Spatial distribution and controlling factors of sediment nitrogen forms in the mangrove wetland at Dongzhai Port, Hainan Province
-
摘要:
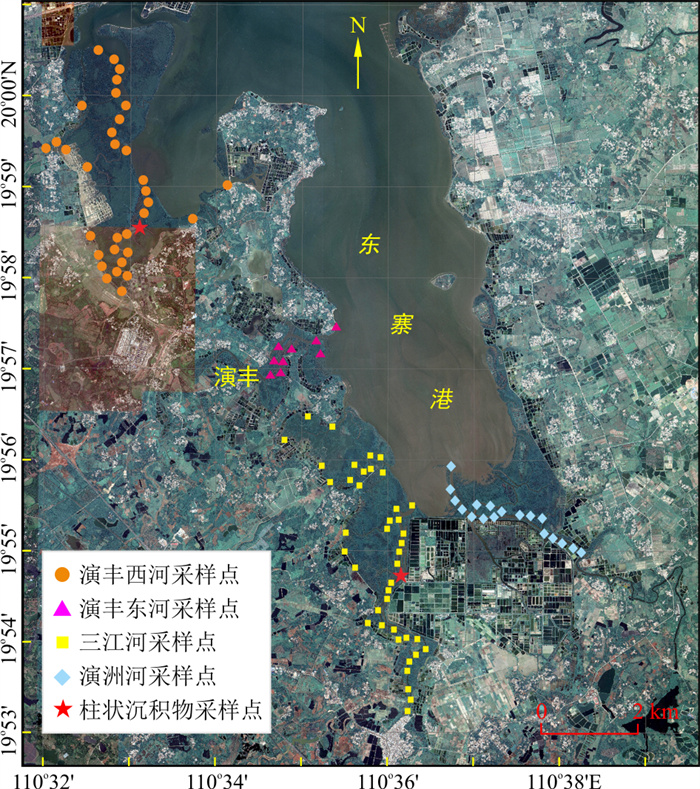
沉积物中氮的赋存形态直接影响其参与生物地球化学循环的进程、途径和贡献大小,探究沉积物中不同氮形态的环境地球化学行为对研究氮的地球化学循环具有重要意义。以海南东寨港红树林湿地沉积物为研究对象,分别采集表层沉积物和柱状沉积物,采用分级浸提法提取不同形态的可转化态氮进行空间分布特征及影响因素分析。结果表明:研究区沉积物中总氮(TN)质量分数在1 149.0~1 690.6 mg/kg之间,总可转化态氮(TTN)的质量分数在464.6~647.5 mg/kg之间,二者均呈现出从上游至入海口逐渐降低的空间分布特征;4种可转化态氮中强氧化剂浸取态氮(SOEF-N)与TTN呈显著正相关,也是最主要的氮形态存在形式。通过沉积物C/N比值分析可知,研究区有机质主要来自污染物的大量排入,东寨港红树林柱状沉积物中TN与含水率、TOC呈极显著的正相关关系,表明氮与有机质具有相似的来源。
Abstract:The occurence of nitrogen in sediments directly affects the process, pathway and contribution of nitrogen in the nature, therefore exploring the environmental geochemical behavior of different nitrogen speciation in sediments is of great significance for studying nitrogen geochemical cycle. In this study, the surface sediment and sediment core were collected in the mangrove wetland at Dongzhai Port, Hainan Province.The different forms of transferable nitrogen were analyzed via hierarchical extraction.The spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors were investigated. The results showed that the contents of total nitrogen (TN) and total transferable nitrogen (TTN) in the sediments ranged from 1 149.2 to 1 690.6 mg/kg and from 464.6 to 647.5 mg/kg, respectively, both of which presented a decreasing trend from the upstream to the estuary. The strong oxidant extracted nitrogen (SOEF-N) is the major nitrogen species in TTN, and positively correlated with TTN contents. According to C/N ratio, the organic matter in the study area is mainly from the discharge of a large number of pollutants.The significant positive correlation between TN, water content and TOC in the mangrove columnar sediments in Dongzhai Port, indicates that nitrogen and organic matter have similar sources.
-
Key words:
- mangrove /
- nitrogen form /
- sediment /
- spatial characteristics /
- Dongzhai Port in Hainan
-
表 1 研究区表层沉积物各形态氮及理化性质的相关性
Table 1. Correlation coefficients of nitrogen species in surface sediments in the study area
pH TOC TN TTN IEF-N WAEF-N SAEF-N SOEF-N pH 1.000 TOC -0.225** 1.000 TN -0.438* 0.209 1.000 TTN -0.357** 0.346 0.931** 1.000 IEF-N -0.608 0.857 -0.519 0.159 1.000 WAEF-N 0.099 0.057 0.670 0.109 0.926** 1.000 SAEF-N -0.335 0.321 0.798** 0.673** 0.111 0.031 1.000 SOEF-N -0.529** 0.968** 0.892** 0.972** 0.173 0.143 0.512* 1.000 注:*表示显著相关性水平在0.05水平; **表示显著相关性在0.01水平 表 2 研究区柱状沉积物各形态氮及理化性质的相关性
Table 2. Correlation of nitrogen species and physicochemical properties of columnar sediments in the study area
pH 含水率 TOC TN TTN IEF-N WAEF-N SAEF-N SOEF-N pH 1.000 含水率 0.511** 1.000 TOC 0.579** 0.788** 1.000 TN 0.464** -0.538** 0.536** 1.000 TTN 0.498** -0.298** 0.867** 0.948** 1.000 IEF-N 0.612** 0.310** 0.393** 0.294* 0.334** 1.000 WAEF-N 0.587 -0.584** 0.479** 0.418** 0.596** 0.308** 1.000 SAEF-N -0.230** -0.420** 0.521** 0.734** 0.777** 0.355** 0.525** 1.000 SOEF-N -0.130** -0.316** 0.779** 0.874** 0.922** 0.158 0.451** 0.486** 1.000 注:*表示显著相关性水平在0.05水平;**表示显著相关性在0.01水平 -
[1] Wu C Y, Chen W, Cao C X, et al. Diagnosis of wetland ecosystem health in the Zoige Wetland, Sichuan of China[J]. Wetlands, 2018, 38(3): 469-484. doi: 10.1007/s13157-018-0992-y [2] Ramesh R, Chen Z, Cummins V, et al. Land-ocean interactions in the coastal zone: Past, present & future[J]. Anthropocene 2015, 12: 85-98. doi: 10.1016/j.ancene.2016.01.005 [3] 王焰新, 甘义群, 邓娅敏, 等. 海岸带海陆交互作用过程及其生态环境效应研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 1-10. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0101Wang Y X, Gan Y Q, Deng Y M, et al. Land-ocean interactions and their eco-environmental effects in the coastal zone: Current progress and future perspectives[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 1-10(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0101 [4] Mitsch W J, Gosselin J G. Wetlands[M]. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold Company Inc., 2000: 89-125. [5] Weedon J T, Kowalchuck G A, Aerts R, et al. Summer warming accelerates subartic peatland nitrogen cycling without changing enzyme pools or microbial community structure[J]. Global Change Biology, 2012, 18: 138-150. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2011.02548.x [6] Liu C, Du Y H, Chen K N, et al. Contrasting exchanges of nitrogen and phosphorus across the sediment-water interface during the drying and re-inundation of littoral eutrophic sediment[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 255: 113356. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113356 [7] Duke N C, Meynecke J O, Dittmann S, et al. A world without mangroves?[J]. Science, 2007, 317: 41-42. [8] Flores-Mireles A L, Winans S C, Holguin G. Molecular characterization of diazotrophic and denitrifying bacteria associated with mangrove roots[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2001, 73(22): 7308-7321. [9] 张志麒, 张一鸣, 黄咸雨, 等. 神农架大九湖泥炭地溶解有机碳季节性变化及其影响因素[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(2): 147-155. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0213Zhang Z Q, Zhang Y M, Huang X Y, et al. Seasonal variations and influencing factors of dissolved organic carbon in pore water from the Dajiuhu peatland in Shennongjia[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(2): 147-155(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0213 [10] 黄艳雯, 杜尧, 徐宇, 等. 洞庭湖平原西部地区浅层承压水中铵氮的来源与富集机理[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 165-174. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0618Huang Y W, Du Y, Xu Y, et al. Source and enrichment mechanism of ammoniumin shallow confined aquifer in the west of Dongting Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6) : 165-174(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0618 [11] Bayen S. Occurrence, bioavailability and toxic effects of trace metals and organic contaminants in mangrove ecosystems: A review[J]. Environment International, 2012, 48: 84-101. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2012.07.008 [12] Chai M W, Li R L, Shi C, et al. Contamination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in urban mangroves of Southern China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 646: 390-399. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.278 [13] 陈宏, 王泓, 吴敏, 等. 淡水湿地生态系统中微生物驱动氮转化过程研究进展[J]. 水利学报, 2020, 51(2): 158-168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLXB202002004.htmChen H, Wang H, Wu M, et al. Recent advances in microbe-driven nitrogen transformation in freshwater wetland ecosystems[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2020, 51(2): 158-168(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLXB202002004.htm [14] 乔永民, 谭键滨, 马舒欣, 等. 深圳红树林湿地沉积物氮磷分布与来源分析[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2018, 41(2): 34-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS201802006.htmQiao Y M, Tan J B, Ma S X, et al. The distribution pattern and sources analysis for nitrogen and phosphorus in core sediment of Shenzhen mangrove wetland[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 41(2): 34-40(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS201802006.htm [15] 王圣瑞, 焦立新, 金相灿, 等. 长江中下游浅水湖泊沉积物总氮、可交换态氮与固定态铵的赋存特征[J]. 环境科学学报, 2008, 28(1): 37-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX200801008.htmWang S R, Jiao L X, Jin X C, et al. Distribution of total exchangeable and fixed nitrogen in the sediments from shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2008, 28(1): 37-43(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX200801008.htm [16] Liu D, Fang Y, Tu Y, et al. Chemical method for nitrogen isotopic analysis of ammonium at natural abundance[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 86: 3787-3792. [17] 周天宇, 李浩帅, 简慧敏, 等. 长江口及邻近海域表层沉积物中氮形态的研究[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2018, 37(2): 281-286. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYHJ201802019.htmZhou T Y, Li H S, Jian H M, et al. Nitrogen forms in surface sediment in the Yangtze River estuary and adjacent area[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2018, 37(2): 281-286 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYHJ201802019.htm [18] 何彩霞, 刘辉利, 张琴, 等. 桂林会仙湿地沉积物氮的赋存形态及分布特征[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2021, 41(3): 608-614. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLGX202103019.htmHe C X, Liu H L, Zhang Q, et al. Existing forms and distribution of nitrogen in the sediment of Huixian wetland of Guilin[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2021, 41(3): 608-614(in Chinese with English abstract). . https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLGX202103019.htm [19] 王禄仕, 柴蓓蓓, 刘虹. 水源水库沉积物中氮的形态分布特征研究[J]. 西安建筑科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2010, 42(5): 734-740. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAJZ201005023.htmWang L S, Chai P P, Liu H. Distributive characteristics of nitrogen forms in sediment of water source reservoir[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Architecture & Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2010, 42(5): 734-740(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAJZ201005023.htm [20] Kazi T U, Jamali M K, Kazi G H. Evaluating the mobility of toxic metals in untreated industrial wastewater sludge using a BCR sequential extraction procedure and a leaching test[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2005, 383: 297-304. [21] 王功芹, 朱珠, 张硕. 海州湾表层沉积物中氮的赋存形态及其生态意义[J]. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36(2): 450-457. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201602011.htmWang G Q, Zhu Z, Zhang S, et al. Nitrogen forms in the surface sediment of Haizhou Bay and their ecological significance[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2016, 36(2): 450-457(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201602011.htm [22] 戴纪翠, 宋金明, 郑国侠, 等. 胶州湾沉积物氮的环境生物地球化学意义[J]. 环境科学, 2007, 28(9): 1924-1928. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ200709003.htmDai J C, Song J M, Zheng G X, et al. Environmental biogeochemical significance of nitrogen in Jiaozhou Bay sediments[J]. Environmental Science, 2007, 28(9): 1924-1928(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ200709003.htm [23] 李学刚, 宋金明, 李宁, 等. 胶州湾沉积物中氮与磷的来源及其生物地球化学特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2005, 36(6): 562-571. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYFZ200506010.htmLi X G, Song J M, Li N, et al. Source and biogeochemical characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus in Jiaozhou Bay sediments[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2005, 36(6): 562-571(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYFZ200506010.htm [24] 赵宝刚, 张夏彬, 昝逢宇, 等. 洪泽湖表层沉积物氮形态分布及影响因素[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(6): 30-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS202006004.htmZhao Baogang, Zhang Xiabin, Zan Fengyu, et al. Distribution and influence factors of nitrogen form in surface sediment of Lake Hongze[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 43(6): 30-38(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS202006004.htm [25] 李青芹, 霍守亮, 昝逢宇, 等. 我国湖泊沉积物营养盐和粒度分布及其关系研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2010, 29(12): 2390-2397. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201012025.htmLi Q Q, Huo S L, Zan F Y, et al. The distribution of nutrients and particle size, their correlations in surface sediments of different lakes, China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2010, 29(12): 2390-2397(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201012025.htm [26] 李家兵, 张党玉, 吴春山, 等. pH对闽江河口湿地沉积物氮素转化关键过程的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2017, 31(1): 272-278. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQS201701045.htmLi J B, Zhang D Y, Wu C S, et al. Effects of pH on the key nitrogen transformation processes of the wetland sediment in the Min River estuary[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 31(1): 272-278(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQS201701045.htm [27] 翟天恩, 张靖天, 华飞, 等. 东部平原湖区沉积物中溶解性有机氮分布特征[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(9): 5001-5008. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJZ201609061.htmZhai T E, Zhang J T, Hua F, et al. Distribution characteristics of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) in the lake sediments of Eastern Plain Region, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2016, 10(9): 5001-5008(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJZ201609061.htm -





 下载:
下载: