Shale formation environment and comprehensive evaluation of shale oil potential of the Lower First Member of Shahejie Formation in Qikou Sag
-
摘要:
渤海湾盆地是目前我国主要的陆相页岩油资源开采区,歧口凹陷位于盆地腹地,是渤海湾盆地内典型的富油气凹陷之一,但长期以来缺少对不同层位页岩形成环境及页岩油潜力的综合评价。选取歧口凹陷沙一下亚段富有机质页岩为研究对象,综合运用地化录井技术和生排烃模拟技术,进行歧口凹陷沙一下亚段页岩沉积特征的描述和页岩油潜力的综合评价。研究结果显示,①歧口凹陷沙一下亚段沉积于水体盐度较高的还原-强还原环境,营养物质丰富,气候炎热湿润,适宜生物大量繁殖,生产力水平高;②结合生排烃模拟实验结果,研究区沙一下亚段页岩生烃能力强、生烃效率高、排油率较低,生成的原油仍大部分残留在页岩中,具有良好的勘探潜力;③研究区沙一下亚段页岩中含有适量碳酸盐矿物,在成岩过程中改善了储集条件,为页岩油提供了良好的储集场所。歧口凹陷西南缘海侵的发生从沉积环境、古生产力及对成岩作用影响等方面促进了沙一下亚段有机质的富集,而有机质富集、生烃强度高以及良好的储集条件共同控制了沙一下亚段页岩油的大面积分布。研究区沙一下亚段页岩油储层可分为碳酸盐岩和混合沉积岩2种类型,综合2种储层的含油性特征后发现,碳酸盐岩矿物含量和脆性指数对页岩含油性有着极大影响。有利勘探区域为构造裂缝发育的宽缓斜坡区和白云岩化程度较高的地区; 有利勘探层段为孔隙和微裂缝发育的白云岩、白云质页岩和灰质页岩层段。该研究成果可为歧口凹陷页岩油的勘探开发提供指导。
Abstract:Bohai Bay Basin is one of the main exploitation areas of continental shale oil resources in China.Qikou Sag, located in the hinterland of the basin, is one of the typical oil and gas rich depressions in Bohai Bay Basin.This paper selects the organic rich shale in the Lower First Member of Shahejie Formation in Qikou Sag as the research object, and comprehensively uses geochemical logging technology and hydrocarbon generation and expulsion simulation technology to describe the shale sedimentary characteristics and comprehensive evaluation of shale oil potential in the Lower First Member of Shahejie Formation in Qikou Sag.The results show that the Lower First Member of Shahejie Formation in Qikou Sag was deposited in the reduction strong reduction environment with high water salinity, rich nutrients, hot and humid climate, suitable for biological mass reproduction and high productivity.Combined with the hydrocarbon generation and expulsion simulation experiment results, the Lower First Member of Shahejie Formation shale in the study area has strong hydrocarbon generation capacity, high hydrocarbon generation efficiency and low oil discharge rate.Most of the generated crude oil is still left in the shale, which has good exploration potential.The Lower First Member of Shahejie Formation shale in the study area contains an appropriate amount of carbonate minerals, which improves the reservoir conditions during diagenesis and provides a good reservoir site for shale oil.The occurrence of transgression in the southwest margin of Qikou Sag affects the enrichment of organic matter in the Lower First Member of Shahejie Formation from the aspects of sedimentary environment, paleoproductivity and its impact on diagenesis.The enrichment of organic matter, high hydrocarbon generation intensity and good reservoir conditions control the large-area distribution of shale oil in the Lower First Member of Shahejie Formation.Shale oil reservoirs in the Lower First Member of Shahejie Formation in the study area can be divided into carbonate rocks and mixed sedimentary rocks.After synthesizing the oil-bearing characteristics of the two reservoirs, it is found that the mineral content and brittleness index of carbonate rocks have a great impact on shale oil-bearing properties.In the process of further exploration, oil reservoirs can be found in the wide and gentle slope area conducive to the formation of structural fractures and the area with high degree of dolomitization in the study area.The favorable exploration intervals are dolomite, dolomitic shale and calcareous shale with developed pores and micro fractures.The research results provide guidance for the exploration and development of shale oil in Qikou Sag.
-
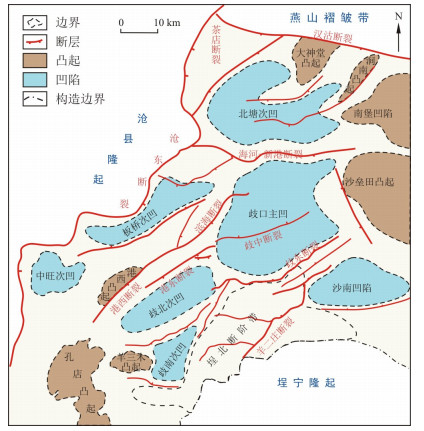
图 1 歧口凹陷构造纲要图(据文献[11])
Figure 1. Structural outline of Qikou Sag
图 2 歧口凹陷构造-地层演化特征(据文献[12])
Figure 2. Characteristics of tectonic and stratigraphic evolution in Qikou Sag
表 1 歧口凹陷沙一下亚段B1井页岩生排烃实验数据
Table 1. Well B1 experimental data of shale hydrocarbon generation and expulsion of the Lower First Member of Shahejie Formation in Qikou Sag
样品编号 样品重量/mg 最终温度/℃ 升温速率/(℃·h-1) Easy-Ro/% C1-C5(气体) C6-14(排油) C14+(排油) C6-14(残留油) C14+(残留油) C6+(总油) C1+(总烃) 排烃效率/% 排油效率/% wB/(mg·g-1) 1 497.36 311.4 20 0.48 0.02 0.01 0.52 0.21 4.18 4.92 4.95 11.16 10.77 2 498.82 335.4 20 0.57 0.04 0.01 0.58 0.26 4.27 5.12 5.16 11.83 10.90 3 499.47 365.8 20 0.68 0.17 0.06 0.92 0.51 7.55 9.03 9.20 12.45 11.10 4 499.56 385.0 20 0.79 0.43 0.16 1.18 1.12 13.45 15.92 16.35 13.19 11.70 5 498.08 408.8 20 0.96 1.05 0.42 1.81 2.19 14.50 18.91 19.96 18.00 15.50 6 497.78 432.0 20 1.19 2.57 1.51 4.38 2.96 6.49 15.34 17.91 47.21 38.38 7 499.79 456.2 20 1.46 5.10 2.41 3.18 3.92 1.84 11.36 16.46 64.98 49.26 注:压力为30MPa 表 2 歧口凹陷B1井沙一下亚段各层段定量评价参数
Table 2. Well B1 quantitative evaluation parameters of each layer of the Lower First Member of Shahejie Formation in Qikou Sag
层段 w(TOC)/% S1+S2/(mg·g-1) S1/(mg·g-1) 脆性指数/% C1 $\frac{1.63\sim 5.28} {2.87}$ $\frac{7.15\sim 32} {14.6}$ $\frac{0.079\sim 0.82} {0.3}$ $\frac{55.6\sim 81} {65.2}$ C2 $\frac{1.65\sim 3.73} {2.81}$ $\frac{8.9\sim 21.8} {15.3}$ $\frac{0.15\sim 0.69} {0.36}$ $\frac{56\sim 72.4} {64.9}$ C3 $\frac{1.03\sim 4.29} {2.56}$ $\frac{1.53\sim 27.85} {13.9}$ $\frac{0.004\sim 1.16} {0.34}$ $\frac{62.1\sim 98} {71}$ C4 $\frac{0.51\sim 4.64} {2.71}$ $\frac{1.53\sim 28.23} {13.9}$ $\frac{0.05\sim 0.77} {0.35}$ $\frac{58.7\sim 100} {68.7}$ C5 $\frac{1.93\sim 4.66} {2.89}$ $\frac{8.06\sim 26.7} {15.4}$ $\frac{0.15\sim 0.65} {0.38}$ $\frac{60.8\sim 74.7} {69.7}$ C6 $\frac{0.4\sim 6.72} {3.23}$ $\frac{1.4\sim 46.6} {19.4}$ $\frac{0.09\sim 1.19} {0.52}$ $\frac{63.4-100} {71.2}$ 注:$ \frac{{\rm{最小值}}\sim {\rm{最大值}}} {{\rm{平均值}}}$ -
[1] Zou C N, Yang Z, Cui J W, et al. Formation mechanism, geological characteristics and development strategy of nonmarine shale oil in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(1): 14-26. [2] 姜在兴. 沉积学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2003.Jiang Z X. Sedimentology[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2003(in Chinese). [3] Advanced Resources International. EIA/ARI world shale gas and shale oil resource assessment[M]. Arlington: U.S. Energy Information Administration, 2015. [4] Soeder D J. The successful development of gas and oil resources from shales in North America[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2018, 163: 399-420. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2017.12.084 [5] 王振升, 滑双君, 于学敏, 等. 歧口凹陷沙河街组烃源岩分级评价及优质烃源岩分布[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2014, 25(12): 1896-1902. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2014.12.1896Wang Z S, Hua S J, Yu X M, et al. Grading evaluation and high quality source rock distribution in Qikou Sag[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2014, 25(12): 1896-1902(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2014.12.1896 [6] 赵贤正, 周立宏, 蒲秀刚, 等. 歧口凹陷歧北次凹沙河街组三段页岩油地质特征与勘探突破[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(6): 643-657. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202006003.htmZhao X Z, Zhou L H, Pu X G, et al. Geological characteristics and exploration breakthrough of shale oil in Member 3 of Shahejie Formation of Qibei Subsag, Qikou Sag[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(6): 643-657(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202006003.htm [7] 周立宏, 陈长伟, 韩国猛, 等. 渤海湾盆地歧口凹陷沙一下亚段地质特征与页岩油勘探潜力[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(8): 2736-2750. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201908019.htmZhou L H, Chen C W, Han G M, et al. Geological characteristics and shale oil exploration potential of lower first member of Shahejie Formation in Oikou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(8): 2736-2750(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201908019.htm [8] 姜文亚, 柳飒. 层序地层格架中优质烃源岩分布与控制因素: 以歧口凹陷古近系为例[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2015, 20(2): 51-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2015.02.006Jiang W Y, Liu S. Distribution and controlling factors of high-quality hydrocarbon source rock in sequential stratigraphic rramework: Taking Paleogene system in Qikou Depression for instance[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2015, 20(2): 51-58(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2015.02.006 [9] 索艳慧, 李三忠, 许立青, 等. 渤海湾盆地大歧口凹陷新生代构造演化与盆地原型[J]. 地质科学, 2015, 50(2): 473-488. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2015.02.008Suo Y H, Li S Z, Xu L Q, et al. Cenozoic structural evolution and prototype basin of the Great Qikou Sag, the Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2015, 50(2): 473-488(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2015.02.008 [10] 王芝尧, 卢异, 杨子玉, 等. 古近系构造样式对油气成藏的影响: 以歧口凹陷为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(1): 85-92. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201301012.htmWang Z Y, Lu Y, Yang Z Y, et al. Influence of paleogene structural pattern on lithologic reservoir: A case study of Qikou Sag[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2013, 24(1): 85-92(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201301012.htm [11] 周立宏, 陈长伟, 韩国猛, 等. 渤海湾盆地歧口凹陷陆相湖盆页岩气富集条件及勘探潜力[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(5): 1-10. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2021.05.001Zhou L H, Chen C W, Han G M, et al. Enrichment conditions and exploration potential of shale gas in continental lake basins in Qikou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(5): 1-10(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2021.05.001 [12] 陈宪保. 歧口凹陷构造演化特征[J]. 地球科学前沿, 2015, 5(6): 449-459. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201301004.htmChen X B. The study of Qikou Sag tectonic style[J]. Advances in Geosciences, 2015, 5(6): 449-459(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201301004.htm [13] Pu X G, Zhou L H, Han W Z, et al. Gravity flow sedimentation and tight oil exploration in lower first member of Shahejie Formation in slope area of Qikou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(2): 153-164. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(14)60018-5 [14] 倪朋勃, 陈伟. X射线衍射全岩录井技术在渤海油田的应用[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2018, 34(5): 56-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201805008.htmNi P B, Chen W. Application of X-Ray diffraction to whole-rock logging in Bohai Oilfeild[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2018, 34(5): 56-60(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201805008.htm [15] 李昂, 袁志华, 张玉清, 等. 元素录井技术在涪陵页岩气田勘探中的应用[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2015, 38(2): 23-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3177.2015.02.006Li A, Yuan Z H, Zhang Y Q, et al. Application of element logging to Fuling Shale-Gas Field[J]. Natural Gas Exploration & Development, 2015, 38(2): 23-26(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3177.2015.02.006 [16] Zhang K, Liu R, Liu Z J. Sedimentary sequence evolution and organic matter accumulation characteristics of the Chang 8-Chang 7 members in the Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation, southwest Ordos Basin, central China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 196: 107751. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2020.107751 [17] Hatch J R. Relationship between inferred redox potential of the depositional environment and geochemistry of the Upper Pennsylvanian(Missourian)Stark Shale Member of the Dennis Limestone, Wabaunsee County, Kansas, USA[J]. Chemical Geology, 1992, 99: 65-88. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(92)90031-Y [18] 王春连, 刘成林, 胡海兵, 等. 江汉盆地江陵凹陷南缘古新统沙市组四段含盐岩系沉积特征及其沉积环境意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2012, 14(2): 165-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201202004.htmWang C L, Liu C L, Hu H B, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and its environmental significance of salt-bearing strata of the Member 4 of Paleocene Shashi Formation in southern margin of Jiangling Depression, Jianghan Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeo Geography, 2012, 14(2): 165-175(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201202004.htm [19] 郑玉龙, 马志强, 王佰长, 等. 黑龙江省柳树河盆地始新统八虎力组油页岩元素地球化学特征及沉积环境[J]. 古地理学报, 2015, 17(5): 689-698. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201505011.htmZheng Y L, Ma Z Q, Wang B C, et al. Geochemistry characteristics and sedimentary environment of oil shale from the Eocene Bahuli Formation in Liushuhe Basin, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2015, 17(5): 689-698(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201505011.htm [20] 张天福, 孙立新, 张云, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地北缘侏罗纪延安组、直罗组泥岩微量、稀土元素地球化学特征及其古沉积环境意义[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(12): 3454-3472. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.12.013Zhang T F, Sun L X, Zhang Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics of the Jurassic Yan'an and Zhiluo Formations in the northern margin of Ordos Basin and their paleoenvironmental implications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016, 90(12): 3454-3472(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.12.013 [21] Zhang K, Liu R, Liu Z J, et al. Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of humid climate events in the Middle-Late Triassic(Ladinian-Carnian)of the Ordos Basin, central China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2021, 131: 105179. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.105179 [22] Timothy W L, Josef P W, David J H, et al. Contrasting sulfur geochemistry and Fe/Al and Mo/Al ratios across the last oxic-to-anoxic transition in the Cariaco Basin, Venezuela[J]. Chemical Geology, 2003, 195: 131-157. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00392-3 [23] Walter E D, James V G, David Z P. Inorganic geochemical indicators of glacial-interglacial changes in productivity and anoxia on the California continental margin[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1997, 61(21): 4507-4518. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00237-8 [24] Thomas J A, Kiyoko K, Hiroyoshi S, et al. Spatial variation in sediment fluxes, redox conditions, and productivity in the Permian-Triassic Panthalassic Ocean[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2011, 308(1/2): 65-83. [25] Wu Z Y, Zhao X Z, Wang E Z, et al. Sedimentary environment and organic enrichment mechanisms of lacustrine shale: A case study of the Paleogene Shahejie Formation, Qikou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2021, 573: 110404. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2021.110404 [26] 陈建渝, 李水福, 田波, 等. 孤南洼陷低熟油成因分析[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1998, 25(5): 34-37. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.1998.05.010Chen J Y, Li S F, Tian B, et al. The genesis of low-mature oil in the Gunan Sag[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1998, 25(5): 34-37(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.1998.05.010 [27] 王铁冠, 钟宁宁, 侯读杰, 等. 低熟油气形成机理与分布[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1995.Wang T G, Zhong N N, Hou D J, et al. The mechanism of formation and distribution of low-mature oil and gas[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1995(in Chinese). [28] 黄第藩, 张大江, 王培荣, 等. 中国未成熟石油成因机制和成藏条件[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2003.Huang D F, Zhang D J, Wang P R, et al. Genetic mechanism and accumulation conditions of immature oil in China[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2003(in Chinese). [29] Yu Z C, Liu K Y, Liu L, et al. Characterization of Paleogene hydrothermal events and their effects on reservoir properties in the Qikou Sag, eastern China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2016, 146: 1226-1241. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2016.08.026 [30] 张江江, 黄鹏, 冯学谦, 等. 歧口凹陷沙一下亚段白云岩储集空间特征研究[J]. 科技导报, 2011, 29(17): 39-44. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2011.17.004Zhang J J, Huang P, Feng X Q, et al. Analysis of reservoir space characteristics of dolomite reservoirs in Sha 1 Lower sub-interval in Qikou Depression[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2011, 29(17): 39-44(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2011.17.004 [31] 郭书生, 杨红君, 廖茂林, 等. 三维定量荧光录井技术在琼东南盆地陵水凹陷气层评价中的应用[J]. 录井工程, 2015, 26(3): 51-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9803.2015.03.012Guo S S, Yang H J, Liao M L, et al. Application of 3D quantitative fluorescence logging technology in gas reservoir evaluation of Lingshui sag, Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Mud Logging Engineering, 2015, 26(3): 51-53(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9803.2015.03.012 [32] Wu Z Y, Zhao X Z, Pu X G, et al. Petroleum resource potential evaluation using insights based on hydrocarbon generation, expulsion, and retention capabilities: A case study targeting the Paleogene Es1 Formation, Qikou Sag[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 208: 109667. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2021.109667 [33] Behar F, Kressmann S, Rudkiewicz J L, et al. Experimental simulation in a confined system and kinetic modelling of kerogen and oil cracking[J]. Advances in Organic Geochemistry, 1992, 19(1/3): 173-189. [34] Sun L N, Tuo J C, Zhang M F, et al. Formation and development of the pore structure in Chang 7 member oil-shale from Ordos Basin during organic matter evolution induced by hydrous pyrolysis[J]. Fuel, 2015, 158: 549-557. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.05.061 [35] 张文正, 杨华, 李剑峰, 等. 论鄂尔多斯盆地长7优质油源岩在低渗透油气成藏富集中的主导作用: 强生排烃特征及机理分析[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2006, 33(3): 289-293. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2006.03.006Zhang W Z, Yang H, Li J F, et al. Leading effect of high-class source rock of Chang 7 in Ordos Basin on enrichment of low permeability oil-gas accumulation: Hydrocarbon generation and expulsion mechanism[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2006, 33(3): 289-293(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2006.03.006 -





 下载:
下载: