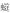Prediction and discrimination of the Middle Carboniferous inner platform shoal distribution at the eastern margin of Pre-Caspian Basin: Taking the North Truwa slope area as an example
-
摘要: 滨里海盆地东缘中石炭统KT-Ⅱ油组广泛发育开阔台地相的台内滩,台地内沉积环境开阔且稳定,地势平坦,台内滩往往呈孤立状漂浮在台地内的微地貌高地,故其分布规律难以预测。钻探实践表明,台内滩相是后期发生建设性成岩改造作用的基础,亦是形成优质储层的主控因素,对其分布进行预测至关重要。为了提高滩体预测准确率,立足于区域沉积演化分析,并逐步开展三维地震属性分析及高分辨率反演,充分结合地震资料的预测性和地质认识的规律性,通过总结相带地质规律对地震储层预测进行补充和甄别,做到地质和地球物理认识上的统一。研究结果表明,地震属性趋势控制下的统计学反演可以较准确地刻画小层级别的薄层滩体空间分布特征。结合沉积规律对预测滩体进行了筛选和分类,其中一类滩体7个,二类滩体4个,三类滩体3个,一类、二类滩体已有钻井证实,符合沉积规律,三类滩体与地质认识相悖,予以筛除。研究成果建立了该区隐蔽型滩体预测的完整技术体系,而且已见到实效,目前针对一类滩体的钻探成功率高达100%。Abstract: The Middle Carboniferous KT-Ⅱoil formation in the eastern margin of the Pre-Caspian Basin is widely developed with open platform facies intra platform beach.The sedimentary environment is open and stable, and the terrain is flat.The intra platform beach often floats in isolated micro geomorphic Highlands in the platform, so its distribution is often difficult to predict.Drilling practice shows that the beach facies in the platform is the basis of constructive diagenesis in the later stage, and it is also the main controlling factor for the formation of high-quality reservoir, so it is very important to predict its distribution.In order to improve the accuracy of beach prediction, based on the analysis of regional sedimentary evolution, and gradually carry out three-dimensional seismic attribute analysis and high-resolution inversion, fully combined with the predictability of seismic data and the regularity of geological knowledge, through summing up the geological law of facies belt, the seismic reservoir prediction is supplemented and screened, so as to achieve the unity of geological and geophysical knowledge.The results show that the statistical inversion under the control of seismic attribute trend can accurately describe the spatial distribution characteristics of thin beach body at the level of small layer.According to the sedimentary law, the predicted beach bodies are screened and classified.Among them, there are 7 first-class beach bodies, 4 second-class beach bodies and 3 third-class beach bodies.The first- and second- class beach bodies have been confirmed by drilling, which are consistent with the sedimentary law.The third-class beach bodies are contrary to the geological understanding and should be screened out.The research results have established a complete technical system for the prediction of concealed beach bodies in this area, and have seen actual results.At present, the success rate of drilling for a class of beach bodies is as high as 100%.
-
图 2 北特鲁瓦KT-Ⅱ层主要岩石类型
a.亮晶有孔虫灰岩,b22井,3 151 m,绿藻、有孔虫分布欠均匀,见生物扰动构造,孔隙以粒间溶孔为主,次为体腔孔;b.亮晶藻骨架灰岩,b4井,3 185.5 m,颗粒以大量原地生成的红、绿藻为主,并组成骨架结构,面孔率达23;c.亮晶藻团块灰岩,b4井,3 124.7 m,藻团块粗大,黏结类、有孔虫、腹足类、红藻等碎片,孔隙不发育,面孔率仅4.3%;d. 亮晶包粒灰岩,b22井,3 208 m,颗粒以藻包粒为主,另见少量红藻,包粒粗大,大部分粒径达粗至砾级,孔隙不发育;e.泥晶生屑灰岩,b4井,3 094 m,生物以有孔虫碎片为主,保存很差,含少量尖角状的陆源石英和鞍山岩喷出岩岩屑;f.泥晶泥灰岩,b4井,3 134 m,结构极细的泥灰质中含少量生屑,破碎极强,富含黏土质,含分散或聚集的黄铁矿较多,并有氧化作用
Figure 2. Main rock types of KT-Ⅱ layer in North Truwa
图 5 KT-Ⅱ段沉积微相剖面对比图(剖面分布位置见图 4-a)
Figure 5. Section comparison of sedimentary microfacies in KT -Ⅱlayer
-
[1] Bagrintseva K I. Carbonate reservoir rocks[M]. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2015. [2] Alotaibi M B, Azmy R, Nasr-El-Din H A. Wettability challenges in carbonate reservoirs[R]. SPE, 2010. [3] 穆龙新, 陈亚强, 许安著, 等. 中国石油海外油气田开发技术进展与发展方向[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(1): 120-128. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202001012.htmMu L X, Chen Y Q, Xu A Z, et al. Development technology progress and development direction of overseas oil and gas fields of PetroChina[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(1): 120-128(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202001012.htm [4] Moore C H, Wade W J. Carbonate reservoirs: Porosity and diagenesis in a sequence stratigraphic framework[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2013. [5] 何伶, 赵伦, 李建新, 等. 碳酸盐岩储集层复杂孔渗关系及影响因素: 以滨里海盆地台地相为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(2): 206-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201402012.htmHe L, Zhao L, Li J X, et al. Complex relationship between porosity and permeability of carbonate reservoirs and itscontrolling factors: A case of platform facies in Pre-Caspian Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(2): 206-214(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201402012.htm [6] 左智峰, 熊鹰, 何为, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中部马五段盐下储层成岩作用与孔隙演化[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(5): 155-164. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201905016.htmZuo Z F, Xiong Y, He W, et al. Diagenesis and porosity evolution of the subsalt member 5 of Majiagou Formation reservoir in the Central Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(5): 155-164(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201905016.htm [7] 武鑫, 王艺霖, 黄敬军, 等. 徐州地区碳酸盐岩溶蚀特征及影响因素分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3): 120-126. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903011.htmWu X, Wang Y L, Huang J J, et al. Dissolution characteristics of carbonate and analysis of the key influence factors in Xuzhou Region[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(3): 120-126(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903011.htm [8] Saini S, Jackson N L, Nordstrom K F. Depth of activation on a mixed sediment beach[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2009, 56(7): 788-791. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2009.02.002 [9] Esrafili D B, Rahimpour B H. Effects of depositional and diagenetic characteristics on carbonate reservoir quality: A case study from the South Pars gas filed in the Persian Gulf[J]. Petroleum Geoscience, 2009, 15(4): 325-344. doi: 10.1144/1354-079309-817 [10] Marsters T H, Kennedy D M. Beach development on an uplifted coral atoll: niue, Southwest Pacific[J]. Geomorphopogy, 2014, 222: 82-91. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2014.03.003 [11] 杨峰, 聂辉, 陈洪涛, 等. 宽频地震数据碳酸盐岩叠前储层预测: 以滨里海盆地东缘B区块为例[J]. 石油物探, 2019, 58(4): 555-562. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2019.04.010Yang F, Nie H, Chen H T, et al. Carbonate reservoir prediction with broadband seismic data: A case study from the East Block B of Pre-Caspian Basin[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2019, 58(4): 555-562(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2019.04.010 [12] 热合麦提·亚尔麦麦提, 李来运, 李加成, 等. 用叠前多参数测井约束反演预测碳酸盐岩储集层: 以哈萨克斯坦希望油田为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2012, 33(1): 130-132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201201039.htmRehemaiti Y, Li L Y, Li J C, et al. Carbonate reservoir prediction using pre-stack multi parameter logging constraint inversion: An example from Hope oilfield in Kazakhstan[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2012, 33(1): 130-132(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201201039.htm [13] 李来运, 贺金胜. 哈萨克斯坦A油田盐下多参数储层预测技术[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2009, 44(1) : 90-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDQ2009S1023.htmLi L Y, He J S. Multi parameter reservoir prediction technology under salt in a oilfield of Kazakhstan[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2009, 44(1) : 90-97(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDQ2009S1023.htm [14] 张宝露, 张敏, 李维锋, 等. 滨里海盆地北特鲁瓦油田上石炭统碳酸盐岩沉积相研究与有利储层预测[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2015, 15(12): 34-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2015.12.005Zhang B L, Zhang M, Li W F, et al. The research of sedimentary facies and prediction of favorable of the upper Carboniferous in North Tluwa Oilfield, Pre-Caspain Basin[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2015, 15(12): 34-42(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2015.12.005 [15] 刘洛夫, 朱毅秀, 胡爱梅, 等. 滨里海盆地盐下层系的油气地质特征[J]. 西南石油学院学报: 自然科学版, 2002, 24(3): 11-15. doi: 10.3863/j.issn.1674-5086.2002.03.004Liu L F, Zhu Y X, Hu A M, et al. Petroleum geology of pre-salt sediments in the Pre-Caspain Basin[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University: Science & Technology Edition, 2002, 24(3): 11-15 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3863/j.issn.1674-5086.2002.03.004 [16] 金树堂, 郑俊章, 于炳松. 滨里海盆地东缘晚古生代层序地层与沉积相[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2015.Jin S T, Zheng J Z, Yu B S. Late Paleozoic sequence stratigraphy and sedimentary facies in the eastern margin of the Pre-Caspian Basin[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2015(in Chinese). [17] 金振奎, 邵冠铭. 石灰岩分类新方案[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2014, 35(2): 235-242. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201402023.htmJin Z K, Shao G M. New classification scheme of limestones[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2014, 35(2): 235-242(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201402023.htm [18] 梁爽, 郑俊章, 张玉攀. 滨里海盆地东南缘晚古生代碳酸盐岩台地特征及控制因素[J]. 地质科技情报, 2013, 32(3): 52-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201303009.htmLiang S, Zheng J Z, Zhang Y P. Characteristics and controlling factors of Late Paleozoic carbonate platform in the southeast part of Pre-Caspian Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2013, 32(3): 52-58(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201303009.htm [19] 沙庆安. 关于滩相沉积[J]. 古地理学报, 1999, 1(3): 8-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX199903001.htmSha Q A. On the beach facies deposition[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography(Chinese Edition), 1999, 1(3): 8-12(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX199903001.htm [20] Saini S, Jackson N L, Nordstrom K F. Depth of activation on a mixed sediment beach[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2009, 56(7): 788-791. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2009.02.002 [21] Marsters T H, Kennedy D M. Beach development on an uplifted coral atoll: Nine, Southwest Pacific[J]. Geomorphology, 2014, 222: 82-91. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000036185756910_1ddd.html [22] 顾家裕, 马锋, 季丽丹. 碳酸盐岩台地类型、特征及主控因素[J]. 古地理学报, 2009, 11(1): 21-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX200901006.htmGu J Y, Ma F, Ji L D. Types, characteristics and main controlling factors of carbonate platform[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography(Chinese Edition), 2009, 11(1): 21-27(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX200901006.htm [23] Esrafili D B, Rahimpour B H. Effects of depositional and diagenetic characteristics on carbonate reservoir quality: A case study from the South Pars gas field in the Persian Gulf[J]. Petroleum Geoscience, 2009, 15 (4): 325-344. [24] 张敏, 尹成明, 寿建峰, 等. 柴达木盆地西部地区古近系及新近系碳酸盐岩沉积相[J]. 古地理学报, 2004, 6(4): 391-400. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX200404001.htmZhang M, Yin C M, Shou J F, et al. Sedimentary facies of Paleogene and Neogene carbonate rocks in western Qaidam Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography(Chinese Edition), 2004, 6(4): 391-400(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX200404001.htm [25] 董运青. 碳酸盐岩微相研究现状与发展展望[J]. 科技视界, 2012 (22): 70-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJSJ201222028.htmDong Y Q. The present situation and development prospect of carbonate microfacies[J]. Science and Technology Vision, 2012 (22): 70-72(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJSJ201222028.htm [26] 王锋, 姜在兴, 周丽清, 等. 阿曼Daleel油田下白垩统Shuaiba组上段碳酸盐岩沉积相模式[J]. 沉积学报, 2007, 25(2): 192-200. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200702004.htmWang F, Jiang Z X, Zhou L Q, et al. Sedimentary facies model on carbonate rock in the upper Shuaiba member of Lower Cretaceous in Daleel Field, Oman[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2007, 25(2): 192-200(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200702004.htm [27] 金振奎, 石良, 高白水. 碳酸盐岩沉积相及相模式[J]. 沉积学报, 2013, 31(6): 965-979. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201306003.htmJin Z K, Shi L, Gao B S. Carbonate facies and facies models[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2013, 31(6): 965-979(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201306003.htm [28] 尹硕, 黄文辉, 金振奎, 等. 滨里海盆地东缘石炭系KT-Ⅱ层碳酸盐岩微相特征与沉积环境研究: 以扎纳若尔地区为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2017, 35(1): 139-149. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201701014.htmYin S, Huang W H, Jin Z K, et al. Characteristics of carbonate microfacies and sedimentary environment of the east margin of Caspian Basin in the Carboniferous KT-Ⅱlayer: A case from Zanazor area[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2017, 35(1): 139-149(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201701014.htm [29] 沈安江, 佘敏, 胡安平, 等. 海相碳酸盐岩埋藏溶孔规模与分布规律初探[J]. 天然气地质学, 2015, 26(10): 1823-1829. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201510002.htmShen A J, She M, Hu A P, et al. Scale and distribution of marine carbonate burial dissolutional pores[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2015, 26(10): 1823-1829(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201510002.htm [30] Per Avseth, Tapan Mukerji, Gary Mavko. 定量地震解释[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2009. [51] Per A, Tapan M, Gary M. Quantitative seismic interpretation[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2009 (in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: