Improved transfer coefficient method considering multistage sliding of rainfall landslides
-
摘要:
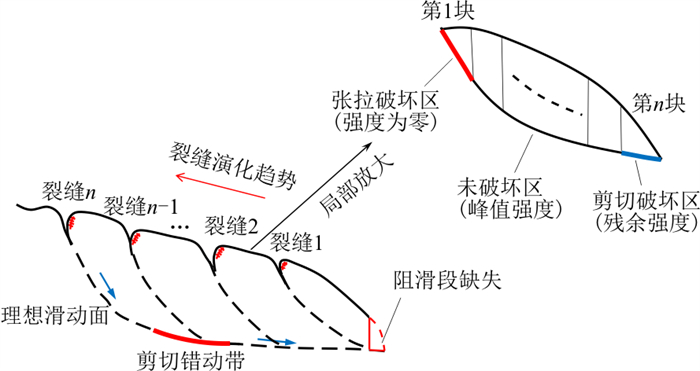
在多级滑坡的渐进破坏过程中, 滑带不同部位的屈服程度和破坏模式不同, 强度参数也不同。在强降雨条件下, 坡表产生的张拉裂缝充水, 会产生静水压力。当前广泛应用的传递系数法对滑带不同位置取同一强度参数, 也尚未考虑到静水压力作用。为此提出了一种考虑静水压力作用和滑带不同部位强度参数差异的改进传递系数法, 对降雨引起的西安市柳西村南部的牛角沟滑坡进行了计算。结果表明: 与不考虑静水压力和滑带不同部位强度参数差异的计算方法比, 改进传递系数法计算的抗滑力相对较小, 剩余下滑力计算结果相对较大, 各级滑坡稳定性系数分别减小了约33.26%、17.92%、24.95和16.94%;而改进前的稳定性系数偏高, 可能会导致支挡工程的安全储备不足。本研究提出的改进传递系数法可为多级滑坡处置提供更安全的参考。
Abstract:In the progressive failure process of multiple landslides, different parts of the slip zone have different yielding degrees and failure modes with different strength parameters. Under strong rainfall conditions, water-filled tension cracks generated on the slope surface give rise to hydrostatic pressure. The current widespread transfer coefficient method, which takes the same strength parameter for different locations of the slip zone, also has not yet taken into account the hydrostatic pressure effect. In this paper, we propose an improved transfer coefficient method which takes into account the hydrostatic pressure effect and the difference in strength parameters of different parts of the slip zone. The results show that, compared with the calculation method without considering the hydrostatic pressure and the difference in strength parameters in different parts of the slip zone, the anti-sliding force calculated by the improved transfer coefficient method is relatively small, the residual sliding force is relatively large, and the stability coefficients of landslides at all levels are reduced by approximately 33.26%, 17.92%, 24.95% and 16.94%, respectively. Based on the high stability coefficient before the improvement, it may lead to insufficient safety reserve of the retaining engineering. The improved transfer coefficient method proposed in this paper can provide a safer reference for multiple landslide disposal.
-
表 1 西安市牛角沟多级滑坡滑带土强度参数取值
Table 1. Slip zone soil strength parameters of the Niujiao gully multiple landslide in Xi′an City
土体状态 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 峰值强度 15.0 14.9 残余强度 12.2 12.1 表 2 西安市牛角沟多级滑坡剩余下滑力计算明细
Table 2. Detailed calculation of the residual sliding force of the multiple landslides in the Niujiao gully landslide, Xi′an City
滑坡级数 条块编号 Wi/(kN·m-1) α/(°) Δα/(°) ψi Ri/(kN·m-1) Ti/(kN·m-1) ψiEi-1/(kN·m-1) 静水推力/(kN·m-1) 第一级滑坡 1 2 810.20 73 / / 493.53 2 838.19 / 151.31 2 4 094.58 16 57 0.32 1 237.42 1 128.06 2 344.66 / 3 3 914.22 16 0 1.00 1 186.51 1 078.37 645.86 / 4 5 106.18 16 0 1.00 518.11 483.62 537.73 / 第二级滑坡 5 3 177.57 79 / / 487.47 3 270.07 / 151.31 6 5 136.10 29 50 0.44 1 363.55 2 488.88 2 782.60 / 7 5 013.10 22 7 0.96 1 400.20 1 877.35 2 348.23 / 8 5 409.02 10 2 0.92 1 589.58 938.80 2 731.82 / 9 2 794.20 10 0 1.00 777.14 484.96 1 870.43 / 第三级滑坡 10 2 499.21 65 / / 403.62 2 415.76 / 151.31 11 4 588.11 35 25 0.73 1 160.51 2 630.47 2 012.14 / 12 4 793.28 14 21 0.84 1 387.64 1 159.02 2 945.36 / 13 4 586.80 14 0 1.00 1 324.61 1 109.09 2 240.74 / 14 2 701.83 10 4 0.98 718.36 468.93 2 025.23 / 第四级滑坡 15 1 962.31 66 / / 321.67 1 943.50 / 151.31 16 3 199.48 29 37 0.64 900.44 1 550.42 1 621.83 / 17 4 054.42 25 4 0.98 1 140.66 1 712.66 1 686.10 / 18 3 781.95 11 14 0.91 1 123.05 721.66 222.74 / 19 2 757.38 10 1 1.00 685.92 478.57 1 612.06 / 表 3 不同条件下的稳定性系数对比
Table 3. Comparison of stability factors under different conditions
滑坡级数 两者均考虑 不考虑相互作用力 不考虑滑带参数取值 两者均不考虑 整体式滑移失稳 第Ⅰ级滑坡 0.626 0.787 0.761 0.938 0.96 第Ⅱ级滑坡 0.788 0.877 0.843 0.960 第Ⅲ级滑坡 0.734 0.878 0.897 0.978 第Ⅳ级滑坡 0.814 0.881 0.950 0.980 -
[1] Bromhead E N, Ibsen M L. A review of landsliding and coastal erosion damage to Historic Fortifications in South East England[J]. Landslides, 2006, 3(4): 341-347. doi: 10.1007/s10346-006-0063-y [2] Wang J, Schweizer D, Liu Q B, et al. Three-dimensional landslide evolution model at the Yangtze River[J]. Engineering Geology, 2021, 292: 106275. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106275 [3] 吴维义. 龙家岩多级滑坡机理分析及其防治技术研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2016.Wu W Y. Research on evolution mechanism and controlling techniques for Longjiayan multi-stage landslide[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2016(in Chinese with English abstract). [4] 仝德富, 谭飞, 苏爱军, 等. 基于多源数据的谭家湾滑坡变形机制及稳定性评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 162-170. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0432Tong F D, Tan F, Su A J, et al. Deformation mechanism and stability evaluation of Tanjiawan landslide based on multi-source data[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 162-170(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0432 [5] Song J, Fan Q Q, Feng T G, et al. A multi-block sliding approach to calculate the permanent seismic displacement of slopes[J]. Engineering Geology, 2019, 255: 48-58. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.04.012 [6] 肖锐铧, 王思敬, 贺小黑, 等. 非均质边坡多级稳定性分析方法[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2013, 35(6): 1062-1068. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201306012.htmXiao R H, Wang S J, He X H, et al. Multi-level stability analysis of inhomogeneous slopes[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(6): 1062-1068(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201306012.htm [7] 张晓奇, 胡新丽, 刘忠绪, 等. 呷爬滑坡滑带土蠕变特性及其稳定性[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 145-153. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0604Zhang X Q, Hu X L, Liu Z X, et al. Creep poperties and stability of sliding zone soil in Gapa landslide[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6): 145-153(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0604 [8] 何淑军, 刘景儒, 吴树仁, 等. 夏呀河多级滑坡三维稳定性模拟分析研究[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2011, 28(11): 24-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2011.11.005He S J, Liu J R, Wu S R, et al. Analysis and research on 3D simulation for stability of Xiayahe multi-stage landslide[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2011, 28(11): 24-29(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2011.11.005 [9] 谭福林, 胡新丽, 张玉明, 等. 牵引式滑坡推力计算方法研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2015, 36(增刊2): 532-538. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2015S2075.htmTan F L, Hu X L, Zhang Y M, et al. Study of calculation method of retrogressive landslide thrust[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(S2): 532-538(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2015S2075.htm [10] 杨登芳, 胡新丽, 徐楚, 等. 基于物理模型试验的多层滑带滑坡变形演化特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(2): 300-308. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0069Yang D F, Hu X L, Xu C, et al. Deformation and evolution characteristics of landslides with multiple sliding zones based on physical model test[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 300-308(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0069 [11] 谭福林, 胡新丽, 张玉明, 等. 不同类型滑坡渐进破坏过程与稳定性研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2016, 37(增刊2): 597-606. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2016S2075.htmTan F L, Hu X L, Zhang Y M, et al. Study of progressive failure processes and stabilities of different types of landslides[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016, 37(S2): 597-606(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2016S2075.htm [12] 何木, 赵其华. 基于方向角修正的改进传递系数法[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护, 2010, 21(1): 79-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZHB201001021.htmHe M, Zhao Q H. Improved transfer coefficient method based on correcting direction angle[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation, 2010, 21(1): 79-82(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZHB201001021.htm [13] 任聪聪. 水库运行期涉水岸坡稳定系数计算的传递系数法改进[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2020.Ren C C. Improvement of transfer coefficient method for stability coefficient of wading slope during reservoir operation[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2020(in Chinese with English abstract). [14] Feng Z K, Xu W J. GPU material point method(MPM) and its application on slope stability analysis[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2021, 80(7): 5437-5449. [15] 范宣梅, 许强, 张倬元, 等. 平推式滑坡成因机制研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2008, 27(增刊2): 3753-3759. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2008S2072.htmFan X M, Xu Q, Zhang Z Y, et al. Study on genetic mechanism of translation landslide[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(S2): 3753-3759(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2008S2072.htm [16] Wang Y K, Sun S W, Liu L. Mechanism, stability and remediation of a large scale external waste dump in China[J]. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, 2019, 37(6): 5147-5166. [17] Tang L S, Zhao Z L, Luo Z G, et al. What is the role of tensile cracks in cohesive slopes?[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 11(2): 314-324. [18] Regmi R K, Jung K, Nakagawa H, et al. Study on mechanism of retrogressive slope failure using artificial rainfall[J]. Catena, 2014, 122: 27-41. [19] 钱家欢, 殷宗泽. 土工原理与计算[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 1996.Qian J H, Yin Z Z. Geotechnical principles and calculations[M]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 1996(in Chinese). [20] 郑颖人, 时卫民, 杨明成. 不平衡推力法与Sarma法的讨论[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2004, 23(17): 3030-3036. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200417030.htmZheng Y R, Shi W M, Yang M C. Discussion on imbalance force method and sarma's method[J]. China Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(17): 3030-3036(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200417030.htm [21] 曲国鹏. 降雨入渗作用下非饱和黄土滑坡稳定性研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2012.Qu G P. Study on the stability of loess slope under rainfall infiltration[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2012(in Chinese with English abstract). -





 下载:
下载: