Genesis of karst groundwater contamination based on system spatial feature recognition
-
摘要:
岩溶地下水系统空间结构复杂, 含水层渗透性强、防污性能差, 一旦发生污染, 污染物扩散迅速且修复难度较大。以南方某岩溶大泉为例, 在水文地质调查的基础上, 结合水化学图解及多元示踪技术, 分析岩溶地下水系统边界及暗河管道分布, 识别岩溶泉的主要污染物、来源及污染途径, 探索岩溶地下水污染成因模式。研究结果表明, Q1岩溶地下水系统为典型的"多源单汇"地下水循环模式, 存在南北2条主要径流通道; 其主要污染物质为锰、菌落总数、氨氮、总磷, 分别为地下水质量标准阈值的17, 14, 7.2, 3.8倍; 建筑垃圾堵塞原有的暗河通道, 工程勘察和强夯活动破坏了垃圾堆场下部天然黏土防渗层, 生活垃圾及渗滤液进入岩溶管道, 两者共同导致了岩溶地下水的污染。该研究对于岩溶地下水系统污染防治工作具有重要的借鉴意义。
Abstract:The karst groundwater system has a complex spatial structure, strong aquifer permeability and poor anti-pollution performance. Once pollution occurs, the pollutants spread rapidly, and the repair is difficult. This study takes the pollution of a large karst spring in South China as an example. On the basis of a karst hydrogeological survey, combined with hydrochemical characteristics and multiple-tracer technology, the boundary of karst groundwater system and the distribution of underground river pipelines were analyzed, and the main pollution sources and pollution routes of the karst spring were identified. In addition, the genetic model of karst groundwater pollution was also explored. These results showe that the Q1 karst groundwater system was a typical "multi-source, single-sink" groundwater circulation pattern with two main runoff channels in the north and south. Manganese, total bacterial counts, ammonia nitrogen and total phosphorus were the main substances exceeding the standard, which were 17, 14, 7.2 and 3.8 times the groundwater quality standard threshold, respectively. The construction waste blocked the original channel of the underground river, forcing the groundwater to divert and flow under the landfill. Engineering investigation and dynamic compaction activities destroyed the natural clay impermeable stratum under the landfill, resulting in the early transport of domestic garbage and leachate entered into the karst pipeline, both of which caused the pollution of karst groundwater. This study provides an important reference for the prevention and control of karst groundwater pollution.
-
Key words:
- groundwater contamination /
- tracer test /
- spatial structure /
- genesis /
- karst water system
-
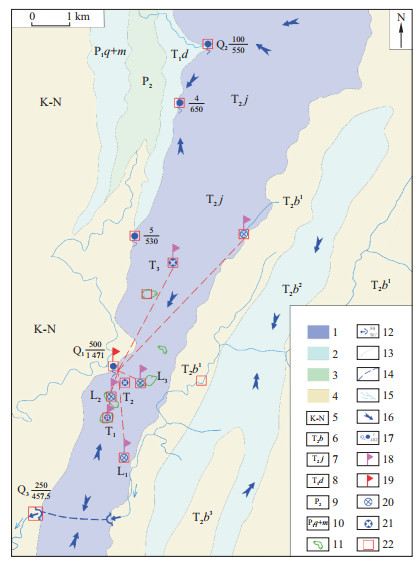
图 1 研究区水文地质条件及取样点位置图
1.强岩溶含水层;2.中等岩溶含水层;3.弱岩溶含水层;4.相对隔水层;5.白垩系-新近系;6.巴东组;7.嘉陵江组;8.大冶组;9.上二叠统;10.栖霞茅口组;11.岩溶洼地;12.暗河出口;13.地质界线$ \frac{\text { 流量 }\left(\mathrm{m}^3 / \mathrm{s}\right)}{\text { 高程 }(\mathrm{m})}$;14.推测暗河管道;15.水系;16.地下水流向;17.岩溶泉;18.示踪剂投放点;19.示踪剂接收点;20.落水洞;21.暗河天窗;22.采样点
Figure 1. Hydrogeological map of the study area and location map of sampling point
图 5 研究区污染物标准指数分布图(图例见图 4)
Ⅰ区为北部生活污水区;Ⅱ区为北部农业和养殖业区;Ⅲ区为垃圾堆场区;Ⅳ区为南部生活污水区
Figure 5. Distribution diagram of the pollutant standard index
表 1 研究区主要落水洞、天窗
Table 1. Main sinkholes and skylights in the study area
类型 落水洞 天窗 L1 L2 L3 L4 T1 T2 T3 高程/m 520.0 485.2 513.0 553.0 470.0 468.0 672.0 流量/(L·s-1) 3 5 1 5 - 100 10 表 2 地下水多元示踪试验情况
Table 2. Groundwater multi-element tracing tests
试验编号 示踪剂投放地点 示踪剂类型 投放时间 投放量/g 1 L1 罗丹明 2019/10/16 9:00 3 000 2 T3 荧光增白剂 2019/10/16 11:00 3 000 3 L3 荧光素钠 2019/10/18 18:00 1 000 4 L2 罗丹明 2019/11/5 12:00 2 000 5 T1 荧光增白剂 2019/11/14 14:00 3 000 6 L4 荧光素钠 2019/11/23 10:00 3 000 表 3 岩溶泉2017, 2019年相关水质指标特征
Table 3. Characteristics of relevant water quality indicators of karst spring in 2017 and 2019
水化学指标 类总大肠杆菌/
(MPN·L-1)菌落总数/
(CFU·mL-1)氨氮 总磷 COD 铜 锌 铬 铅 镉 砷 锰 汞 ρB/(mg·L-1) ρB/(μg·L-1) Ⅲ类标准 10 000 100 0.5 0.2 20 1 000 1 000 50 10 5 10 100 1 2017年 194 100 0.02 0.02 0.92 0.74 2.1 0.071 0.2 0.000 15 0.146 2.98 0.000 62 2019年 3 500 1 400 3.6 0.76 9.24 7.4 25.5 1.1 1.9 0.02 1.9 1 700 0.01 2019年较Ⅲ类水 0.35倍 14倍 7.2倍 3.8倍 0.46倍 0.007倍 0.025倍 0.02倍 0.19倍 0.004倍 0.19倍 17倍 0.01倍 2019年较2017年 18倍 14倍 180倍 38倍 10倍 10倍 12倍 155倍 9倍 133倍 13倍 570倍 16倍 表 4 地下水示踪试验成果
Table 4. Results of the groundwater tracing test
投放地点 L1 T3 L3 T1 监测地点 Q1 Q1 Q1 Q1 示踪剂 罗丹明 荧光增白剂 荧光素钠 荧光增白剂 投放量/g 3 000 3 000 1 000 2 000 投放点-监测点距/m 2 600 3 000 630 2 000 浓度产生响应时间/h 110 25.5 3.5 245.5 浓度达到峰值时间/h 132 26.5 4 249.2 浓度恢复正常时间/h 144 31 4.5 267.5 滞后时间/h 110 25.5 3.5 245.5 延迟时间/h 32 5.5 1 22 最快流速/(m·h-1) 27 117 180 6.1 平均流速/(m·h-1) 22.7 110 158 6 表 5 岩溶地下水及潜在污染源主要污染物含量
Table 5. Main pollutant contents in karst groundwater and potential pollution sources
水化学指标 氨氮/(mg·L-1) 总磷/(mg·L-1) 锰/(μg·L-1) 菌落总数/(CFU·mL-1) 岩溶泉Q1 3.2~3.86 3.64~4.21 5.3~17.8 12~39 生活污水 0.13~0.56 3.10~4.23 0.007~0.204 1.4~6.8 农业和养殖业污水 2.32~2.7 1.2~2.33 1.35~2.65 6.8~9.2 垃圾渗滤液 7.04 27 51.3 34.7 -
[1] Jürgen M, Abrahan M. Editorial overview: Management of groundwater resources and pollution prevention[J]. Current Opinion in Environmental Science & Health, 2022, 28: 100365. [2] Jiang W, Wang G, Sheng Y, et al. Isotopes in groundwater(2H, 18O, 14C) revealed the climate and groundwater recharge in the Northern China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 666: 298-307. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.245 [3] 苗晋杰, 靳继红, 杜东, 等. 首都副中心及重点区域地下水环境质量评价与问题成因[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2020, 43(3): 7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ202003004.htmMiao J J, Jin J H, Du D, et al. Valuation of groundwater environmental quality and causes of problems in the capital sub-center and key regions[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2020, 43(3): 7(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ202003004.htm [4] Li P, He X, Li Y, et al. Occurrence and health implication of fluoride in groundwater of loess aquifer in the Chinese Loess Plateau: A case study of Tongchuan, Northwest China[J]. Exposure & Health, 2019, 11(2): 95-107. [5] 周晓妮, 王振兴, 苗青壮, 等. 漳河流域典型区浅层地下水水化学特征分析[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2020, 43(3): 265-270. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2020.03.011Zhou X N, Wang Z X, Miao Q Z, et al. Study the shallow groundwater chemical characteristics in the typical area of Zhanghe catchment basin[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2020, 43(3): 265-270(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2020.03.011 [6] Wang Z X, Wu R, Huang K, et al. Structure identification of a karst groundwater system based on high-resolution rainfall-hydrological response characteristics[J/OL]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2021. doi: 10.1007/511356-021-17880-x. [7] 郭绪磊, 周宏, 罗明明, 等. 黄陵穹隆周缘岩溶水流系统特征及成因[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(1): 328-340. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0033Guo X L, Zhou H, Luo M M, et al. Characteristics and genesis of karst water flow system around Huangling anticline[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(1): 328-340(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0033 [8] Wang Z J, Guo X L, Kuang Y, et al. Recharge sources and hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in a heterogeneous karst water system in Hubei Province, Central China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2022, 136: 105165. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2021.105165 [9] Nimmo J R, Horowitz C, Mitchell L. Discrete-storm water-table fluctuation method to estimate episodic recharge[J]. Ground Water, 2015, 53(2): 282-292. doi: 10.1111/gwat.12177 [10] 蒋忠诚, 夏日元, 时坚, 等. 西南岩溶地下水资源开发利用效应与潜力分析[J]. 地球学报, 2006, 27(5): 495-502. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2006.05.012Jiang Z C, Xia R Y, Shi J, et al. The application effects and exploitation capacity of karst underground water resources in Southwest China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica 2006, 27(5): 495-502(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2006.05.012 [11] 吴华英, 李腾芳, 程瑞瑞, 等. 我国岩溶地下水受污染的原因与污染特征[J]. 中国矿业, 2021, 30(增刊1): 4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA2021S1023.htmWu H Y, Li T F, Cheng R R, et al. Causes and characteristics of the pollution of karst groundwater in China[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2021, 30(S1): 4(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA2021S1023.htm [12] 卢丽, 王喆, 裴建国, 等. 西南地区典型岩溶地下水系统污染模式[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2018, 16(6): 89-96. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NSBD201806014.htmLu L, Wang Z, Pei J G, et al. Study on pollution model of typical karst groundwater system in area of southwest China[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2018, 16(6): 89-96(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NSBD201806014.htm [13] 高旭波, 王万洲, 侯保俊, 等. 中国北方岩溶地下水污染分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(3): 287-298. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202003001.htmGao X B, Wang W Z, Hou B J, et al. Analysis of karst groundwater pollution in northern China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(3): 287-298(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202003001.htm [14] 谢先军, 刘红杏, 高爽, 等. 典型纳污坑塘周边地下水污染来源识别及其健康风险评估[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 34-42. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0104Xie X J, Liu H X, Gao S, et al. Source identification and health risk assessment of groundwater pollution in typical sewage pits and ponds[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 34-42(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0104 [15] 夏日元, 蒋忠诚, 邹胜章, 等. 岩溶地区水文地质环境地质综合调查工程进展[J]. 中国地质调查, 2017, 4(1): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDC201701001.htmXia R Y, Jiang Z C, Zou S Z, et al. Progress of hydrogeology and environmental geology comprehensive survey in karst area[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2017, 4(1): 1-10(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDC201701001.htm [16] Wang Z J, Yue F J, Lu Ji, et al. New insight into the response and transport of nitrate in karst groundwater to rainfall events[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021: 818: 151727. [17] 刘长礼, 王秀艳, 吕敦玉, 等. 中国南方岩溶地下水面源污染风险评价及防控对策[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(6): 910-918. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201706008.htmLiu C L, Wang X Y, Lü D Y, et al. Risk assessment and control countermeasures of southern China's karst groundwater areal source pollution[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(6): 910-918(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201706008.htm [18] Traian B, Mina B, Danny I, et al. Potential for natural attenuation of domestic and agricultural pollution in karst groundwater environments[J]. Water, 2022, 14(10): W14101597. [19] 孙斌, 邢立亭, 李常锁. 趵突泉泉域岩溶水典型污染组分变化特征及污染途径[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(6): 810-818. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201806002.htmSun B, Xing L T, Li C S. Variation of typical pollution components and pollution way of karst water in Baotu Spring region[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(6): 810-818(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201806002.htm [20] 何愿, 张颖, 朱明. 桂江流域地下水污染途径及防控措施研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2015, 34(4): 387-394. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201504012.htmHe Y, Zhang Y, Zhu M. The pollutant infiltration pathways and measures to control groundwater pollution in the Guijiang River drainage system[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2015, 34(4): 387-394(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201504012.htm [21] 段俭君, 李卿. 南方煤矿区喀斯特泉污染源识别及污染通道探查方法[J]. 能源与环保, 2019, 41(11): 62-66. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZMT201911016.htmDuan J J, Li Q. Identification of karst spring pollution sources and exploration method of pollution channels in southern coal mine area[J]. China Energy and Environmental Protection, 2019, 41(11): 62-66(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZMT201911016.htm [22] 孟舒然, 吕敦玉, 张建羽, 等. 基于地统计技术的地下水硝酸盐的污染源解析研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2021, 44(增刊2): 197-204. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS2021S2024.htmMeng S R, Lü D Y, Zhang J Y. Sources apportionment of groundwater nitrate using statistical technology[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 44(S2): 197-204(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS2021S2024.htm [23] 常威, 谭家华, 黄琨, 等. 地下水多元示踪试验在岩溶隧道水害预测中的应用: 以张吉怀高铁兰花隧道为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(3): 400-408. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202003014.htmChang W, Tan J H, Huang K, et al. Application of groundwater multi-element tracing tests to water hazard prediction of karst tunnels: An example of the Lanhua tunnel on the Zhangjiajie-Jishou-7Huaihua high-speed railway[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(3): 400-408(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202003014.htm [24] 程烯, 万军伟, 黄琨, 等. 荧光示踪剂的干扰实验研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2019, 38(5): 795-803. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201905019.htmCheng X, Wan J W, Huang K, et al. Experimental study on the interference of fluorescent tracer[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2019, 38(5): 795-803(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201905019.htm [25] 常威. 复杂岩溶水系统识别及其在隧道涌水量预测的应用[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2021.Chang W. Study on the identification of complex karst water system and its application in tunnel water disaster prediction: A case study of Zhangjiajie-Jishou-Huaihua high-speed railway Daqing mountain tunnel[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2021(in Chinese with English abstract). [26] Panno S V, Kelly W R, Martinsek A T, et al. Estimating background and threshold nitrate concentrations using probability graphs[J]. Ground Water, 2010, 44(5): 697-709. [27] Pastén-Zapata E, Ledesma-Ruiz R, Harter T, et al. Assessment of sources and fate of nitrate in shallow groundwater of an agricultural area by using a multi-tracer approach: Science direct[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 470/471(2): 855-864. -





 下载:
下载: