Shear strength attenuation law and mechanism of gravel-soil under immersion
-
摘要:
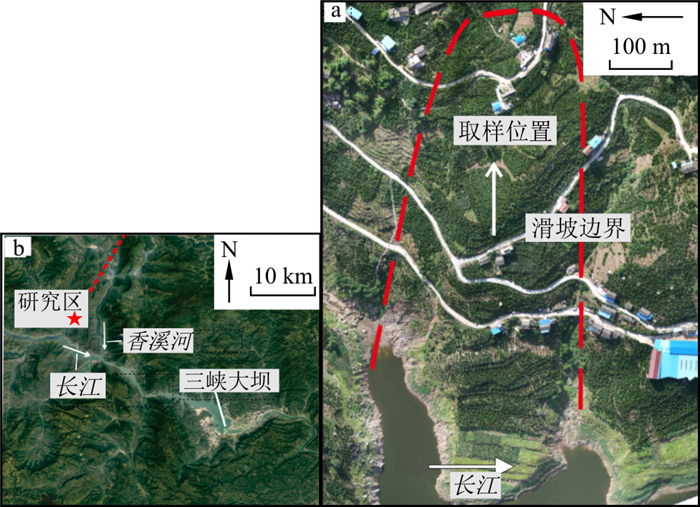
水库蓄水后, 滑坡体碎石土经受长时期的浸泡, 力学性质发生改变, 从而影响滑坡整体稳定性。为探究浸泡对碎石土力学性质的影响规律, 选取三峡库区马家沟滑坡后缘未经受长期浸泡作用的碎石土进行大型直剪试验, 分析了不同浸泡天数下碎石土的剪切力学性质。试验结果表明: 浸泡40 d后, 碎石土黏聚力下降幅度达39%, 内摩擦角下降幅度为8.3%;碎石土黏聚力在浸泡前期快速下降, 下降速率随浸泡天数增加而降低, 浸泡20 d后, 黏聚力基本达到稳定。为探究碎石土抗剪强度降低的原因和机理, 对粉质黏土(碎石土细粒成分)进行了三轴剪切试验、激光粒度分析及浸出液阳离子分析等试验, 揭示了碎石土抗剪强度的衰减机理为: 浸泡作用下, 碎石土中的粉质黏土发生矿物溶解、离子交换与吸附作用, 土体中大颗粒细化, 胶结作用减弱, 进而导致碎石土整体抗剪强度降低。研究结果对库区碎石土滑坡评价与治理具有一定的指导意义。
Abstract:After a reservoir is filled with water, the gravel-soil of a slope is immersed, and the mechanical properties are changed, which affects the stability of the slope. To investigate the influence of immersion on the mechanical properties of gravel-soil, the gravel-soil at the back edge of the slope that has not been immersed was used and large-scale direct shear tests were performed to obtain the shear mechanical properties of gravel-soil after different immersion days. The test results show that after 40 days of immersion, the cohesion of gravel-soil decreases by 39% and the internal friction angle decreases by 8.3%; the cohesion of gravel-soil decreases significantly in the initial stage of immersion and the decay rate decreases with the increasing number of days of immersion.After 20 days of immersion, the cohesion does not decrease significantly with the increase of immersion days. To reveal the reason and mechanisms of shear reduction in gravel-soil, triaxial shear tests, laser particle size analysis and leachate cation analysis were performed on silty clay (fine-grained component of gravel-soil). The results indicate that the shear strength of gravel-soil is attenuated by mineral dissolution, ion exchange and adsorption of the silty clay in gravel-soil. The large particles in the soil are refined, and the cementation is reduced, which reduces the overall shear strength of the gravel-soil. This study has certain significance for the evaluation and management of gravel soil landslides in reservoir areas.
-
表 1 碎石土中粉质黏土的物理性质
Table 1. Physical properties of the fine-grained composition of gravelly soils
天然重度/(g·cm-3) 相对密度 天然含水率/% 塑限/% 液限/% 1.92 2.72 14.2 19.25 30.46 -
[1] 孙一清, 李德营, 殷坤龙, 等. 三峡库区堆积层滑坡间歇性活动预测: 以白水河滑坡为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(5): 195-203. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201905021.htmSun Y Q, Li D Y, Yin K L, et al. Prediction of intermittent activity of mounded landslides in the Three Gorges Reservoir area: An example of the Baishui River landslide[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(5): 195-203(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201905021.htm [2] Huang D, Gu D M, Song Y X, et al. Towards a complete understanding of the triggering mechanism of a large reactivated landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Engineering Geology, 2018, 238: 36-51. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.03.008 [3] Wang J, Su A, Xiang W, et al. New data and interpretations of the shallow and deep deformation of Huangtupo No. 1 riverside sliding mass during seasonal rainfall and water level fluctuation[J]. Landslides, 2016, 13(4): 795-804. doi: 10.1007/s10346-016-0712-8 [4] Hu X, Zhang M, Sun M, et al. Deformation characteristics and failure mode of the Zhujiadian landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2015, 74(1): 1-12. doi: 10.1007/s10064-013-0552-x [5] Tang H, Li C, Hu X, et al. Deformation response of the Huangtupo landslide to rainfall and the changing levels of the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2015, 74(3): 933-942. doi: 10.1007/s10064-014-0671-z [6] He C, Hu X, Xu C, et al. Model test of the influence of cyclic water level fluctuations on a landslide[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2020, 17(1): 191-202. doi: 10.1007/s11629-019-5713-9 [7] 郭子正, 殷坤龙, 唐扬, 等. 库水位下降及降雨作用下麻柳林滑坡稳定性评价与预测[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(4): 260-265. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2017.0435Guo Z Z, Yin K L, Tang Y, et al. Evaluation and prediction of the stability of the Maliulin landslide under the effect of reservoir water level decline and rainfall[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(4): 260-265(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2017.0435 [8] 唐朝晖, 孔涛, 柴波. 降雨作用碎石土堆积层滑坡变形规律[J]. 地质科技情报, 2012, 31(6): 168-173. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201206028.htmTong Z H, Kong T, Chai B. Deformation patterns of landslides on gravel soil accumulations by rainfall[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2012, 31(6): 168-173(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201206028.htm [9] Wen B, Ji B. Variation in residual strength of the large-scale landslides' slip zones in the Three Gorges Reservoir of China[M]. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2019. [10] 唐晓松, 邓楚键, 郑颖人, 等. 三峡库区碎石土地基浸水试验研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2008, 4(2): 226-229. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0836.2008.02.006Tang X S, Deng C K, Zheng Y R, et al. Experimental study on the flooding of gravel foundation in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2008, 4(2): 226-229(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0836.2008.02.006 [11] 汤连生. 水-土化学作用的力学效应及机理分析[J]. 中山大学学报: 自然科学版, 2000, 39(4): 104-109. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0529-6579.2000.04.024Tang L S. Mechanical effects and mechanism analysis of water-soil chemistry[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2000, 39(4): 104-109(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0529-6579.2000.04.024 [12] Venkatarama Reddy B V, Latha M S. Influence of soil grading on the characteristics of cement stabilised soil compacts[J]. Materials and Structures, 2014, 47(10): 1633-1645. doi: 10.1617/s11527-013-0142-1 [13] Ham T, Nakata Y, Orense R P, et al. Influence of gravel on the compression characteristics of decomposed granite soil[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2010, 136(11): 1574-1577. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000370 [14] 唐建一, 徐东升, 刘华北. 含石量对土石混合体剪切特性的影响[J]. 岩土力学, 2018, 39(1): 93-102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201801013.htmTang J Y, Xu D S, Liu H B. Influence of stone content on the shear properties of soil-stone mixtures[J]. Geotechnics, 2018, 39(1): 93-102(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201801013.htm [15] 江强强, 徐杨青, 王浩. 不同含石量条件下土石混合体剪切变形特征的试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2020, 28(5): 951-958. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202005003.htmJiang Q Q, Xu Y Q, Wang H. Experimental study on the shear deformation characteristics of soil-stone mixtures under different stone content conditions[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(5): 951-958(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202005003.htm [16] 邓华锋, 原先凡, 李建林, 等. 土石混合体直剪试验的破坏特征及抗剪强度取值方法研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2013, 32(增刊2): 4065-4072. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2013S2133.htmDeng H F, Yuan Y F, Li J L, et al. Study on the damage characteristics and shear strength value of soil-rock mixture in direct shear test[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2013, 32(S2): 4065-4072(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2013S2133.htm [17] Ying C, Hu X, Zhou C, et al. Analysis of chemo-mechanical behavior of silty soil under long-term immersion in saline reservoir water[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2020, 80(1): 627. [18] 丛璐. 侏罗系砂泥岩互层岩体流变特性及其对抗滑桩嵌固效果影响研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2018.Cong L. Study on the rheological characteristics of Jurassic sand mudstone interbedded rock and its influence on the effect of anti-slip pile embedment[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2018(in Chinese with English abstract). [19] 薛亚东, 岳磊, 李硕标. 含水率对土石混合体力学特性影响的试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2015, 23(1): 21-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201501005.htmXue Y D, Yue L, Li S B. Experimental study on the effect of water content on the mechanical properties of soil-stone mixtures[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2015, 23(1): 21-29(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201501005.htm [20] 俞隽, 孙洪浩, 郑霄阳. 块石含量对土石混合体剪切力学特性的影响[J]. 南通大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 19(3): 83-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NGZK202003011.htmYu J, Sun H H, Zheng X Y. Effect of lumpy stone content on the shear mechanical properties of soil-stone mixtures[J]. Journal of Nantong University: Natural Science Edition, 2020, 19(3): 83-89(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NGZK202003011.htm [21] 聂良佐. 重塑土物理力学特性试验参数的影响因素分析[J]. 实验技术与管理, 2007, 24(12): 30-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYJL200712011.htmNie L Z. Analysis of the factors influencing the test parameters of physical and mechanical properties of remodeled soils[J]. Experimental Technology and Management, 2007, 24(12): 30-34(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYJL200712011.htm [22] 聂良佐. 原状土结构损伤重塑后强度、变形和渗透性变化机理研究[J]. 岩土工程界, 2008, 11(7): 23-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJS200807029.htmNie L Z. Study on the mechanism of strength, deformation and permeability changes after structural damage remodeling of in-situ soils[J]. Geotechnical Engineering, 2008, 11(7): 23-25(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJS200807029.htm [23] 曹荣国, 范建华, 马中骏, 等. 原状粉质黏土抗剪强度的恢复试验研究[J]. 路基工程, 2016(4): 143-145. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LJGC201604034.htmCao R G, Fan J H, Ma C J, et al. Experimental study on the recovery of shear strength of in-situ powdered clay[J]. Roadbed Engineering, 2016(4): 143-145(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LJGC201604034.htm [24] 中华人民共和国建设部. 土工试验方法标准: GB/T50123-2019[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2019: 22-26.Ministry of Construction of the People's Republic of China. Standard for Shijiazhuang test methods: GB/T50123-2019[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2019: 22-26(in Chinese with English abstract). -





 下载:
下载: