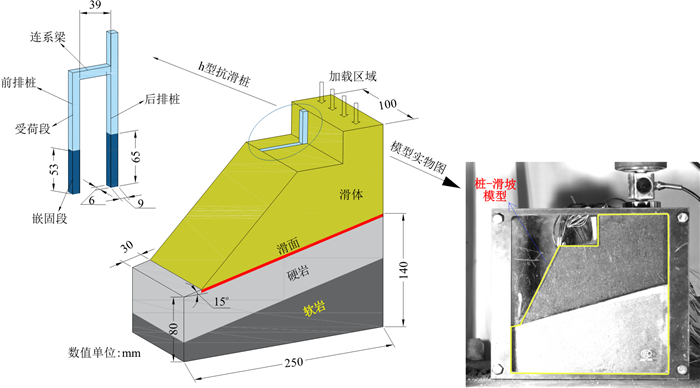
Physical model tests on the interaction of h-type stabilizing piles and landslides in bedrock with upper hard and lower weak strata
-
摘要:
组合式抗滑桩是加固大型滑坡的有效防护措施, 但上硬下软等复合地层中h型抗滑桩的加固机理仍有待深入研究。基于一套自主研发的上硬下软地层滑坡-h型抗滑桩物理模型试验装置, 综合应力应变监测、激光测距仪、高速相机与粒子图像测速(PIV)技术研究了上硬下软地层滑坡中h型桩的位移、内力响应规律与滑体变形破坏特征, 揭示了上硬下软地层条件下h型桩与滑坡相互作用机理。研究结果表明, 在坡顶荷载逐渐增加的条件下, h型桩加固的上硬下软地层滑坡的演化阶段可划分为蠕变阶段、匀速变形阶段、加速变形阶段和破坏阶段4个阶段。受连系梁影响, 前排桩与后排桩桩顶位移较小, 应变最大值出现在靠近滑面深度处; 后排桩弯矩呈"S"型分布, 前排桩弯矩呈三角形分布, 负弯矩最大值位于连系梁下方20 cm处。随着硬岩体积分数(
φ β)增加, 桩顶位移逐渐减小, 前、后排桩最大弯矩值也逐渐减小, 但硬岩体积分数超过60%后最大弯矩值变化幅度较小。当φ β=20%和40%时, 后排桩土压力总体呈抛物线形式; 当φ β=60%和80%时, 土压力总体呈反"S"型, 且滑面附近出现第二个土压力峰值; 前排桩土压力分布形式均为抛物线型。试验结果可为组合式抗滑桩加固机理研究和设计提供理论支撑。Abstract:Combined stabilizing piles are an effective measure to reinforce large-scale landslides with complex strata. However, the reinforcement mechanism of h-type stabilizing piles in composite strata, such as strata with upper hard and lower weak bedrock, still needs to be studied in depth. Based on a set of self-developed physical devices for landslide-h-type stabilizing piles in bedrock with upper hard and lower weak strata, monitoring of stress and strain, laser range finder, high speed camera, and particle image velocimetry (PIV) techniques were adopted to study the internal forces and displacement of h-type stabilizing piles in landslides bedrock with upper hard and lower weak strata and the deformation characteristics of landslides, through which the interaction mechanism between h-type anti-sliding piles and landslides were revealed. The results showed that under the loading at the tope of the landslide, the h-type stabilizing pile reinforced landslide exhibited progressive failure characterized by four stages of creep, constant-speed deformation, accelerated deformation, and failure. Influenced by the beam, the displacement of the pile head and front and rear piles is small, but the piles have the maximum strain near the sliding mass. The bending moment of the rear piles showed an "S" type distribution curve, while that of the front piles showed a triangular distribution curve, and the maximum negative bending moment occurred at a depth of 20 cm below the beam. With the increase in the volume content of the hard stratum (
φ β), the displacement of the pile head gradually decreased, and the maximum bending moment of the front and rear piles gradually decreased and tended to be stable asφ β exceeded 60%. Whenφ β was 20% and 40%, the soil pressure behind the rear piles showed a parabolic distribution curve; whenφ β was 60% and 80%, it changed to the reverse "S" distribution curve, and the second maximum value occurred near the sliding surface. The soil pressure behind the front piles showed a parabolic distribution type versus the change ofφ β. The results of this study can provide a theoretical reference for understanding the reinforcement mechanisms and design theories of combined stabilizing piles. -
表 1 物理模型试验材料相关参数
Table 1. Geotechnical parameters for model testing materials
材料名称 密度ρ/(g·cm-3) 弹性模量
E/GPa黏聚力
с/kPa内摩擦角
φ/(°)滑体 1.93 0.024 11.1 22.7 硬岩 2.07 4.35 105.0 28.0 软岩 1.99 2.08 45.5 19.3 抗滑桩 0.95 1.03 — — 表 2 后、前排桩最大弯矩比
Table 2. Ratio of the maximum bending moment of the rear pile to the front pile
时间/min 后、前排桩最大正弯矩比/% 后、前排桩最大负弯矩比/% 5 61.16 93.73 15 69.89 109.87 25 77.31 107.98 35 84.12 89.39 45 86.26 82.35 55 85.56 76.46 表 3 25 min时不同工况前、后排桩桩身最大弯矩
Table 3. List of maximum bending moments of the front and rear piles for different working conditions at 25 min
φB/% 后排桩最大弯矩/(N·m) 前排桩最大弯矩/(N·m) 20 0.283 0.349 40 0.234 0.263 60 0.161 0.103 80 0.168 0.164 100 0.163 0.147 -
[1] 刘伟. 我国地质灾害调查统计与分析[J]. 采矿技术, 2021, 21(5): 100-103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2900.2021.05.029Liu W. Statistics and analysis of geological hazard surveys in China[J]. Mining Technology, 2021, 21(5): 100-103(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2900.2021.05.029 [2] Ito T, Matsui T. Methods to estimate lateral force acting on stabilizing piles[J]. Soils and Foundations, 1975, 15(4): 43-59. doi: 10.3208/sandf1972.15.4_43 [3] 常强. 双排桩治理边坡的数值模拟研究[J]. 黑龙江水利科技, 2022, 50(4): 37-39, 179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HSKJ202204011.htmChang Q. Numerical simulation of slope treatment by double row piles[J]. Heilongjiang Water Science and Technology, 2022, 50(4): 37-39, 179(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HSKJ202204011.htm [4] 李云凤. 非极限状态双排桩支护结构内力变形情况分析[J]. 兰州工业学院学报, 2022, 29(2): 25-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LZGD202202005.htmLi Y F. Analysis of internal force deformation of non-limit state double row pile retaining structure[J]. Journal of Lanzhou Institute of Technology, 2022, 29(2): 25-30(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LZGD202202005.htm [5] 闫玉平, 肖世国. 双排抗滑桩后侧推力分布物理模型试验[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2022, 33(2): 79-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH202202010.htmYan Y P, Xiao S G. Physical model test on landslide thrust distribution on double-row stabilizing piles[J]. Chinese Journal of Geological Hazards and Prevention, 2022, 33(2): 79-87(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH202202010.htm [6] 张建文, 付正道. 双排桩加固滑坡桥基模型试验与数值模拟研究[J]. 高速铁路技术, 2019, 10(3): 30-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSTL201903007.htmZhang J W, Fu Z D. Model test and numerical simulation of bridge foundation with front and rear anti-slide piles in landslide section[J]. High-speed Railway Technology, 2019, 10(3): 30-36(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSTL201903007.htm [7] 王秀丽, 于光明, 陈美合. 边坡品字型抗滑桩加固效果监测分析[J]. 兰州理工大学学报, 2016, 42(3): 121-127. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5196.2016.03.025Wang X L, Yu G M, Chen M H. Monitoring and analysis of reinforcement effect of slope with pyramid-disposed anti-slide piles[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University of Technology, 2016, 42(3): 121-127(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5196.2016.03.025 [8] 金兆鑫, 袁维红, 胡建琴, 等. 品字型抗滑桩工作性能的影响因素及优化设计[J]. 兰州石化职业技术学院学报, 2017, 17(3): 36-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4067.2017.03.012Jin Z X, Yuan W H, Hu J Q, et al. Influential factors and optimizing design for triangle anti slide piles working performance[J]. Journal of Lanzhou Institute of Petrochemical Technology, 2017, 17(3): 36-39(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4067.2017.03.012 [9] 任永忠, 朱彦鹏. "品"字型抗滑桩有限元计算方法及工程应用[J]. 工程勘察, 2015, 43(4): 32-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKC201504007.htmRen Y Z, Zhu Y P. Finite element calculation method and engineering application of the three piles of facing each other[J]. Engineering Surveys, 2015, 43(4): 32-37(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKC201504007.htm [10] Wang Z H, Zhou J. Three-dimensional numerical simulation and earth pressure analysis on double-row piles with consideration of spatial effects[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University: Science A(Applied Physics & Engineering), 2011, 12(10): 758-770. [11] 于航, 邢皓枫. h型抗滑桩结构内力及土压力分布研究[J]. 低温建筑技术, 2020, 42(5): 96-100. doi: 10.13905/j.cnki.dwjz.2020.05.024Yu H, Xing H F. Internal force and earth pressure distribution of h-type anti-slide pile structure[J]. Cryogenic Building Technology, 2020, 42(5): 96-100(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.13905/j.cnki.dwjz.2020.05.024 [12] 王羽, 赵波. h型抗滑桩结构机理与工程数值分析研究[J]. 公路工程, 2015, 40(6): 5-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0610.2015.06.002Wang Y, Zhao B. The structural mechanism and numerical simulation of h-type anti-sliding pile[J]. Road Works, 2015, 40(6): 5-9(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0610.2015.06.002 [13] 王继晟, 熊传祥. h型抗滑桩工作性状有限元分析[J]. 土工基础, 2014, 28(1): 53-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TGJC201401017.htmWang J S, Xiong C X. Finite element analysis of h-type piles for landslide mitigations[J]. Geotechnical Foundations, 2014, 28(1): 53-56(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TGJC201401017.htm [14] Liu X R, Kou M M, Feng H, et al. Experimental and numerical studies on the deformation response and retaining mechanism of h-type anti-sliding piles in clay landslide[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2018, 77: 163. doi: 10.1007/s12665-018-7360-3 [15] Ding Y, Wang P, Yu S. A new method for deformation monitoring on H-pile in SMW based on BOTDA[J]. Measurement, 2015, 70: 156-168. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2015.02.027 [16] 欧孝夺, 唐迎春, 崔伟, 等. h型抗滑桩模型试验及数值模拟[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2012, 31(9): 1936-1943. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.09.026Ou X D, Tang Y C, Cui W, et al. Model test and numerical simulation of h-shaped anti-sliding pile[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 31(9): 1936-1943(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.09.026 [17] Li C D, Wu J J, Tang H M, et al. Model testing of the response of stabilizing piles in landslides with upper hard and lower weak bedrock[J]. Engineering Geology, 2016, 204: 65-76. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.02.002 [18] Conte E, Troncone A, Vena M. Nonlinear three-dimensional analysis of reinforced concrete piles subjected to horizontal loading[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2013, 49: 123-133. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2012.10.013 [19] 姚文敏. 基于水致岩体劣化的三峡库区侏罗系地层水库滑坡抗滑桩嵌固机理及其优化研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2020.Yao W M. Embedded mechanism and optimization of stabilizing piles for reservoir landslides in Jurassic strata of Three Gorges Reservoir region based upon water induced deterioration of rock mass[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2020(in Chinese with English abstract). [20] 雍睿. 三峡库区侏罗系地层推移式滑坡-抗滑桩相互作用研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2014.Yong R. Interaction between thrust load caused landslideand antislide pile in Jurassic strata in Three Gorges Reservoir region[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2014(in Chinese with English abstract). [21] 韩振雷. 基于软硬相间地层条件下抗滑桩受力特性研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2020.Han Z L. Study on the interaction between anti-slide pile and embedded rock mass under the condition of soft and hard interphase strata[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2020(in Chinese with English abstract). [22] 王旋, 胡新丽, 周昌, 等. 基于物理模型试验的滑坡-抗滑桩位移场变化特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(4): 103-108. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0413Wang X, Hu X L, Zhou C, et al. Model test on the displacement field characteristics of the landslide stabilizing piles[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(4): 103-108(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0413 [23] Liu D M, Xu W L, Zhao Y Z. Experimental study of the flow field of a high head model pump turbine based on PIV technique[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2021, 33(5): 1045-1055. doi: 10.1007/s42241-021-0092-y [24] Meng W, Xu L, Zhenya L, et al. Application of PIV technique in model test of frost heave of unsaturated soil[J]. Journal of Cold Regions Engineering, 2020, 34(3): 04020014-04020014. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)CR.1943-5495.0000216 [25] 杨登芳, 胡新丽, 徐楚, 等. 基于物理模型试验的多层滑带滑坡变形演化特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(2): 300-308. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0069Yang D F, Hu X L, Xu C, et al. Deformation and evolution characteristics of landslides with multiple sliding zones based on physical model test[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 300-308(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0069 [26] 中国地质灾害防治工程行业协会. 抗滑桩治理工程设计规范(试行): T/CAGHP003-2018[S]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2018.Chinese Association of Geological Hazard Prevention. Design specification for anti-sliding piles of improvement engineering: T/CAGHP003-2019[S]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2018(in Chinese). [27] Xiong S, Li C D, Yao W M, et al. Physical model tests and numerical modeling of stabilizing mechanism of portal double-row piles in landslides with interbedded weak and hard bedrock[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2022, 81: 101. [28] 赵海南. h型抗滑桩受力特性的试验研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2020.Zhao H N. Experimental study on the stress characteristics of h-type anti-slide pile[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2020(in Chinese with English abstract). -





 下载:
下载: