Structural graded ore-controlling rule and ore-controlling structural combination pattern of Daliangzi lead-zinc deposit in southwestern Sichuan
-
摘要:
大梁子铅锌矿床位于扬子地块西南缘的川西南矿集区内,矿体展布明显受构造控制。针对该矿床构造分级控矿规律与控矿构造组合样式不清的问题,基于矿田地质力学理论与方法,通过不同级别的典型控矿构造力学性质鉴定及不同期次构造筛分,厘清了控矿构造组合样式及其形成机理。研究表明,成矿构造体系为印支晚期NE向构造带,在NW-SE向主压应力作用下,矿床内形成的不同级别构造分级控制了矿床、矿体和矿脉的展布;形成不同尺度的控矿构造组合样式:矿床尺度的走滑为主断裂-褶皱构造组合、矿体尺度的为“多”字型、“入”字型及“黑色破碎带”构造组合。本研究为该矿床深部及外围找矿勘查提供了重要依据。
Abstract:The Daliangzi lead-zinc deposit is located in the southwestern Sichuan ore concentration area in the southwestern margin of the Yangtze block, and the ore body′s occurrence obviously controlled by the structure.Aiming at the problem of unclear ore-controlling rules and combinations of ore-controlling structures, based on the theory and method of ore field geomechanics, through the identification of the mechanical properties of typical ore-controlling structures at different levels and the structural screening of different stages, the ore-controlling structures, assemblages and their formation mechanisms were clarified. The research shows that the metallogenic structural system is the late Indosinian NE structural belt.Under the NW-SE principal compressive stress, the resulting structures of different scales control the occurrence of the ore deposit, ore body and ore vein; At the same time, form various structural assemblages: strike-slip at the deposit scale is dominated by fault-fold tectonic assemblages, and orebody-scale assemblages are "multi-shaped", "in-shaped" and "black fractured zone" structural assemblages.This study provides an important basis for prospecting and exploration in the deep and peripheral parts of the deposit.
-
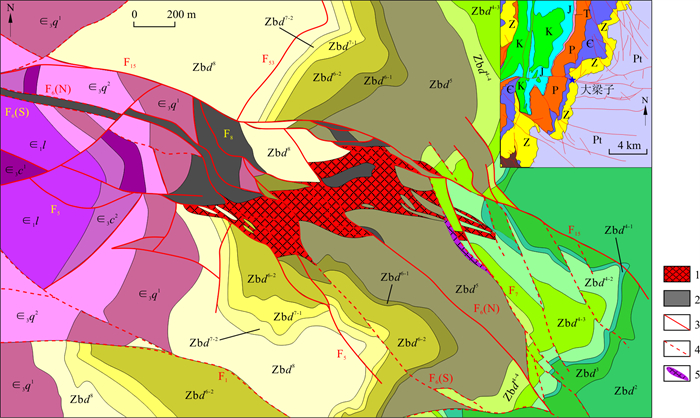
图 1 大梁子铅锌矿区地质简图[12]
∈1l.下寒武统龙王庙组白云质灰岩;∈3c2.上寒武统沧浪铺组上段泥质灰岩;∈3c1.上寒武统沧浪铺组下段石英砂岩;∈3q2.上寒武统筇竹寺组上段页岩;∈3q1.上寒武统筇竹寺组下段石英砂岩;Zbd8.上震旦统灯影组八段条带状白云岩;Zbd7-2.上震旦统灯影组七段2层含磷质白云岩;Zbd7-1.上震旦统灯影组七段1层含磷白云岩;Zbd6-2.上震旦统灯影组六段2层硅质白云岩;Zbd6-1.上震旦统灯影组六段1层条带状白云岩;Zbd5.上震旦统灯影组五段细晶硅质白云岩;Zbd4-4.上震旦统灯影组四段4层含燧石结核硅质白云岩;Zbd4-3.上震旦统灯影组四段3层泥砂质白云岩;Zbd4-2.上震旦统灯影组四段2层砂质白云岩;Zbd4-1.上震旦统灯影组四段1层板状硅质岩;Zbd3.上震旦统灯影组三段砂泥质白云岩;Zbd2.上震旦统灯影组二段含藻白云岩;1.矿体;2.“黑破带”;3.实测断层;4.推测断层;5.构造破碎带
Figure 1. Geological diagram of the Daliangzi lead-zinc mining area
图 8 1 884 m中段Z770-Z775点断裂素描图
①深灰色-黑色硅质碎裂白云岩;②灰色-深灰色硅质碎裂白云岩;③黑色白云岩胶结棱角状灰白色硅质白云岩角砾;④深灰色-黑色白云岩胶结灰白色硅质白云岩角砾;Ⅰ.深灰色硅质碎裂白云岩,含灰白色次棱角状硅质白云质角砾;Ⅱ.黑破带(黑色含炭质,非常破碎),见细脉状方解石,无角砾;Ⅲ.断裂面F3-1(左)与F3-2(右);Ⅳ.黄铁矿硫化物胶结黑色角砾,见方解石细脉;Ⅴ.F7断裂面;Ⅵ.深灰色-黑色硅质白云岩胶结灰白色强硅化碎裂白云岩角砾;Ⅶ.断裂面F4-1与F4-3;Ⅷ.断裂面F5与F6;Ⅸ.深灰色-黑色白云岩胶结灰白色硅质白云岩角砾;Ⅹ.黑色白云岩胶结棱角状灰白色硅质白云岩角砾;Py.黄铁矿;Sp.闪锌矿;Ga.方铅矿
Figure 8. Z770-Z775 point fracture sketch in the middle section of 1 884 m
图 9 9号勘探线剖面图[13]
Figure 9. Sectional view of No.9 exploration line
图 12 大梁子铅锌矿床1号主矿体群Ⅶ、Ⅷ号矿块与2号矿体群平面图[13]
Figure 12. Plan of No.1 ore body Ⅶ, No.Ⅷ ore body and No.2 ore body of the Dalangzi lead-zinc deposit
表 1 大梁子铅锌矿断裂构造及其矿化蚀变特征简表
Table 1. Summary table of the fault structure and its mineralization and alteration characteristics of the Daliangzi lead-zinc mine
走向 等级 产状 形态特征 力学性质 构造岩特征 矿化蚀变特征 走向/(°) 倾角/(°) 倾向 NW 一级 NW60~70 70~85 SW 舒缓波状、波状、较平直、紧闭 右行张(扭)性-左行扭(压)性 碎裂岩、碎斑岩、碎粒岩、片理化 Py、Lim、Ga、Sp、Dol 二级 NW30~70 60~85 SW 舒缓波状、微波状、平直 右行张(扭)性-左行压(扭)性 碎斑岩、碎粉岩、片理化 Py、Lim、Ga、Sp、Gal 三级 NW30~70 65~85 SW/NE 舒缓波状、波状 张扭性-压扭性 碎裂岩、碎粉岩、碎斑岩、断层泥 Py、Lim、Ga、Sp 四级 NW20~50 60~80 SW/NE 锯齿状、舒缓波状、波状、缓波状 张(扭)性、压扭性、扭性 碎裂岩、碎粉岩、碎斑岩 Lim、Ga NE 三级 NW30~85 30~60 NW 舒缓波状、缓波状、较平直 压扭性 碎裂岩、碎粒岩、碎斑岩、片理化 Py、Ga、Sp、Cal 四级 NW65~70 42~85 SE 舒缓波状、波状、较平直 压扭性 碎裂岩、碎粒岩、碎斑岩、片理化 Py、Lim、Ga、Sp、Cal EW 三级 EW 80~90 S/N 锯齿状、波状 右行扭(张)性 碎粒岩、碎粉岩 Dol 四级 EW 60~85 S/N 舒缓波状、缓波状 压扭性 碎粉岩 Py、Cal、Dol SN 三级 SN 30~55 E/W 舒缓波状、波状 左行扭性-右行扭性 碎裂岩、碎粒岩、碎斑岩 Dol 四级 SN 60~85 E/W 舒缓波状、波状、平直 左行扭(压)性 碎裂岩、碎粒岩、碎斑岩 Py、Cal 注:Py.黄铁矿;Lim.褐铁矿化;Ga.方铅矿;Sp.闪锌矿;Dol.白云石;Cal.方解石 -
[1] 韩润生, 张艳, 王峰, 等. 滇东北矿集区富锗铅锌矿床成矿机制与隐伏矿定位预测[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019.Han R S, Zhang Y, Wang F, et al. The metallogenic mechanism of the germanium-rich lead-zinc deposit in the northeastern Yunnan ore concentration area and the prediction of concealed deposits[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019(in Chinese). [2] 王则江, 汪岸儒. 四川天宝山、大梁子铅锌矿床古岩溶洞穴沉积成因研究[J]. 地质与勘探, 1985, 10(2): 10-17.Wang Z J, Wang A R. Study on the depositional genesis of ancient karst caves in the Tianbaoshan and Daliangzi lead-zinc deposits in Sichuan[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 1985, 10(2): 10-17(in Chinese with English abstract). [3] 王小春. 四川大梁子铅锌矿床的成因分析[J]. 矿产与地质, 1991, 3(1): 151-156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD199103001.htmWang X C. Genetic analysis of the Daliangzi lead-zinc deposit in Sichuan[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 1991, 3(1): 151-156(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD199103001.htm [4] Zheng M H, Wang X C. Ore genesis of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit in Sichuan, China[J]. Economic Geology, 1991, 86(4): 831-846. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.86.4.831 [5] 胡建中. 会东大梁子铅锌银矿床成矿构造及成矿模式新认识[J]. 四川地质学报, 1993, 1(8): 40-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCDB199301008.htmHu J Z. A new understanding of the metallogenic structure and metallogenic model of the Dalangzi lead-zinc-silver deposit in Huidong[J]. Acta Geology of Sichuan, 1993, 1(8): 40-68(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCDB199301008.htm [6] 朱赖民. 大梁子铅锌矿床成矿过程分析[J]. 西南矿产地质, 1997, 11(1): 35-38.Zhu L M. Analysis on the metallogenic process of the Dalangzi lead-zinc deposit[J]. Mineral Geology of Southwest China, 1997, 11(1): 35-38(in Chinese with English abstract). [7] 蒋济兵, 刘兴林. 会东大梁子铅锌矿矿床成因探讨[J]. 矿业研究与发展, 1999, 19(9): 36-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYK1999S2009.htmJiang J B, Liu X L. Discussion on the genesis of the Daliangzi lead-zinc deposit in Huidong[J]. Mining Research and Development, 1999, 19(9): 36-37(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYK1999S2009.htm [8] 林方成. 四川会东大梁子铅锌矿床成因新探[J]. 矿床地质, 1994, 2(3): 126-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ402.003.htmLin F C. A new exploration of the genesis of the Daliangzi lead-zinc deposit in Huidong, Sichuan[J]. Mineral Deposits, 1994, 2(3): 126-136(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ402.003.htm [9] 李发源, 顾雪祥, 付绍洪, 等. MVT铅锌矿床定年方法评述[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2003, 3(4): 163-167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK200303004.htmLi F Y, Gu X X, Fu S H, et al. A review of dating methods for MVT lead-zinc deposits[J]. Contributions to Geological Prospecting, 2003, 3(4): 163-167(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK200303004.htm [10] 李泽琴, 王奖臻, 倪师军, 等. 川滇密西西比河谷型铅锌矿床成矿流体来源研究: 流体Na-Cl-Br体系的证据[J]. 矿物岩石, 2002, 22(4): 38-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS200204007.htmLi Z Q, Wang J Z, Ni S J, et al. Study on the source of ore-forming fluids from the Mississippi valley-type lead-zinc deposits in Sichuan and Yunnan: Evidence from the fluid Na-Cl-Br system[J]. Mineral Petrology, 2002, 22(4): 38-41(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS200204007.htm [11] 王奖臻, 李朝阳, 李泽琴, 等. 川滇地区密西西比河谷型铅锌矿床成矿地质背景及成因探讨[J]. 地质地球化学, 2001, 29(2): 41-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ200102006.htmWang J Z, Li C Y, Li Z Q, et al. Discussion on the metallogenic geological background and genesis of the Mississippi valley-type lead-zinc deposits in the Sichuan-Yunnan area[J]. Geology and Geochemistry, 2001, 29(2): 41-45(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ200102006.htm [12] 王乾, 顾雪祥, 付绍洪, 等. 四川大梁子铅锌矿床闪锌矿中镉富集规律及其意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2006, 25(3): 291-292. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200603013.htmWang Q, Gu X X, Fu S H, et al. Enrichment of cadmium in sphalerite in Daliangzi lead-zinc deposit, Sichuan and its significance[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2006, 25(3): 291-292(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200603013.htm [13] 张长青, 毛景文, 袁波, 等. 四川省会东县大梁子铅锌矿控矿因素研究及矿体定位预测项目研究报告[R]. 北京: 中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所, 2014.Zhang C Q, Mao J W, Yuan B, et al. Research report on ore-controlling factors and ore body positioning prediction project of the Daliangzi lead-zinc deposit in Huidong County, Sichuan Province[R]. Beijing: Institute of Mineral Resources, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2014(in Chinese). [14] 武俊婷, 李国猛, 李义邦, 等. 川滇黔接壤区MVT铅锌矿床年代学研究进展及成矿构造背景[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(4): 134-144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201904014.htmWu J T, Li G M, Li Y B, et al. Progress in chronology research and metallogenic tectonic background of MVT lead-zinc deposits in the contiguous area of Sichuan, Yunnan and Guizhou[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(4): 134-144(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201904014.htm [15] 黄智龙, 陈进, 韩润生, 等. 云南会泽超大型铅锌矿床地球化学及成因: 兼论峨眉山玄武岩与铅锌成矿的关系[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2004.Hang Z L, Chen J, Han R S, et al. Geochemistry and genesis of the Huize super-large lead-zinc deposit in Yunnan: A discussion on the relationship between the Emeishan basalt and lead-zinc mineralization[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2004(in Chinese). [16] 孔志岗, 吴越, 张锋, 等. 川滇黔地区典型铅锌矿床成矿物质来源分析: 来自S-Pb同位素证据[J]. 地学前缘, 2018, 25(1): 125-137. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201801011.htmKong Z G, Wu Y, Zhang F, et al. Analysis of the source of minerals from typical lead-zinc deposits in Sichuan, Yunnan and Guizhou: Evidence from S-Pb isotope[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2018, 25(1): 125-137(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201801011.htm [17] 孙家骢, 韩润生. 矿田地质力学理论与方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016.Song J C, Han R S. Theory and methods of mine geomechanics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016(in Chinese). [18] 吴建标, 韩润生, 冯志兴, 等. 川西南大梁子铅锌矿区F15主控断裂及其控矿作用机制[J/OL]. 地质通报: (2021-4-21)[2022-05-19]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.4648.P.20210421.1319.002.html.Wu J B, Han R S, Feng Z X, et al. The F15 main-controlling fault and its ore-controlling mechanism in the Daliangzi lead-zinc mining area in southwestern Sichuan[J/OL]. Geological Bulletin: (2021-4-21)[2022-05-19]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.4648.P.20210421.1319.002.html (in Chinese with English abstract). [19] 刘彦良, 高雅, 魏金栋. 甘肃省车路沟北金矿找矿方向探讨: 来自阿尔金断裂带东段"金三角"金矿控矿因素对比研究的启迪[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 198-209. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0034Liu Y L, Gao Y, Wei J D. Discussion on the prospecting direction of the Chelugou borth gold mine in Gansu Province: Enlightenment from the comparative study on the ore-controlling factors of the "golden triangle" gold mine in the eastern segment of the Altun fault zone[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 198-209(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0034 [20] 汤济广, 汪凯明, 秦德超, 等. 川东南南川地区构造变形与页岩气富集[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 11-21. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0502Tang J G, Wang K M, Qing D C, et al. Structural deformation and shale gas enrichment in Nanchuan area, southeastern Sichuan[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 11-21(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0502 [21] 李萧, 吴礼明, 王丙贤, 等. 渝东南地区龙马溪组构造应力场数值模拟及裂缝有利区预测[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(6): 24-31. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0603Li X, Wu L M, Wang B X, et al. Numerical simulation of tectonic stress field of Longmaxi Formation in southeastern Chongqing and prediction of favorable fracture area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(6): 24-31(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0603 -





 下载:
下载: