Temperature field and dynamic types of shallow groundwater in the northwest inland basin: A case study of the Jiuquan East Basin
-
摘要: 温度是地下水的固有属性,地下水温度场和动态特征是地下水流系统的外在表现。为揭示地下水开采等人类活动影响下西北内陆盆地浅层地下水温度场特征与地下水流系统的关系,基于多点位、长序列、高精度的地下水温度监测数据,在酒泉东盆地开展了地下水温度场及动态特征研究。结果表明:酒泉东盆地浅层地下水温度9.33~20.77℃不等,平均水温为13.54℃,自地下水补给区至排泄区,沿地下水径流方向,浅层地下水温度逐渐升高;循环深度相近的不同地下水流系统对比表明,浅层地下水温度与地下水动力条件呈负相关,地表水入渗补给大、水动力条件强的水流系统地下水平均温度低,入渗补给小、水动力条件弱的地下水平均温度高;浅层地下水温度动态受自然地下水循环和地下水开采等人类活动共同影响,从山前地下水补给区到中游绿洲区再到下游排泄区,浅部地下水温度动态可划分为4种基本类型,依次分别为河流补给型、水温稳定型、开采相关型、正弦波动型。Abstract: Temperature is an inherent property of groundwater.Groundwater temperature field and dynamic characteristics are objective manifestations of groundwater flow system.Based on multi-point, long series and high precision groundwater temperature monitoring data, the characteristics of shallow groundwater temperature distribution and dynamic type of water temperature in Jiuquan East Basin are studied, in order to reveal the relationship between the characteristics of shallow groundwater temperature field and groundwater flow system under the influence of human activities such as groundwater exploitation in northwest inland basin.The results show that the shallow groundwater temperature ranges from 9.33℃ to 20.77℃, and the average water temperature is 13.54℃.From the recharge area to the discharge area, the shallow groundwater temperature increases gradually along the direction of groundwater runoff, and the average groundwater temperature in January is higher than that in July.The comparison of different groundwater flow systems with similar circulation depth shows that the shallow groundwater temperature is negatively correlated with groundwater dynamic conditions.The average groundwater temperature of the water flow system with large surface water recharge and strong hydrodynamic conditions is lower, and that of the water flow system with small recharge and weak hydrodynamic conditions is higher.The temperature dynamics of shallow groundwater are affected by human activities such as natural groundwater circulation and groundwater exploitation.From groundwater recharge area to oasis area in the middle reaches and drainage area in the lower reaches, the temperature dynamic of shallow groundwater can be divided into four basic types, which are river recharge type, water temperature stability type, groundwater exploitation related type and sinusoidal fluctuation type respectively.
-
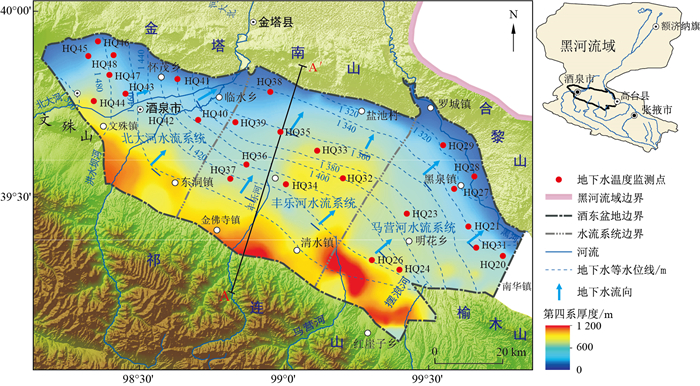
表 1 酒泉东盆地浅层地下水监测点地下水温度统计
Table 1. Groundwater temperature statistics of shallow groundwater monitoring points in Jiuquan East Basin
分区 孔号 孔深/m 水位埋深/m 最高水温 最低水温 水温变幅 1月平均水温 7月平均水温 年均水温 水温/℃ 马营河水流系统 HQ20 60.0 3.42 11.18 10.06 1.12 10.97 10.08 10.52 HQ21 120.0 10.40 12.20 11.36 0.84 12.32 11.33 11.55 HQ23 178.0 2.42 16.03 15.55 0.48 15.97 15.72 15.90 HQ24 263.6 123.10 16.25 16.08 0.17 16.24 16.20 16.20 HQ26 335.6 113.56 14.90 14.83 0.07 14.89 14.88 14.87 HQ27 61.8 5.10 15.54 13.83 1.71 15.51 13.82 14.90 HQ28 34.2 4.15 15.70 12.70 3.00 13.42 13.71 13.49 HQ29 24.2 5.21 16.28 13.18 3.10 15.55 13.70 14.68 HQ31 120.0 21.63 11.88 11.77 0.11 11.85 11.87 11.82 平均值 1.18 14.08 13.48 13.77 丰乐河水流系统 HQ32 112.0 10.99 15.26 14.50 0.77 15.13 15.12 15.00 HQ33 138.0 2.01 18.50 18.00 0.50 18.14 18.39 18.24 HQ34 79.0 28.92 13.45 12.78 0.67 14.14 12.86 13.25 HQ35 106.0 2.79 22.39 19.45 2.94 20.00 22.30 20.77 HQ36 86.0 30.35 14.90 13.82 1.08 14.52 14.00 14.73 HQ37 144.0 46.31 13.74 13.59 0.15 13.68 13.73 13.69 HQ38 85.6 3.09 16.40 16.28 0.12 16.28 16.32 16.36 HQ39 134.0 3.83 17.28 12.12 5.16 16.82 13.38 15.55 平均值 1.42 16.09 15.76 15.95 北大河水流系统 HQ40 74.0 6.54 14.00 10.95 3.05 12.47 12.68 12.63 HQ41 113.0 1.97 10.58 9.64 0.94 9.68 9.95 9.77 HQ42 120.0 30.46 10.75 10.49 0.26 10.65 10.64 10.69 HQ43 233.0 19.84 10.31 10.01 0.30 10.23 10.19 10.04 HQ44 240.0 108.16 9.49 9.13 0.36 9.35 9.34 9.33 HQ45 118.0 60.36 12.20 11.75 0.45 12.02 11.88 11.89 HQ46 110.0 17.19 13.05 12.79 0.26 12.94 13.02 12.98 HQ47 239.0 48.57 11.01 10.84 0.17 10.96 10.99 10.96 HQ48 130.2 16.24 12.35 11.99 0.36 12.24 12.30 12.28 平均值 0.68 11.17 11.22 11.17 酒泉东盆地平均值 1.08 13.69 13.40 13.54 -
[1] 张人权, 梁杏, 靳孟贵, 等. 水文地质学基础[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2018.Zhang R Q, Liang X, Jin M G, et al. Fundamentals of hydrogeology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2018(in Chinese). [2] 林学钰, 方燕娜, 廖资生, 等. 全球气候变暖和人类活动对地下水温度的影响[J]. 北京师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2009, 45(增刊1): 452-457. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BSDZ2009Z1004.htmLin X Y, Fang Y N, Liao Z S, et al. Impact of global warming and human activities on groundwater temperature[J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University : Natural Science Edition, 2009, 45(S1): 452-457(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BSDZ2009Z1004.htm [3] 连英立, 张光辉, 聂振龙, 等. 西北内陆张掖盆地地下水温度变化特征及其指示意义[J]. 地球学报, 2011, 32(2): 195-203. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2011.02.08Lian Y L, Zhang G H, Nie Z L, et al. Groundwater temperature variation in the Zhangye inland Basin of Northwest China and its indications[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2011, 32(2): 195-203(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2011.02.08 [4] 吴志伟, 宋汉周. 地下水温度示踪理论与方法研究进展[J]. 水科学进展, 2011, 22(5): 733-740. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKXJ201105023.htmWu Z W, Song H Z. Temperature as a groundwater tracer: Advances in theory and methodology[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2011, 22(5): 733-740(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKXJ201105023.htm [5] Bredehoeft J D, Papaopulos I S. Rates of vertical groundwater movement estimated from the Earth's thermal profile[J]. Water Resources Research, 1965, 1(2): 325-328. doi: 10.1029/WR001i002p00325 [6] Bodvarsson G S, Kwicklis E, Shan C, et al. Estimation of percolation flux from borehole temperature data at Yucca Mountain, Nevada[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2003, 62: 3-22. [7] Makoto T, Jun S, Takeshi U. Transient effects of surface temperature and groundwater flow on subsurface temperature in Kumamoto Plain, Japan[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 2003, 28(9): 477-486. [8] Fairley J P, Nicholson K N. Imaging lateral groundwater flow in the shallow subsurface using stochastic temperature fields[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2005, 321(1): 276-285. [9] 张发旺, 王贵玲, 侯新伟, 等. 地下水循环对围岩温度场的影响及地热资源形成分析: 以平顶山矿区为例[J]. 地球学报, 2000, 21(2): 142-146. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2000.02.006Zhang F W, Wang G L, Hou X W, et al. An analysis of the formation of geothermal resources and the effects of groundwater circulation on the wall rock temperature field: Taking the Pingdingshan Mining Field as an example[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2000, 21(2): 142-146(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2000.02.006 [10] 尹立河. 鄂尔多斯盆地白垩系地下水循环与温度场数值模拟[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2007.Yin L H. Groundwater circulation and heat simulation study in the Cretaceous Basin, the Ordos Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2007(in Chinese with English abstract). [11] 陈植华, 孙璐, 龚星. 马坑铁矿疏干条件下地下水温度场特征及其指示意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2012, 31(5): 136-142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201205019.htmChen Z H, Sun L, Gong X. Characteristics of groundwater temperature field and its indicative significance under drainage condition of Makeng Iron Mine[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2012, 31(5): 136-142(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201205019.htm [12] An R, Jiang X W, Wang J Z, et al. A theoretical analysis of basin-scale groundwater temperature distribution[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2015, 23(2): 397-404. doi: 10.1007/s10040-014-1197-y [13] 马瑞, 董启明, 孙自永, 等. 地表水与地下水相互作用的温度示踪与模拟研究进展[J]. 地质科技情报, 2013, 32(2): 131-137. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201302018.htmMa R, Dong Q M, Sun Z Y, et al. Using heat to trace and model the surface water-groundwater interactions: A review[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2013, 32(2): 131-137(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201302018.htm [14] 徐连三, 华杉, 刘红卫, 等. 地下水源热泵运行期间地下水流场和温度场的变化规律研究[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2020, 34(4): 609-614. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK202004025.htmXu L S, Hua S, Liu H W, et al. Research on variation laws of groundwater flow field and temperature field during operation of groundwater source heat pump[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2020, 34(4): 609-614(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK202004025.htm [15] 董海洲, 陈建生. 利用孔中温度场分布确定堤坝渗透流速的热源法模型研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2003, 30(5): 40-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2003.05.009Dong H Z, Chen J S. Model research of heat source method by using water temperature distribution in borehole to determine seepage velocity of dyke[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2003, 30(5): 40-43(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2003.05.009 [16] 李奋其. 酒泉盆地形成机制与演化[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2004.Li F Q. Formative mechanics and evolvement of Jiuquan Basin[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2004(in Chinese with English abstract). [17] 任晓辉. 酒泉东盆地地下水水化学特征及演化机理研究[D]. 济南: 山东科技大学, 2020.Ren X H. Study on hydrochemical characteristics and evolution mechanisms of groundwater in the Jiuquan East Basin[D]. Jinan: Shandong University of Science and Technology, 2020(in Chinese with English abstract). [18] 梁杏, 张婧玮, 蓝坤, 等. 江汉平原地下水化学特征及水流系统分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 21-33. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0103Liang X, Zhang J W, Lan K, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater and analysis of groundwater flow systems in Jianghan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 21-33(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0103 [19] 江欣悦, 李静, 郭林, 等. 豫北平原浅层地下水化学特征与成因机制[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 290-300. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0511Jiang X Y, Li J, Guo L, et al. Chemical characteristics and formation mechanism of shallow groundwater in the northern Henan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 290-300(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0511 [20] 李文鹏, 郝爱兵. 中国西北内陆干旱盆地地下水形成演化模式及其意义[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 1999, 26(4): 30-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG904.008.htmLi W P, Hao A B. Groundwater formation and evolution model and its significance in arid inland basins of Northwest China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 1999, 26(4): 30-34(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG904.008.htm [21] 张光辉, 聂振龙, 王金哲, 等. 黑河流域水循环过程中地下水同位素特征及补给效应[J]. 地球科学进展, 2005, 20(5): 511-519. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2005.05.005Zhang G H, Nie Z L, Wang J Z, et al. Isotopic characteristic and recharge effect of groundwater in the water circulation of Heihe River basin[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2005, 20(5): 511-519(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2005.05.005 [22] 聂振龙, 陈宗宇, 程旭学, 等. 黑河干流浅层地下水与地表水相互转化的水化学特征[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2005, 35(1): 48-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ20050100A.htmNie Z L, Chen Z Y, Cheng X X et al. The chemical information of the interaction of unconfined groundwater and surface water along the Heihe River, northwestern China[J]. Joumal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2005, 35(1): 48-53(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ20050100A.htm [23] 聂振龙. 黑河干流中游盆地地下水循环及更新性研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2005.Nie Z L. Study on groundwater circulation and renewability in the middle reaches of Heihe River valley, Northwest China[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2005(in Chinese with English abstract). [24] 陈宗宇, 万力, 聂振龙, 等. 利用稳定同位素识别黑河流域地下水的补给来源[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2006, 33(6): 9-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2006.06.003Chen Z Y, Wan L, Nie Z L, et al. Identification of groundwater recharge in the Heihe Basin using environmental isotopes[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2006, 33(6): 9-14(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2006.06.003 [25] 王文祥, 李文鹏, 蔡月梅, 等. 黑河流域中游盆地水文地球化学演化规律研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(4): 184-193. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202104025.htmWang W X, Li W P, Cai Y M, et al. The hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in the middle reaches of the Heihe River basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(4): 184-193(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202104025.htm [26] 王贵玲, 刘峰, 王婉丽. 我国陆区浅层地温场空间分布规律研究(一)[J]. 供热制冷, 2015, 16(2): 52-54.Wang G L, Liu F, Wang W L. Spatial distribution and law of shallow geothermal in continental China(PART Ⅰ)[J]. Heating & Refrigeration, 2015, 16(2): 52-54(in Chinese). [27] Luhmann A J, Covington M D, Peters A J, et al. Classification of thermal patterns at karst springs and cave streams[J]. Groundwater, 2011, 49(3): 324-335. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2010.00737.x -





 下载:
下载: