Structural characteristics and tectonic evolution of Mesozoic-Cenozoic faults in the Shunbei area, Tarim Basin
-
摘要:
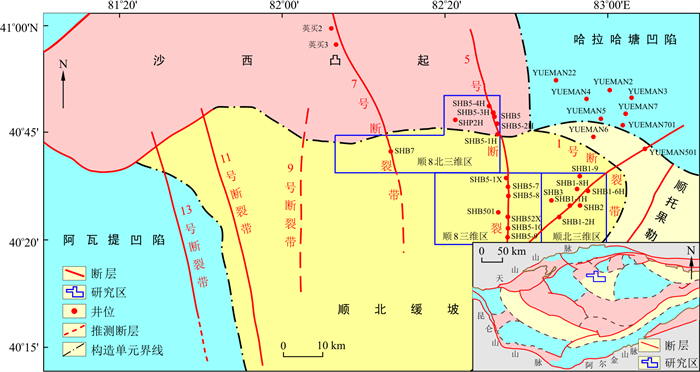
塔里木盆地顺北地区古生界油气资源非常丰富, 此外在中新生界也发现了良好的油气显示, 揭示出该区中新生界也具有较好的油气勘探潜力。因此, 为了揭示对顺北地区中新生界油气成藏具有关键控制因素的断裂构造特征及其发育机制, 通过对顺北地区最新三维地震资料的精细构造解释, 系统分析了该区中新生界断裂构造的类型、几何学特征及其成因演化。研究表明: 顺北地区中新生界断裂以张性正断层为主, 发育少量逆断层和走滑断层, 该区断裂发育数量众多但单条断裂规模较小、平面上呈杂乱展布且具有明显的分区分层的差异活动特征。与区域动力背景和盆地演化阶段相统一, 顺北地区中新生界断裂演化经历了印支、燕山和喜山期3个阶段多期次伸展-挤压构造旋回, 而且该区所处的构造位置、下伏中二叠统火成岩地层特征及下三叠统柯吐尔组砂泥岩塑性层等对中新生界断裂的形成演化具有重要控制作用。通过对顺北地区连通T90~T50界面通源断裂的精细刻画, 揭示出在5号断裂带中部和7号断裂带中南部存在两大通源断裂发育区, 上述两地区部分断裂由T90界面往上一直断到T50界面之上, 对古生界油气向中新生界垂向输导具有建设性作用, 为该区中新生界油气的有利勘探区带。
Abstract:Oil and gas resources in the Shunbei area of the Tarim Basin are rich in Paleozoic strata.Recent petroleum exploration indicates that Mesozoic-Cenozoic sedimentary rocks have a good potential in hydrocarbon extraction. In this study, recently acquired 3D seismic surveys were used to systematically analyze fault types, geometrical characteristics, and evolution of Mesozoic-Cenozoic faults in the Shunbei area. The objective is to understand the characteristics and development mechanisms of faults that have the key controlling factors of hydrocarbon accumulation.In the Shunbei area, the dominant faults are tensional normal faults with few thrust faults and strike-slip faults. The district has many small scale, disorderly distributed faults. Combined with the regional setting and basin evolution stage, we suggest that the development of Mesozoic-Cenozoic faults in the Shunbei area experienced three tectonic cycles during the Indosinian, Yanshanian, and Himalayan periods. The structural position, middle Permian igneous rocks, and the sandy mudstone of the Lower Triassic Tongketuer Formation have significant control on fault evolution.Detailed interpretation of faults in the T90-T50 stratigraphic interval in the Shunbei area shows that the central part of the No.5 fault and south central part of the No.7 fault are two large faults that connect downward to the source rock of the basin. In these two areas, some faults cut upward through T90 to T50, which is good forvertical migration of hydrocarbon from Paleozoic to Mesozoic-Cenozoic strata and therefore are ideal locations for petroleum exploration.
-
Key words:
- faults /
- tectonic evolution /
- Mesozoic-Cenozoic /
- Shunbei area /
- Tarim Basin
-
图 4 顺北地区中新生界典型逆断层地震剖面特征图(地层代号同图 3)
Figure 4. Seismic section shows the typical Mesozoic-Cenozoic reverse fault in the Shunbei area
图 8 顺北地区中新生界断裂典型剖面特征图(地层代号同图 3)
Figure 8. Seismic section shows the typical profile combination feature of Mesozoic-Cenozoic faults in the Shunbei area
-
[1] 焦方正. 塔里木盆地顺托果勒地区北东向走滑断裂带的油气勘探意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2017, 38(5): 831-839. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201705001.htmJiao F Z. Significance of oil and gas exploration in NE strike-slip fault belts in Shuntuoguole area of Tarim Basin[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 2017, 38(5): 831-839 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201705001.htm [2] 焦方正. 塔里木盆地顺北特深碳酸盐岩断溶体油气藏发现意义与前景[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(2): 207-216. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201802002.htmJiao F Z. Significance and prospects of the ultra-deep carbonate fault-karst reservoirs in the Shunbei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 2018, 39(2): 207-216 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201802002.htm [3] 邬光辉, 成丽芳, 刘玉魁, 等. 塔里木盆地寒武-奥陶系走滑断裂系统特征及其控油作用[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2011, 32(3): 239-243. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201103008.htmWu G H, Cheng L F, Liu Y K, et al. Strike-slip fault system of the Cambrian-Ordovician and its oil-controlling effect in Tarim Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2011, 32(3): 239-243 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201103008.htm [4] 孙东, 杨丽莎, 王宏斌, 等. 塔里木盆地哈拉哈塘地区走滑断裂体系对奥陶系海相碳酸盐岩储层的控制作用[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2015, 26(增刊1): 80-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX2015S1011.htmSun D, Yang L S, Wang H B, et al. Strike-slip fault system in Halahatang area of the Tarim Basin and its control on reservoirs of Ordovician marine carbonate rock[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2015, 26(S1): 80-87 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX2015S1011.htm [5] 田鹏, 马庆佑, 吕海涛. 塔里木盆地北部跃参区块走滑断裂对油气成藏的控制[J]. 石油实验地质, 2016, 38(2): 156-161. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201602003.htmTian P, Ma Q Y, Lü H T. Strike-slip faults and their controls on hydrocarbon reservoirs in the Yuecan block of the northern Tarim Uplift, Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2016, 38(2): 156-161 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201602003.htm [6] 李培军, 陈红汉, 唐大卿, 等. 塔里木盆地顺南地区中-下奥陶统NE向走滑断裂及其与深成岩溶作用的耦合关系[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(1): 93-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201701008.htmLi P J, Chen H H, Tang D Q, et al. Coupling relationship between NE strike-slip fault of the Middle-Lower Ordovician of Shunnan area, Tarim Basin, Northwest China[J]. Earth Science, 2017, 42(1): 93-104 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201701008.htm [7] 杨勇, 汤良杰, 郭颖, 等. 塔中隆起NNE向走滑断裂特征及形成机制[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(5): 1569-1578. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201605007.htmYang Y, Tang L J, Guo Y, et al. Deformation characteristics and formation mechanism of NNE-trending strike-slip faults in Tazhong Uplift[J]. Geology in China, 2016, 43(5): 1569-1578 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201605007.htm [8] 张艳萍, 吕修祥, 于红枫, 等. 塔中隆起两组走滑断裂对岩溶储层发育的控制机制[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(5): 663-673. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201605007.htmZhang Y P, Lü X X, Yu H F, et al. Controlling mechanism of two strike-slip fault groups on the development of the Ordovician karst reservoirs in the Tazhong Uplift, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2016, 37(5): 663-673 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201605007.htm [9] 韩俊, 曹自成, 邱华标, 等. 塔中北斜坡奥陶系走滑断裂带与岩溶储集体发育模式[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2016, 37(2): 145-151. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201602005.htmHan J, Cao Z C, Qiu H B, et al. Model for strike-slip fault zones and karst reservoir development of Ordovician in northern slope of Tazhong Uplift, Tarim Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2016, 37(2): 145-151 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201602005.htm [10] 董马超, 吕海涛, 蒲仁海, 等. 塔中东部走滑断裂带特征及油气地质意义[J]. 石油物探, 2016, 55(6): 840-850. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2016.06.009Dong M C, Lü H T, Pu R H, et al. Characteristics of the strike-slip fault belt and its hydrocarbon geological significance in the eastern area of central Tarim Basin[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2016, 55(6): 840-850 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2016.06.009 [11] 李鹏飞, 崔德育, 田浩男. 塔里木盆地塔北地区X区块断溶体刻画方法与效果[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2017, 52(1): 189-194. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDQ2017S1031.htmLi P F, Cui D Y, Tian H N. Method and effect of fragmentation of X-block in Tabei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2017, 52(1): 189-194 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDQ2017S1031.htm [12] 邱华标, 印婷, 曹自成, 等. 塔里木盆地塔中北坡走滑断裂特征与奥陶系油气勘探[J]. 海相油气地质, 2017, 22(4): 44-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ201704006.htmQiu H B, Yin T, Cao Z C, et al. Strike-slip fault and Ordovician petroleum exploration in northern slope of Tazhong Uplift, Tarim Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2017, 22(4): 44-52 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ201704006.htm [13] 吕海涛, 张哨楠, 马庆佑. 塔里木盆地中北部断裂体系划分及形成机制探讨[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(4): 444-452. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201704003.htmLü H T, Zhang S N, Ma Q Y. Classification and formation mechanism of fault systems in the central and northern Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2017, 39(4): 444-452 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201704003.htm [14] 魏国齐, 贾承造, 施央申, 等. 塔北隆起北部中新生界张扭性断裂系统特征[J]. 石油学报, 2001, 22(1): 19-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200101003.htmWei G Q, Jia C Z, Shi Y S, et al. Characteristics of the torsional fault system of the Mesozoic and Cenozoic in the northern Tarim Uplift[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2001, 22(1): 19-24 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200101003.htm [15] 刘红旭, 董文明, 刘章月, 等. 塔北中新生代构造演化与砂岩型铀成矿作用关系: 来自磷灰石裂变径迹的证据[J]. 世界核地质科学, 2009, 26(3): 125-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYD200903004.htmLiu H X, Dong W M, Liu Z Y, et al. Mesozoic-Cenozoic tectonic evolution and its relation to sandstone-type uranium mineralization in northern Tarim area: Evidence from apatite fission track[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 2009, 26(3): 125-133 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYD200903004.htm [16] 丁孝忠, 林畅松, 刘景彦, 等. 塔里木盆地白垩纪-新近纪盆山耦合过程的层序地层响应[J]. 地学前缘, 2011, 18(4): 144-157. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201104011.htmDing X Z, Lin C S, Liu J Y, et al. The sequence stratigraphic response to the basin-orogence coupling process of Cretaceous-Neogene in the Tarim Basin, China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2011, 18(4): 144-157 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201104011.htm [17] 宁飞, 金之钧, 张仲培, 等. 塔中北坡走滑断裂成因机理与油气成藏[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(1): 98-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201801011.htmNing F, Jin Z J, Zhang Z P, et al. Mechanism of strike-slip faulting and hydrocarbon accumulation in northern slope of Tazhong area[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 2018, 39(1): 98-106 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201801011.htm [18] 邓尚, 李慧莉, 张仲培, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北及邻区主干走滑断裂带差异活动特征及其与油气富集的关系[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(5): 878-888. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201805004.htmDeng S, Li H L, Zhang Z P, et al. Characteristics of differential activities in major strike-slip fault zones and their control on hydrocarbon enrichment in Shunbei area and its surroundings, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(5): 878-888 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201805004.htm [19] 周铂文, 陈红汉, 云露, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北地区一间房组台地碳酸盐岩异常泥质含量与断裂带距离及裂缝发育关系[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 93-102. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0609Zhou B W, Chen H H, Yun L, et al. Relationship between argillaceous content and distance to main faulted zone and fractures development in the platform carbonate rocks of Yijianfang Formation in Shunbei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6): 93-102 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0609 [20] 汤良杰, 漆立新, 邱海峻, 等. 塔里木盆地断裂构造分期差异活动及其变形机理[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(8): 2569-2583. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201208023.htmTang L J, Qi L X, Qiu H J, et al. Poly-phase differential fault movement and hydrocarbon accumulation of the Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(8): 2569-2583 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201208023.htm [21] 崔军文, 唐哲民. 塔里木盆地构造格架和构造应力场分析[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(1): 231-242. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201101016.htmCui J W, Tang Z M. Tectonic framework of the Tarim Basin and its tectonic stress field analysis[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(1): 231-242 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201101016.htm [22] 何登发, 贾承造, 李德生, 等. 塔里木多旋回叠合盆地的形成与演化[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2005, 26(1): 64-77. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200501009.htmHe D F, Jia C Z, Li D S et al. Formation and evolution of polycyclic superimposed Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2005, 26(1): 64-77 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200501009.htm [23] 杨克绳. 塔里木盆地的构造演化[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2005, 21(2): 25-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT200502008.htmYang K S. Tectonic evolution of the Tarim Basin[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2005, 21(2): 25-29 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT200502008.htm [24] Wang S L, Shu L S, Zhu W B, et al. Mesozoic faults in the NE Tarim(western China) and the implications on collisions in the southern Eurasian margin[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 56: 191-199. [25] Klemd R. The collision between the Yili and Tarim blocks of the southwestern Altaids[C]//Anon. Geochemical and age constraints of a leucogranite dike crosscutting the HP-LT metamorphic belt in the Chinese Tianshan Orogen. Beijing: Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2012: 118-131. [26] 魏国齐, 贾承造, 李本亮. 我国中西部前陆盆地的特殊性和多样性及其天然气勘探[J]. 高校地质学报, 2005, 11(4): 552-557. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200504011.htmWei G Q, Jia C Z, Li B L. Particularty and diversity of the foreland basins in the central and western China and the natural gas exploration in the foreland basins[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2005, 11(4): 552-557 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200504011.htm [27] 庞菲菲, 唐永, 宋换新, 等. 库车前陆盆地东部侏罗系逆冲构造变形及应力演化分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 123-135. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0509Pang F F, Tang Y, Song H X, et al. Analysis of deformation and stress evolution of thrust structure: A case of Jurassic in east Kuqa subbasin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 123-135 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0509 [28] 杜林涛, 李亚林, 刘洋. 西藏羌塘地体中生代中-晚期不整合事件及其构造意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 61-71 doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0405Du L T, Li Y L, Liu Y. Unconformable event and its tectonic significance at Middle-Late Mesozoic of Qiangtang terrane, Tibet[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 61-71 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0405 [29] 高长林, 吉让寿, 黄泽光. 中国西部新特提斯洋与构造变革及盆地[J]. 中国西部油气地质, 2006, 2(4): 355-361.Gao C L, Ji R S, Huang Z G. Relationship among the Neo-Tethys tectonic diktyogenises and basins in West China[J]. West China Petroleum Geosciences, 2006, 2(4): 355-361 (in Chinese with English abstract). -





 下载:
下载: