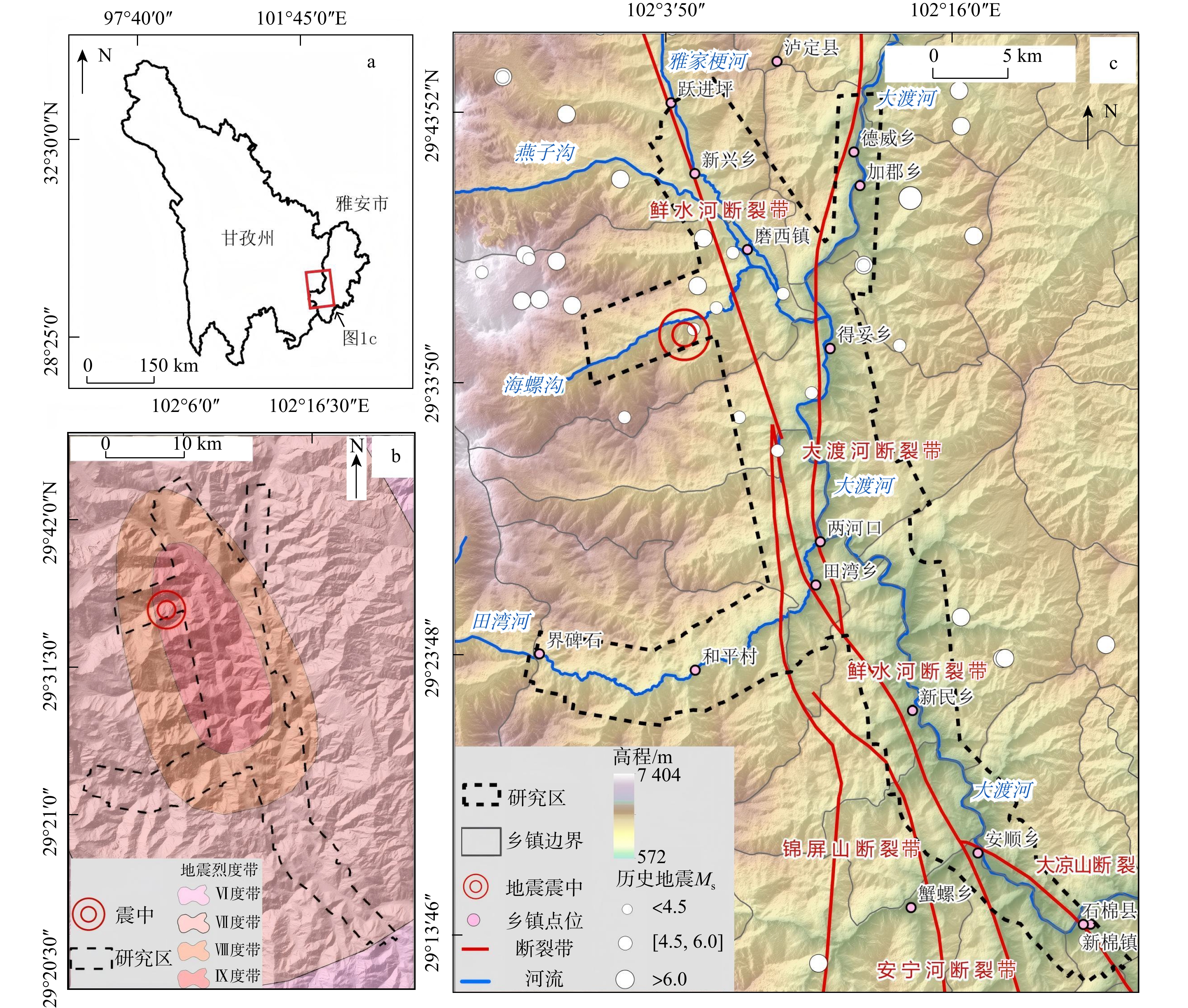
研究地震诱发滑坡的空间分布规律,不仅能为灾区地质灾害隐患排查、灾情评估等提供重要依据,同时对后期灾后重建、灾后安置选址以及地质灾害防治等工作具有重要意义。以2022年9月5日四川甘孜泸定县
M s 6.8级地震为例,首先基于获取得到的震后0.2 m分辨率光学影像(digital orthophoto map,简称DOM)和0.5 m分辨率的数字高程模型(digital elevation matrix,简称DEM),采用人工目视三维遥感解译地震诱发滑坡,再结合野外调查修正,确定最终地震诱发滑坡数量,并在此基础上分析地震诱发滑坡分布与地形地貌、地质构造、地震因子等地质背景的关系。结果表明:①此次泸定地震事件在约680 km2的研究区内引发了9248 处滑坡,且以中、小型滑坡为主,滑坡面积密度最高集中在鲜水河断裂、大渡河断裂以及锦屏山断裂3条断裂交汇处;滑坡总面积约45.57 km2,平均滑坡面积可达4941 m2。②本次地震滑坡分布主要受地面峰值加速度PGA 以及断裂构造影响,多分布在PGA > 0.6g (g 为重力加速度),距发震断裂两侧1 km范围内;此外滑坡的发育还与距水系及道路距离呈负相关;局部受地形因素影响滑坡主要发育在高程1200 ~2400 m、坡度30°~60°、坡向E及SE向区域,且地层岩性多为硬岩。③此次泸定地震的滑坡数量及面积与震级关系也遵循指数分布;同时由于此次解译基础数据精度较高,解译得到的地震滑坡数量相比于其他文献而言更多,最小面积更小,总面积更大。本研究成果已应用于泸定地震灾区的灾后恢复重建工作,为提高抗灾能力和降低地震风险提供了科学依据。Abstract:Objective The spatial distribution analysis of earthquake-induced landslides offers critical insights for identifying potential geological disasters in affected regions, which is fundamental for informing post-disaster reconstruction planning, relocation strategies, site selection processes, and the development of effective geological disaster mitigation measures.
Methods Taking the earthquake that struck Luding County, Ganzi, Sichuan Province, on September 5, 2022, as a case study, earthquake-induced landslides were initially identified using artificial visual 3D remote sensing data. This analysis was based on an optical image (DOM) with a resolution of 0.2 meter and a digital elevation model (DEM) with a resolution of 0.5 meter, both acquired post-earthquake. Field investigations and subsequent corrections were performed to validate and finalize the landslide inventory. Subsequently, the relationships between the distribution of earthquake-induced landslides and various geological factors, including topography, geological structures, and earthquake parameters, were systematically analyzed.
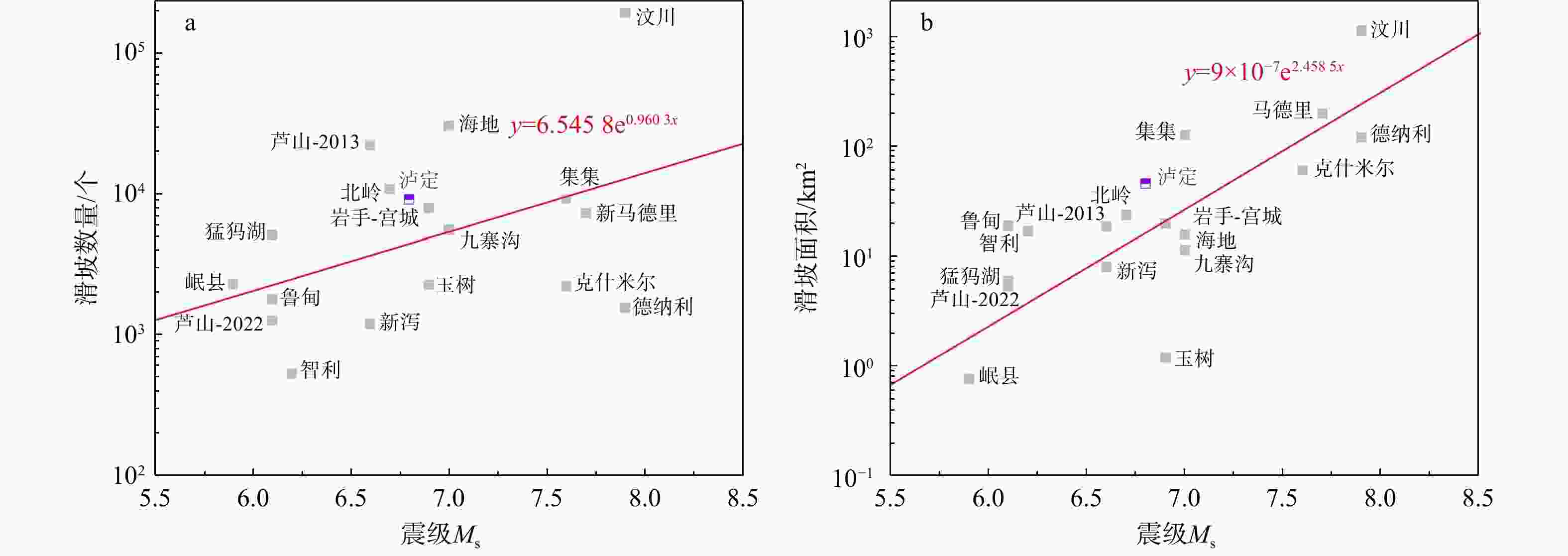
Results ①The Luding earthquake triggered
9248 landslides, covering an area of approximately 680 km2, with the majority classified as small- to medium-sized. The highest landslide density was observed at the tectonic intersection of the Xianshuihe fault, Daduhe fault, and Jinping mountain fault. The cumulative landslide area reached approximately 45.57 km2, with an average landslide area of4941 m2. ② The spatial distribution of landslide in the earthquake-affected region is predominantly controlled byPGA and fault structures, with the majority of landslides concentrated in areas wherePGA exceeds 0.6g and within 1 km on either side of the seismogenic fault. Furthermore, landslide occurrence exhibits a negative correlation with proximity to water systems and roads. At a local scale, topographic factors significantly influence landslide distribution, with the highest frequency observed at elevations ranging from1200 to2400 m, on slopes inclined between 30° and 60°, and predominantly facing east or southeast. Additionally, landslides are more prevalent in areas underlain by hard rock strata. ③ The number and area of landslides exhibit an exponential relationship with the magnitude of the Luding earthquake. Leveraging high-precision data, our analysis identified a significantly higher number of earthquake-induced landslides compared to previous studies, with a reduced minimum landslide area and an increased total affected area.Conclusion The findings of this study have been implemented to support post-disaster recovery and reconstruction efforts in the Luding earthquake-affected region, providing a scientific basis for enhancing resilience and reducing future earthquake risks.
-
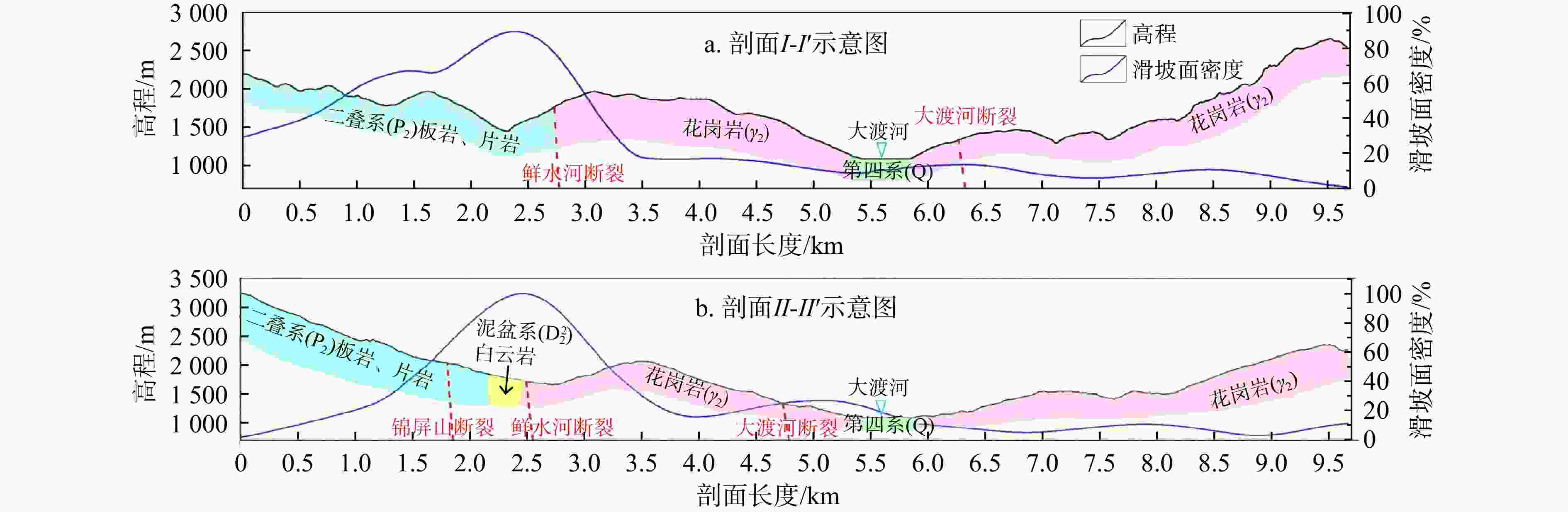
图 5 地震滑坡面密度、高程、地层岩性的剖面图(剖面位置见图4b)
Figure 5. Profile of area density, elevation and stratum lithology of earthquake-induced landslide
表 1 地震滑坡控制因子分级
Table 1. Classification of controlling factors of earthquake-induced landslide
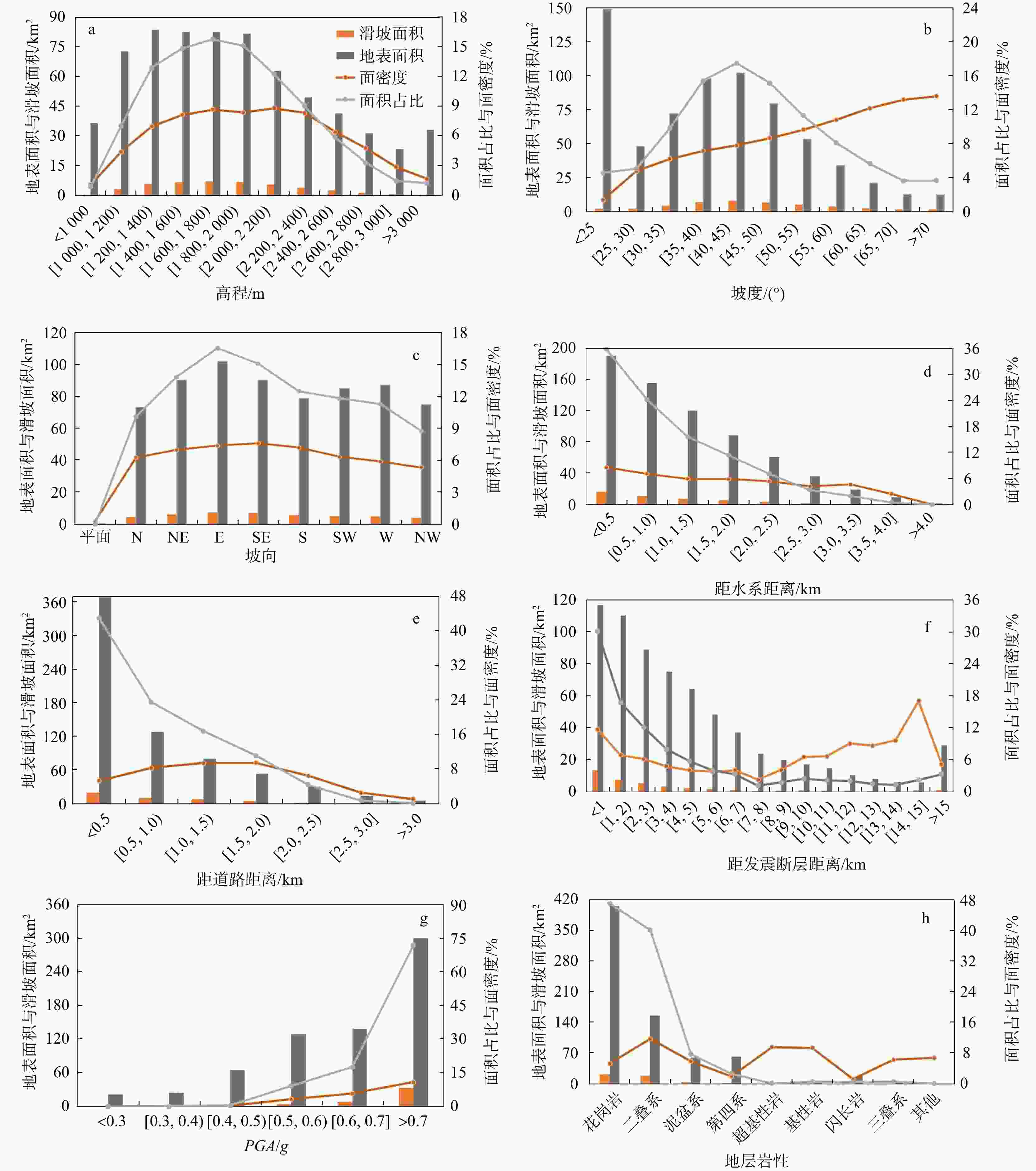
因子类型 因子名称 因子分级 地形地貌 高程/m < 1000 , [1000 ,1200 ), [1200 ,1400 ), [1400 ,1600 ), [1600 ,1800 ), [1800 ,2000 ), [2000 ,2200 ),
[2200 ,2400 ], [2400 ,2600 ), [2600 ,2800 ), [2800 ,3000 ], >3000 坡度/(°) < 25, [25, 30), [30, 35), [35, 40), [40, 45), [45, 50), [50, 55), [55, 60), [60, 65), [65, 70], > 70 坡向 平面,N, NE, E, SE, S, SW, W, NW 距水系距离/km < 0.5, [0.5, 1.0), [1.0, 1.5), [1.5, 2.0), [2.0, 2.5), [2.5, 3.0), [3.0, 3.5), [3.5, 4.0], > 4.0 距道路距离/km < 0.5, [0.5, 1.0), [1.0, 1.5), [1.5, 2.0), [2.0, 2.5), [2.5, 3.0], > 3.0 地质参数 地层岩性 三叠系,二叠系,泥盆系,第四系,基性岩,超基性岩,花岗岩,闪长岩,其他 地震参数 距发震断层距离/km [0, 1), [1, 2), [2, 3), [3, 4), [4, 5), [5, 6), [6, 7), [7, 8), [8, 9), [9, 10], [10, 11), [11, 12), [12, 13), [13, 14), [14, 15], > 15 PGA/g < 0.3, [0.3, 0.4), [0.4, 0.5), [0.5, 0.6), [0.6, 0.7], > 0.7 表 2 不同文献得到的泸定地震相关结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of Luding earthquake related results from different documents
文献来源 研究区面积/km2 滑坡数量/个 滑坡总面积/km2 滑坡最小面积/m2 高程/m 坡度/(°) 坡向 距发震断层距离/km 地层岩性 文献[1-2] 419.2 3633 13.78 49 1200 ~1400 40~45 E 1 花岗岩 文献[3] 2600 4528 28.1 / 1200 ~1500 40~45 / 1 花岗岩 文献[21] 3056 2692 47 220.77 1800 ~2000 40~45 E 1 砂岩板岩 文献[25] 19000 8685 30.7 / / / / 2 / 文献[26] 4393 5007 17.36 65 1300 ~1500 40~50 E 1 花岗岩 文献[40] 166 513 8.88 / 1400 ~2200 40~45 E、SE 3 / 本研究 682 9248 46 15.5 1600 ~1800 40~45 E 0.5 花岗岩 -
[1] 范宣梅, 王欣, 戴岚欣, 等. 2022年Ms 6.8级泸定地震诱发地质灾害特征与空间分布规律研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2022, 30(5): 1504-1516.FAN X M, WANG X, DAI L X, et al. Characteristics and spatial distribution pattern of Ms 6.8 Luding earthquake occurred on September 5, 2022[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2022, 30(5): 1504-1516. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] 王欣, 方成勇, 唐小川, 等. 泸定Ms 6.8地震诱发滑坡应急评价研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2023, 48(1): 25-35.WANG X, FANG C Y, TANG X C, et al. Research on emergency evaluation of landslides induced by the Luding Ms 6.8 earthquake[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2023, 48(1): 25-35. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] ZHAO B, HU K H, YANG Z J, et al. Geomorphic and tectonic controls of landslides induced by the 2022 Luding earthquake[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2022, 19(12): 3323-3345. doi: 10.1007/s11629-022-7732-8 [4] 魏旭, 彭志忠, 刘兴臣, 等. 泸石高速公路沿线历史地震诱发滑坡遥感调查及发育分布规律[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(2): 386-396.WEI X, PENG Z Z, LIU X C, et al. Remote sensing investigation and development distribution of historical earthquake-induced landslides along Lushi Expressway[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(2): 386-396. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 李传友, 孙凯, 马骏, 等. 四川泸定6.8级地震: 鲜水河断裂带磨西段局部发起、全段参与的一次复杂事件[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(6): 1648-1666. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.06.017LI C Y, SUN K, MA J, et al. The 2022 Ms 6.8 Luding earthquake: A complicated event by faulting of the moxi segment of the Xianshuihe fault zone[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2022, 44(6): 1648-1666. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.06.017 [6] 邓建辉, 韦晓, 戴仕贵, 等. 泸定地震诱发灾害特征分析[J]. 工程科学与技术, 2024, 56(1): 117-126.DENG J H, WEI X, DAI S G, et al. Characterization analysis of triggered disasters in the Luding earthquake[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2024, 56(1): 117-126. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] 孙东, 杨涛, 曹楠, 等. 泸定Ms 6.8地震同震地质灾害特点及防控建议[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(3): 476-493.SUN D, YANG T, CAO N, et al. Characteristics and mitigation of coseismic geohazards associated with the Luding Ms 6.8 earthquake[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2023, 30(3): 476-493. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 唐辉明. 重大滑坡预测预报研究进展与展望[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(6): 1-13.TANG H M. Advance and prospects of major landslides prediction and forecasting[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(6): 1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 张佳佳, 陈龙, 李元灵, 等. 2022年9月5日泸定Ms 6.8地震的同震地质灾害发育特征及主控因素分析[J]. 地震学报, 2023, 45(2): 167-178. doi: 10.11939/jass.20220215ZHANG J J, CHEN L, LI Y L, et al. Development characteristics and controlling factors of coseismic geohazards triggered by the Luding Ms 6.8 earthquake occurred on September 5, 2022[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 2023, 45(2): 167-178. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11939/jass.20220215 [10] 许冲, 徐锡伟, 吴熙彦, 等. 2008年汶川地震滑坡详细编目及其空间分布规律分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2013, 21(1): 25-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2013.01.004XU C, XU X W, WU X Y, et al. Detailed catalog of landslides triggered by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake and statistical analyses of their spatial distribution[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2013, 21(1): 25-44. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2013.01.004 [11] 许冲. 2008年汶川地震滑坡编录及其量化成果[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 87(增刊1): 307-308.XU C. Landslide catalogue of the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake and its quantitative results[J]. Acta Ceologica Sinica, 2013, 87(S1): 307-308. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 殷跃平. 汶川八级地震地质灾害研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2008, 16(4): 433-444. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2008.04.001YIN Y P. Researches on the geo-hazards triggered by Wenchuan earthquake, Sichuan[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2008, 16(4): 433-444. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2008.04.001 [13] XU C, XU X W, SHYU J B H. Database and spatial distribution of landslides triggered by the Lushan, China Mw 6.6 earthquake of 20 April 2013[J]. Geomorphology, 2015, 248: 77-92. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.07.002 [14] 张佳佳, 李海兵, 赵国华, 等. 2013年四川芦山地震次生山地灾害发育规律[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(5): 898-907.ZHANG J J, LI H B, ZHAO G H, et al. Features of secondary mountain hazards triggered by the 2013 Lushan earthquake, Sichuan Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2015, 34(5): 898-907. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] LING S X, SUN C W, LI X N, et al. Characterizing the distribution pattern and geologic and geomorphic controls on earthquake-triggered landslide occurrence during the 2017 Ms 7.0 Jiuzhaigou earthquake, Sichuan, China[J]. Landslides, 2021, 18(4): 1275-1291. doi: 10.1007/s10346-020-01549-6 [16] 许冲, 王世元, 徐锡伟, 等. 2017年8月8日四川省九寨沟Ms7.0地震触发滑坡全景[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(1): 232-260. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2018.01.017XU C, WANG S Y, XU X W, et al. A panorama of landslides triggered by the 8 August 2017 Jiuzhaigou, Sichuan Ms 7.0 earthquake[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2018, 40(1): 232-260. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2018.01.017 [17] ZHAO B, LI W L, SU L J, et al. Insights into the landslides triggered by the 2022 Lushan Ms6.1 earthquake: Spatial distribution and controls[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(17): 4365. doi: 10.3390/rs14174365 [18] 范宣梅, 方成勇, 戴岚欣, 等. 地震诱发滑坡空间分布概率近实时预测研究: 以2022年6月1日四川芦山地震为例[J]. 工程地质学报, 2022, 30(3): 729-739.FAN X M, FANG C Y, DAI L X, et al. Near real time prediction of spatial distribution probability of earthquake-induced landslides: Taking the Lushan earthquake on June 1, 2022 as an example[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2022, 30(3): 729-739. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] HAKAN T, LUIGI L. Completeness index for earthquake-induced landslide inventories[J]. Engineering Geology, 2020, 264: 105331. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105331 [20] HUANG Y D, XIE C C, LI T, et al. An open-accessed inventory of landslides triggered by the Ms 6.8 Luding earthquake, China on September 5, 2022[J]. Earthquake Research Advances, 2023, 3(1): 37-44. [21] 铁永波, 张宪政, 卢佳燕, 等. 四川省泸定县Ms 6.8级地震地质灾害发育规律与减灾对策[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2022, 49(6): 1-12.TIE Y B, ZHANG X Z, LU J Y, et al. Characteristics of geological hazards and it's mitigations of the Ms 6.8 earthquake in Luding County, Sichuan Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(6): 1-12. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 陈博, 李振洪, 黄武彪, 等. 2022年四川泸定Mw6.6级地震诱发地质灾害空间分布及影响因素[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2022, 44(6): 971-985.CHEN B, LI Z H, HUANG W B, et al. Spatial distribution and influencing factors of geohazards induced by the 2022 Mw 6.6 Luding (Sichuan, China)earthquake[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2022, 44(6): 971-985. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] 张宪政, 铁永波, 李光辉, 等. 四川泸定Ms 6.8级地震区湾东河流域泥石流活动性预测[J]. 地质力学学报, 2022, 28(6): 1035-1045.ZHANG X Z, TIE Y B, LI G H, et al. Characteristics and risk assessment of debris flows in the Wandong catchment after the Ms 6.8 Luding earthquake[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2022, 28(6): 1035-1045. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] XIONG J, CHEN H Y, ZENG L, et al. Coseismic landslide sediment increased by the "9.5" Luding earthquake, Sichuan, China[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2023, 20(3): 624-636. doi: 10.1007/s11629-022-7770-2 [25] ZHANG J Q, YANG Z J, MENG Q K, et al. Distribution patterns of landslides triggered by the 2022 Ms 6.8 Luding earthquake, Sichuan, China[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2023, 20(3): 607-623. doi: 10.1007/s11629-022-7772-0 [26] XIAO Z K, XU C, HUANG Y D, et al. Analysis of spatial distribution of landslides triggered by the Ms 6.8 Luding earthquake in China on September 5, 2022[J]. Geoenvironmental Disasters, 2023, 10(1): 3. doi: 10.1186/s40677-023-00233-w [27] 张雨, 明冬萍, 赵文祎, 等. 基于高分光学卫星影像的泸定地震型滑坡提取与分析[J]. 自然资源遥感, 2023, 35(1): 161-170.ZHANG Y, MING D P, ZHAO W Y, et al. The extraction and analysis of Luding earthquake-induced landslide based on high-resolution optical satellite images[J]. Remote Sensing for Natural Resources, 2023, 35(1): 161-170. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] 邓博, 张会, 柏君, 等. 利用机载LiDAR的深圳市斜坡类地质灾害危险性评价[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2024, 49(8): 1377-1391.DENG B, ZHANG H, BAI J, et al. Hazard evaluation of the slope based on airborne LiDAR data in Shenzhen, China[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2024, 49(8): 1377-1391. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] YUSOFF H H M, RAZAK K A, YUEN F, et al. Mapping of post-event earthquake induced landslides in Sg. Mesilou using LiDAR[J]. IOP Conference Series(Earth and Environmental Science), 2016, 37: 012068. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/37/1/012068 [30] LIU W, YAMAZAKI F, MARUYAMA Y. Detection of earthquake-induced landslides during the 2018 Kumamoto earthquake using multitemporal airborne lidar data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(19): 2292. doi: 10.3390/rs11192292 [31] RUIZ P, CARR M J, ALVARADO G E, et al. Coseismic landslide susceptibility analysis using LiDAR data PGA attenuation and GIS: The case of Poás volcano, costa rica, central America[M]. Berlin, Germary: Springer International Publishing, 2019: 79-118. [32] 孟华君, 乔建平, 田宏岭, 等. 小区域地震地质灾害空间分布特点分析方法探讨[J]. 工程地质学报, 2014, 22(1): 14-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2014.01.003MENG H J, QIAO J P, TIAN H L, et al. Method discussion on spatial distribution analysis of earthquake induced geohazards in small region[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2014, 22(1): 14-23. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2014.01.003 [33] 赵方彬, 王运生, 寇瑞斌, 等. 四川珙县下软上硬山岭地貌斜坡地震动响应特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(2): 279-287.ZHAO F B, WANG Y S, KOU R B, et al. Seismic dynamic response characteristics of the lower soft and upper hard mountain slopes in Gongxian, Sichuan[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(2): 279-287. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] 王佳运, 张成航, 高波, 等. 玉树震区地质灾害分布规律与发育特征[J]. 工程地质学报, 2013, 21(4): 508-515.WANG J Y, ZHANG C H, GAO B, et al. Distribution regularity and development characteristics of geohazards in Yushu earthquake area[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2013, 21(4): 508-515. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] 杨秀元, 姚亚辉, 田运涛. 云南鲁甸“8·3”震后地质灾害发育特征与分布规律[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2018, 18(24): 16-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2018.24.003YANG X Y, YAO Y H, TIAN Y T. Development law and distribution characteristics of geological hazards after "8·3" earthquake in Ludian, Yunnan[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2018, 18(24): 16-21. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2018.24.003 [36] 蒋涛, 崔圣华. 川滇地区典型强震诱发滑坡分布对比研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2022, 22(31): 13662-13671. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2022.31.007JIANG T, CUI S H. Comparative study on the distribution of typical strong earthquake-induced landslides in Sichuan and Yunnan regions[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2022, 22(31): 13662-13671. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2022.31.007 [37] XU C. Preparation of earthquake-triggered landslide inventory maps using remote sensing and GIS technologies: Principles and case studies[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2015, 6(6): 825-836. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2014.03.004 [38] 许冲, 徐锡伟, 于贵华. 玉树地震滑坡分布调查及其特征与形成机制[J]. 地震地质, 2012, 34(1): 47-62.XU C, XU X W, YU G H. Study on the characteristics, mechanism, and spatial distribution of Yushu earthquake triggered landslides[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2012, 34(1): 47-62. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] ZOU Y, QI S W, GUO S F, et al. Factors controlling the spatial distribution of coseismic landslides triggered by the Mw 6.1 Ludian earthquake in China[J]. Engineering Geology, 2022, 296: 106477. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106477 [40] 刘甲美, 王涛, 杜建军, 等. 四川泸定Ms 6.8级地震诱发崩滑灾害快速评估[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2023, 50(2): 84-94.LIU J M, WANG T, DU J J, et al. Emergency rapid assessment of landslides induced by the Luding Ms 6.8 earthquake in Sichuan of China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(2): 84-94. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: