Movement characteristics and formation mechanism of the "6·10" Pengjiadong high speed landslide in Xingren
-
摘要:
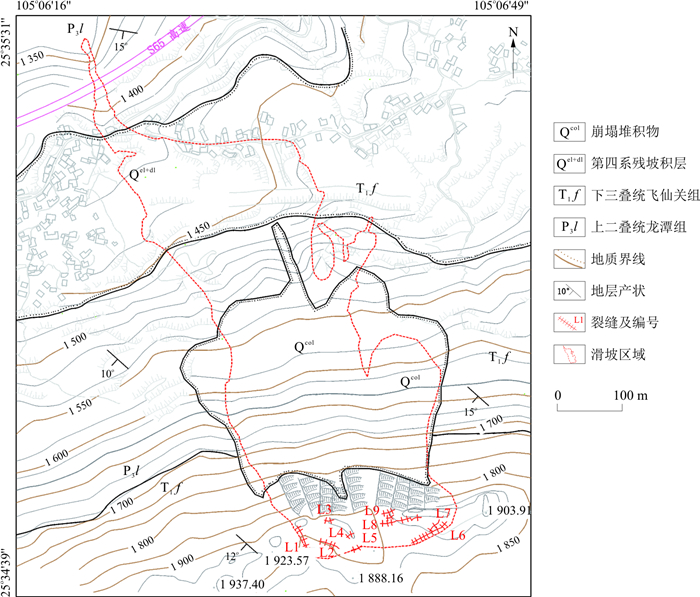
2021年6月10日20时30分左右, 贵州省兴仁彭家洞发生高速滑坡, 滑坡体高速运动沿途铲刮坡面崩塌堆积体, 造成3人遇难, 18栋房屋损毁。通过对滑坡发生前后影像资料遥感解译、灾害发生现场详细的地质调查及室内综合分析等技术手段, 对彭家洞滑坡的特征进行了详细描述, 阐明了滑坡发生的运动特征与形成机理。研究表明: 斜坡地形"上陡-中缓-下陡"与岩土结构"上硬下软"是滑坡形成的内在因素, 人类工程活动、强降雨的饱水加载和下渗软化作用是滑坡形成的外在因素; 滑坡平面形态呈折线形, 根据运动特征和堆积结构将滑坡分为滑源区(Ⅰ)、铲刮-流通区(Ⅱ)、铲刮堆积区(Ⅲ)3个区; 滑坡是由危岩带形成、滑坡孕育及斜坡失稳3个阶段孕育形成的挤压-推移式高速滑坡。研究结果对贵州类似的斜坡地带及岩土结构区域开展防灾减灾工作具有较强的指导作用。
Abstract:At approximately 20:30 on June 10, 2021, a high-speed landslide occurred in Pengjiadong in Xingren. The landslide mass moved at a high speed and scraped the slope collapse accumulation along the way, killed 3 people and damaged 18 houses. Through remote sensing interpretation of image data before and after the landslide, detailed geological investigation of the disaster site and indoor comprehensive analysis, the characteristics of the landslide were described in detail, and the movement characteristics and formation mechanism of the landslide were clarified. The research shows that the slope terrain with the feature of "steep up-moderate slow down-steep down" and the geotechnical structure with the feature of "hard up and soft down" were the internal factors of the landslide, while human engineering activities, saturated loading of heavy rainfall and infiltration softening were the external factors of the landslide. The plane shape of the landslide was polygonal. According to the movement characteristics and accumulation structure, the landslide was divided into three areas: sliding source area (Ⅰ), shoveling-circulation area (Ⅱ) and shoveling accumulation area (Ⅲ). The landslides was a high-speed compression-push landslide formed by the formation of dangerous rock zones, landslide initiation and slope collapse. The research shows that the in-depth study of the movement characteristics and disaster formation mechanism of the Pengjiadong landslide has a strong guiding role for disaster prevention and reduction in similar slope areas and geotechnical structure areas in Guizhou.
-
-
[1] 殷跃平. 斜倾厚层山体滑坡视向滑动机制研究: 以重庆武隆鸡尾山滑坡为例[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2010, 29(2): 217-226. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201002002.htmYin Y P. Mechanism of apparent dip slide of inclined bed ding rock slide: A case study of Jiweishan rockslide in Wulong, Chongcling[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 29(2): 217-226(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201002002.htm [2] 殷跃平. 汶川8级地震滑坡高速远程特征分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2009, 17(2): 153-166. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.02.002Yin Y P. Rapid and long run-out features of landslides trig-gered by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2009, 17(2): 153-166(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.02.002 [3] 殷跃平, 朱继良, 杨胜元, 等. 贵州关岭大寨高速远程滑坡-碎屑流研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2010, 18(4): 445-454. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.04.002Yin Y P, Zhu J L, Yang S Y, et al Study on remote landslide debris flow of Dazhai Expressway in Guanling, Guizhou[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2010, 18(4): 445-454(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.04.002 [4] 易连兴. 西南岩溶山区复合水动力场滑坡影响模式: 以关岭县大寨滑坡为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2020, 47(4): 43-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202004006.htmYi L X. Impact model of landslide with complex hydrodynamic field in karst mountain areas of southwest China: A case study of the Dazhai landslide in Guanling County[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(4): 43-50(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202004006.htm [5] 孔纪名, 田述军, 阿发友, 等. 贵州关岭"6·28"特大滑坡特征和成因[J]. 山地学报, 2010, 28(6): 725-731. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2010.06.012Kong J M, Tian S J, A F Y, et al Characteristics and causes of "6·28" landslide in Guanling, Guizhou[J]. Journal of Mountain Regions, 2010, 28(6): 725-731(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2010.06.012 [6] 郑光, 许强, 巨袁臻, 等. 2017年8月28日贵州纳雍县张家湾镇普洒村崩塌特征与成因机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2018, 26(1): 223-240. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201801023.htmZheng G, Xu Q, Ju Y Z, et al. The pusacun rock avalanche on August 28, 2017 in Zhangjiawan Nayongxian, Guizhou: Characteristics and failure mechanism[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(1): 223-240(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201801023.htm [7] 肖锐铧, 陈红旗, 冷洋洋, 等. 贵州纳雍"8·28"崩塌破坏过程与变形破坏机理初探[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2018, 29(1): 3-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201801002.htmXiao R H, Chen H Q, leng Y Y, et al. Preliminary analysis on the failure process and mechanism of the August 28 collapse in Nayong County, Guizhou Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Geological Hazards and Prevention, 2018, 29(1): 3-9(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201801002.htm [8] 许世民, 殷跃平, 邢爱国, 等. 基于地震信号的贵州纳雍崩塌-碎屑流运动特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2020, 31(2): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH202002001.htmXu S M, Yin Y P, Xing A G, et al. Characteristic analysis of the Nayong rock avalanche's kinematics based on seismic signals[J]. Chinese Journal of Geological Hazards and Prevention, 2020, 31(2): 1-8(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH202002001.htm [9] 郑光, 许强, 刘秀伟, 等. 2019年7月23日贵州水城县鸡场镇滑坡-碎屑流特征与成因机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2020, 28(3): 541-556. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202003012.htmZheng G, Xu Q, Liu X W, et al. The Jichang landslide on July 23, 2019 in Shuicheng, Guizhou: Characteristics and failure mechanism[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(3): 541-556(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202003012.htm [10] 李华, 史文兵, 朱要强, 等. 贵州省水城县"7·23"灾难性滑坡形成机制研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2020, 29(6): 188-198. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZH202006020.htmLi H, Shi W B, Zhu Y Q, et al. Study on the formation mechanism of "7·23" catastrophic landslide in Shuicheng County, Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of natural disasters, 2020, 29(6): 188-198(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZH202006020.htm [11] 李壮, 高杨, 贺凯, 等. 贵州省六盘水水城高位远程滑坡流态化运动过程分析[J]. 地质力学学报, 2020, 26(4): 520-532. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX202004009.htmLi Z, Gao Y, He K, et al. Analysis of fluidization movement process of high-level remote landslide in Shuicheng, Liupanshui, Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2020, 26(4): 520-532(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX202004009.htm [12] 陈理. 四川茂县新磨村高速滑坡启动机理研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2020.Chen L. Study on starting mechanism of Xinmocun high speed landslide in Mao County, Sichuan[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020(in Chinese with English abstract). [13] 马国涛. 四川峨眉抓口寺高速岩质滑坡成灾机理[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2019.Ma G T. Disaster mechanism of high-speed rock landslide in zhaokousi, Emei, Sichuan[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019(in Chinese with English abstract). [14] 肖盛燮, 周小平, 杨海清, 等. 二维高速滑坡力学模型[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2006, 25(3): 456-461. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200603003.htmXiao S X, Zhou X P, Yang H Q, et al. Two-dimensional high-speed landslide mechanics model[J]. Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(3): 456-461(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200603003.htm [15] 刘艺梁, 陈健翔, 高晨曦, 等. 基于滑面分区段力学模型的高速滑坡运动过程能量转化研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(2): 139-146. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0061Liu Y L, Chen J X, Gao C X, et al. Energy conversion of the high-speed landslide movement process based on a slid-ing surface partition mechanical model[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 139-146(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0061 [16] Yamaguchi H, Yoshida K, KuroshimaI, et al. Slakingand shearpropertiesofmudstone[C]//Anon. ISRM International Symposium: International Society for Rock Mechanics, 1988. [17] 卢操, 晏鄂川, 张瑜, 等. 降雨作用下青石镇政府后山堆积层滑坡渗流与稳定性[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 139-147. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0215Lu C, Yan E C, Zhang Y, et al. Seepage and stability of Houshan accumulation landslide of Qingshi Town Government under rainfall[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 139-147(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0215 [18] 柴波, 余宏明, 殷坤龙. 鄂西北山区降雨型边坡失稳模式和评价方法[J]. 工程地质学报, 2008, 16(3): 45-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200803008.htmChai B, Yu H M, Yin K L. Instability model and evaluation method of rainfall induced slope in mountainous area of northwest Hubei[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2008, 16(3): 45-50(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200803008.htm [19] 柴波, 殷坤龙, 汪洋, 等. 基于影响因素分布模型的滑坡稳定性敏感分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2007, 28(12): 2624-2628. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX200712030.htmChai B, Yin K, Wang Y, et al. Sensitivity analysis of landslide stability based on influencing factor distribution model[J]. Geotechnical Mechanics, 2007, 28(12): 2624-2628(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX200712030.htm [20] 栗倩倩, 史绪山, 柴波, 等. 台风-非台风降雨型滑坡的多时段临界雨量值预测模型[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(2): 267-273. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0076Li Q Q, Shi X SH, Chai B, et al. Multiduration critical rainfall prediction model of typhoons and non-typhoon rainfall landslide[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 267-273(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0076 [21] 吴艾祺, 宋飞, 闵瑶臻, 等. 岐山县宋家尧村滑坡基本特征与演化机理分析[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(2): 190-197. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201902024.htmWu A Q, Song F, Min Y Z, et al Analysis on basic characteristics and evolution mechanism of landslide in songjiayao village, Qishan County[J]. Northwest Geology, 2019, 52(2): 190-197(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201902024.htm [22] 许强, 彭大雷, 亓星, 等. 2015年4·29甘肃黑方台党川2#滑坡基本特征与成因机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2016, 24(2): 167-180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201602001.htmXu Q, Peng D L, Qi X, et al Study on basic characteristics and genetic mechanism of Dangchuan 2 landslide in Heifangtai, Gansu Province on April 29, 2015[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2016, 24(2): 167-180(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201602001.htm [23] 许强. 滑坡的变形破坏行为与内在机理[J]. 工程地质学报, 2012, 20(2): 145-151. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201202001.htmXu Q. Deformation and failure behavior and internal mechanism of landslide[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2012, 20(2): 145-151. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201202001.htm [24] 许强, 董秀军, 邓茂林, 等. 2010年7·27四川汉源二蛮山滑坡-碎屑流特征与成因机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2010, 18(5): 609-622. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201005004.htmXu Q, Dong X J, Deng M L, et al Study on characteristics and genetic mechanism of ermanshan landslide debris flow in Hanyuan, Sichuan on July 27, 2010[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2010, 18(5): 609-622(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201005004.htm [25] 朱赛楠, 殷跃平, 黄波林, 等. 三峡库区大型单斜顺层新生滑坡变形特征与失稳机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2021, 29(3): 657-667. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202103009.htmZhu S N, Yin Y P, Huang B L, et al. Study on deformation characteristics and instability mechanism of large monoclinic bedding newborn landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2021, 29(3): 657-667(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202103009.htm [26] 朱赛楠, 殷跃平, 李滨. 大型层状基岩滑坡软弱夹层演化特征研究: 以重庆武隆鸡尾山滑坡为例[J]. 工程地质学报, 2018, 26(6): 1638-1647. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201806026.htmZhu S N, Yin Y P, Li B. Study on the evolution characteristics of weak interlayer of large layered bedrock landslide: Taking Jiweishan landslide in Wulong, Chongqing as an example[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(6): 1638-1647(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201806026.htm [27] 李滨, 殷跃平, 高杨, 等. 西南岩溶山区大型崩滑灾害研究的关键问题[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2020, 47(4): 5-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202004002.htmLi B, Yin Y P, Gao Y, et al Key problems in the study of large-scale collapse and slide disasters in karst mountainous areas of Southwest China[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(4): 5-13(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202004002.htm [28] 陈春利, 殷跃平, 李同录. 窑洞开挖诱发浅层黄土滑坡的变形机理模拟[J]. 地质通报, 2013, 32(12): 1962-1967. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201312010.htmChen C L, Yin Y P, Li T L. Simulation of deformation mechanism of shallow loess landslide induced by cave excavation[J]. Geological Bulletin, 2013, 32(12): 1962-1967(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201312010.htm [29] 巨能攀, 李龙起, 黄润秋. 陡倾顺层斜坡动力失稳机理分析[J]. 工程科学与技术, 2018, 50(3): 54-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCLH201803007.htmJun E P, Li L Q, Huang R Q. Analysis of dynamic instability mechanism of steep bedding slope[J]. Engineering Science and Technology, 2018, 50(3): 54-63(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCLH201803007.htm -





 下载:
下载: