Microstructure characteristics and genetic analysis of tight reservoirs with different provenance systems: A case study of Fanjiachuan and Nanliang region of Chang 6 reservoir in Longdong area, Ordos Basin
-
摘要:
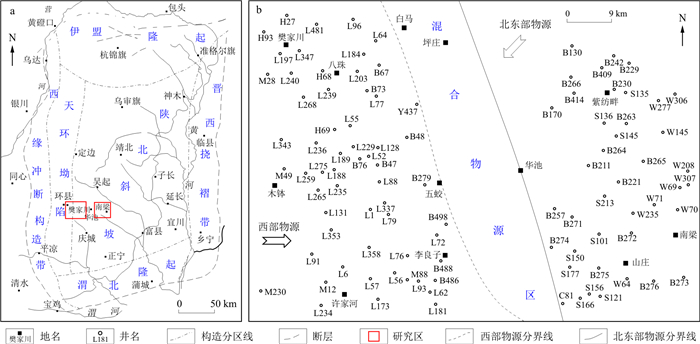
鄂尔多斯盆地致密油气资源丰富,其中陇东地区长6储层的发育受多物源体系的控制,成为当前研究热点,但目前对不同物源控制的砂体微观结构特征差异等缺乏深入了解,制约了该地长6储层的勘探与评价。通过铸体薄片鉴定、镜下观察、X衍射及恒速压汞分析等实验手段,开展了不同物源体系控制下的储层微观结构特征研究,对比分析了沉积微相对储层发育的影响,建立了对应的孔隙演化模型,并探讨了主要成岩作用对储层致密化的控制。结果表明:①喉道是控制储层渗透率的主要因素,北东部物源沉积区较西部物源沉积区的喉道发育状况更好,渗透率更高;②随着渗透率升高,受北东部物源控制的南梁地区半径大于0.50 μm的较大喉道对渗透率的贡献明显增加;③沉积微相是控制不同物源体系砂体物性的重要因素,受北东部物源控制的南梁地区的砂质碎屑流和浊流砂体物性均好于受西部物源控制的樊家川地区;压实作用是造成储层致密化的主要原因,受不同物源体系储层伊利石和绿泥石含量差异的影响,北东部物源沉积区压实减孔量(19.29%)小于西部物源沉积区(22.32%)。该研究成果对不同物源体系致密油的后期评价具有指导意义。
Abstract:Ordos Basin is rich in tight oil and gas resources.The multi-source system controls the development of Chang 6 reservoir in Longdong area. However, the current study on the microstructural characteristics of sand bodies is weak, which has restricted the exploration and evaluation of Chang 6 reservoir in this area. In this study, we used microstructural analysis by thin sections, X-ray diffraction and constant-speed mercury intrusion analysis to identify the microstructure characteristics of reservoirs, and to compare the influence of sedimentary microstructures on reservoir development. Based on these information, we establish corresponding pore evolution models, and discuss the control mechanisms of main diagenesis on reservoir densification. Our results can concluded as followed.①Throats are the main factor to control the permeability of the reservoir. The northeast provenance area shows better throat development and higher permeability than the western provenance area; ②As the permeability increases, the contribution of large throats to the permeability increases significantly in Nanliang area; ③Sedimentary microfacies can be important factors to control the physical properties of sand bodies in different provenance systems. The physical properties of sandy clastic flow and turbidity current sand bodies are better in Nanliang area than those in Fanjiachuan area.Compaction can be the major reason for reservoir densification.Affected by the content difference of illite and chlorite in reservoirs of different provenance systems, the amount of compaction reduction in the northeast provenance deposition area (19.29%) is less than that in the western provenance deposition area (22.32%).The new results have guiding significance to evaluate the late evaluation of tight oil from different provenance systems.
-
图 3 鄂尔多斯盆地樊家川和南梁地区长6致密储层孔喉类型
a.粒间孔及片状、管束状喉道,B269井,1 861.0 m,铸体薄片;b.粒间孔,W66井,1 799.8 m,SEM;c.岩屑溶孔,L434井,2 286.1 m,铸体薄片;d.粒内溶孔,W63井,1 991.2 m,SEM;e.少量碎屑发生伊利石蚀变,晶间孔隙发育,B269井,1 934.2 m,SEM;f.晶间孔,B240井,2 164.2 m,SEM;g.晶间孔,W66井,1 812.6 m,SEM;h.微裂隙,L368井,2 245.2 m,铸体薄片;i.微裂隙,L58井,2 121.9 m
Figure 3. Pore throat types of Chang 6 tight reservoir in Fanjiachuan and Nanliang area, Ordos Basin
图 9 鄂尔多斯盆地樊家川和南梁地区长6重力流沉积构造特征
a.鲍马序列BD段,L312井,2 035.6 m;b.鲍马序列DE段,S157井,1 902.9 m;c.沟模,L312井,2 053.0 m;d.泥火焰构造,L330井,2 134.6 m;e.块状砂岩,砂质碎屑流,C120井,1 926.7 m;f.块状砂岩,砂质碎屑流,C80井,1 978.5 m;g.块状砂岩含黑色泥岩漂砾,B269井,1 869.9 m;h.块状砂岩含黑色泥岩漂砾,W62井,1 798.0 m
Figure 9. Structure characteristics of gravity flow sedimentary of Chang 6 reservoir in Fanjiachuan and Nanliang area, Ordos Basin
图 13 鄂尔多斯盆地樊家川和南梁地区长6储层成岩作用特征
a.千枚岩岩屑受压充填孔隙,L434井,2 294.0 m,铸体薄片;b.黑云母受挤压变形强烈,B275井,2 004.5 m,铸体薄片;c.伊利石充填孔喉,B278井,1 845.3 m,SEM;d.部分孔隙中充填丝片状伊利石,W66井,1 812.6 m,SEM;e.少量碎屑溶蚀蚀变绿泥石黏土矿物,W64井,1 913.3 m,SEM;f.孔隙衬里绿泥石,B253井,2 063.5 m,SEM;g.钙质胶结,B239井,2 104.9 m,铸体薄片;h.钙质胶结,L54井,1 931.8 m,铸体薄片;i.铁白云石充填孔隙,M80井,2 315.2 m,铸体薄片;j.铁方解石充填孔隙,W65井,1 876.8 m,铸体薄片;k.微孔,见石英加大,L181井,1 892.7 m,铸体薄片;l.自生石英充填孔隙,W66井,1 799.8 m,SEM
Figure 13. Diagenesis characteristics of Chang 6 reservoir in Fanjiachuan and Nanliang area, Ordos Basin
表 1 鄂尔多斯盆地樊家川和南梁地区长6储层储集空间类型
Table 1. Reservoir space type of Chang 6 reservoir in Fanjiachuan and Nanliang area, Ordos Basin
地区 粒间孔/% 粒间溶孔/% 长石溶孔/% 岩屑溶孔/% 晶间孔/% 微裂隙/% 面孔率/% 樊家川 1.06 0.06 0.91 0.13 0.03 0.01 2.20 南梁 1.26 0.03 1.39 0.11 0.03 0.02 2.84 表 2 鄂尔多斯盆地樊家川和南梁地区长6储层样品的恒速压汞孔喉结构参数
Table 2. Constant velocity mercury injection pore throat structure parameters of the samples of Chang 6 reservoir in Fanjiachuan and Nanliang area, Ordos Basin
地区 井号 样品号 孔隙度/% 气测渗透率/10-3 μm2 平均孔隙半径/μm 平均喉道半径/μm 平均孔喉比 进汞饱和度/% 总计 孔隙 喉道 樊家川 L447 1 6.29 0.013 155.53 0.16 1071.30 16.08 6.57 9.51 L330 2 9.36 0.055 167.43 0.29 721.22 53.84 36.06 17.78 B518 3 13.00 0.169 151.47 0.36 488.61 45.13 26.33 18.80 B259 4 12.51 0.290 127.40 0.57 327.05 64.31 47.45 16.86 B480 5 10.05 0.060 128.29 0.34 484.77 44.98 26.73 18.25 B116 6 7.63 0.150 157.70 0.29 654.00 46.40 31.97 14.43 B465 7 8.15 0.120 122.37 0.28 436.42 23.11 7.33 15.78 L87 8 8.59 0.150 140.29 0.41 452.88 37.17 6.13 31.04 平均 9.45 0.126 143.81 0.34 579.53 41.38 23.57 17.81 南梁 W63 1 6.25 0.036 167.67 0.25 747.83 52.58 31.32 21.26 W65 2 9.70 0.080 163.07 0.30 644.51 54.86 40.67 14.19 B275 3 13.16 0.175 164.26 0.44 525.26 62.00 41.43 20.57 S156 4 8.95 0.120 117.43 0.96 127.44 28.88 4.07 24.81 S141 5 11.98 0.110 121.01 0.21 721.12 30.47 16.23 14.24 B518 6 11.28 0.450 131.51 0.99 185.06 67.48 32.63 34.85 B483 7 8.32 0.102 135.20 0.72 236.89 33.74 4.38 29.36 平均 9.95 0.153 142.88 0.55 455.44 47.14 24.39 22.75 表 3 鄂尔多斯盆地樊家川和南梁地区长6储层砂岩填隙物组合及物性特征
Table 3. Sandstone interstitial composition and physical properties of Chang 6 reservoir in Fanjiachuan and Nanliang area, Ordos Basin
地区 主要填隙物wB/% 孔隙特征/% 物性特征 高岭石 伊利石 绿泥石 网状黏土 方解石 铁方解石 铁白云石 硅质 粒间孔 面孔率 孔隙度/% 渗透率/10-3 μm2 樊家川 0.06 7.13 0.72 0.07 0.47 1.29 2.62 1.15 1.06 2.20 9.05 0.17 南梁 0.05 4.16 2.98 0.28 0.26 1.86 1.19 1.14 1.26 2.84 10.77 0.32 -
[1] Fu Q L, Hu S Y, Xu Z H, et al. Depositional and diagenetic controls on deeply buried Cambrian carbonate reservoirs: Longwangmiao Formation in the Moxi-Gaoshiti area, Sichuan Basin, southwestern China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 117: 104318. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104318 [2] 黄延章. 低渗透油层渗流机理[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1998.Huang Y Z. Seepage mechanism of low permeability reservoir[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1998(in Chinese). [3] 杨晓萍, 赵文智. 低渗透储层成因机理及优质储层形成与分布[J]. 石油学报, 2007, 28(4): 57-61. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2007.04.011Yang X P, Zhao W Z. Origin of low-permeability reservoir and distribution of favorable reservoir[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2007, 28(4): 57-61(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2007.04.011 [4] 贺静, 冯胜斌, 黄静, 等. 物源对鄂尔多斯盆地中部延长组长6砂岩孔隙发育的控制作用[J]. 沉积学报, 2011, 29(1): 80-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201101010.htmHe J, Feng S B, Huang J, et al. Effects of provenance on porosity development of Chang 6 sandstone of the Yanchang Formation in the center of Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2011, 29(1): 80-87(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201101010.htm [5] 邵远, 文佳涛, 程文, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地环县地区上三叠统长63物源分析及沉积体系[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2012, 12(33): 8807-8814. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2012.33.001Shao Y, Wen J T, Cheng W, et al. Provenances analysis and depositional systems of Upper Triassic Chang 63 sand set in Huanxian region in Ordos Basin[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2012, 12(33): 8807-8814(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2012.33.001 [6] 侯明才, 李旭, 邓敏. 鄂尔多斯盆地环县地区三叠系长8-长6油层组沉积相特征[J]. 成都理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 38(3): 241-248. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2011.03.001Hou M C, Li X, Deng M. Study on the sedimentary environment of Chang 8-6 oil-bearing formations of Yanchang Formation in Huanxian area, Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology: Science & Technology Edition, 2011, 38(3): 241-248(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2011.03.001 [7] 邓敏, 侯明才, 李旭. 鄂尔多斯盆地环县地区延长组长8-长6油层组基准面旋回结构样式及其储层地质意义[J]. 山东科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 30(2): 48-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3767.2011.02.009Deng M, Hou M C, Li X. The structural pattern of base-level cycle and its geological significance for the Chang 8-Chang 6 reservoir groups of the Yanchang Formation in Huan County, Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2011, 30(2): 48-57(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3767.2011.02.009 [8] 代勇. 鄂尔多斯盆地上里塬地区长6、长8储层非均质性研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2008.Dai Y. A study on heterogeneities of Chang 6 and Chang 8 reservoirs of Yanchang Formation at Shangliyuan area in Ordos Basin[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University, 2008(in Chinese with English abstract). [9] 戴群雄. 华池-南梁地区长6储层特征研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2014.Dai Q X. Reseach on characteristics of Chang 6 reservoir in Huachi-Nanliang region[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2014(in Chinese with English abstract). [10] 马瑶, 李文厚, 欧阳征健, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地南梁西区长6油层组砂岩低孔超低渗储层特征及主控因素[J]. 地质通报, 2013, 32(9): 1471-1476. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2013.09.017Ma Y, Li W H, Ouyang Z J, et al. Reservoir characteristics and main control factors of Chang 6 oil-bearing formation in western Nanliang area of Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2013, 32(9): 1471-1476(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2013.09.017 [11] 赵天林, 罗静兰, 邓媛, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地南梁西区延长组层序地层格架与生储盖组合特征[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2013, 25(5): 49-58, 64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201305012.htmZhao T L, Luo J L, Deng Y, et al. Sequence stratigraphic framework and source-reservoir-caprock assemblage of Yanchang Formation in western Nanliang area, Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2013, 25(5): 49-58, 64(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201305012.htm [12] Wang J J, Wu S H, Li Q, et al. Characterization of the pore-throat size of tight oil reservoirs and its control on reservoir physical properties: A case study of the Triassic tight sandstone of the sediment gravity flow in the Ordos Basin, China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 186: 106701. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106701 [13] 魏钦廉, 郑荣才, 肖玲, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地吴旗地区长6储层特征及影响因素分析[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2007, 19(4): 45-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX200704007.htmWei Q L, Zheng R C, Xiao L, et al. Influencing factors and characteristics of Chang 6 reservoir in Wuqi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2007, 19(4): 45-50(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX200704007.htm [14] 杨华, 刘自亮, 朱筱敏, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘上三叠统延长组物源与沉积体系特征[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(2): 10-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201302004.htmYang H, Liu Z L, Zhu X M, et al. Provenance and depositional systems of the Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in the southwestern Ordos Basin, China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(2): 10-18(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201302004.htm [15] 李鹏飞, 徐论勋, 李建明, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地华庆地区长6期物源分析[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2010, 30(2): 61-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD201002010.htmLi P F, Xu L X, Li J M, et al. Provenances of the Chang-6 oil measures in the Huaqing region, Orodos Basin[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2010, 30(2): 61-65(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD201002010.htm [16] 廖建波, 李智勇, 龙礼文, 等. 物源交会作用对油气富集的影响: 以鄂尔多斯盆地中部华庆地区长6段沉积期为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2013, 34(1): 20-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201301008.htmLiao J B, Li Z Y, Long L W, et al. The effect of provenance intersection on the petroleum enrichment: An example from Chang-6 Member in Huaqing area of central Orodos Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2013, 34(1): 20-23(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201301008.htm [17] Cao B F, Sun W, Li J. Reservoir petrofacies: A tool for characterization of reservoir quality and pore structures in a tight sandstone reservoir: A study from the sixth Member of Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 199: 108294. [18] 刘翰林, 杨友运, 王凤琴, 等. 致密砂岩储集层微观结构特征及成因分析: 以鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区长6段和长8段为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(2): 223-234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201802005.htmLiu H L, Yang Y Y, Wang F Q, et al. Micro pore and throat characteristics and origin of tight sandstone reservoirs: A case study of the Triassic Chang 6 and Chang 8 members in Longdong area, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(2): 223-234(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201802005.htm [19] Meng M M, Ge H K, Shen Y H. Evaluation of the pore structure variation during hydraulic fracturing in marine shale reservoirs[J]. Journal of Energy Resources Technology, 2021, 143(8): 083002. [20] Li P, Zheng M, Bi H. Pore throat structure and fractal characteristics of tight oil sandstone: A case study in the Ordos Basin, China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2017, 149: 665-674. [21] 杨智峰, 曾溅辉, 韩菲, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南部长6-长8段致密砂岩储层微观孔隙特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2017, 28(6): 909-919. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201706011.htmYang Z F, Zeng J H, Han F, et al. Characterization of microscopic pore texture of Chang 6-Chang 8 members tight sandstone reservoirs in the southwestern part of Ordos Basin, China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2017, 28(6): 909-919(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201706011.htm [22] 杨华, 付金华, 何海清, 等. 鄂尔多斯华庆地区低渗透岩性大油区形成与分布[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(6): 641-648. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201206002.htmYang H, Fu J H, He H Q, et al. Formation and distribution of large low-permeability lithologic oil regions in Huaqing, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(6): 641-648(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201206002.htm [23] 王华, 陈思, 巩天浩, 等. 牵引流化重力流沉积过程与堆积机制: 以渤海湾盆地歧口凹陷为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 95-104. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0111Wang H, Chen S, Gong T H, et al. Sedimentary process and accumulation mechanism of traction fluidization gravity flow: An example from Qikou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 95-104(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0111 [24] Zhang N, He M C, Zhang B, et al. Pore structure characteristics and permeability of deep sedimentary rocks determined by mercury intrusion porosimetry[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2016, 27(4): 670-676. [25] Beard D C, Weyl P K. Influence of texture on porosity and permeability of unconsolidated sand[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1973, 57(2): 349-369. [26] Yousuf AH F, Zhao Y C, Liu H P, et al. Origin and reservoir properties of deep-water gravity flow sediments in the Upper Triassic Ch6-Ch7 members of the Yanchang Formation in the Jinghe Oilfield, the southern Ordos Basin, China[J]. Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 2019, 37(4): 1227-1252. [27] 李智, 叶加仁, 曹强, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗独贵加汗区带下石盒子组储层特征及孔隙演化[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 49-60. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0404Li Z, Ye J R, Cao Q. Reservoir characteristics and pore evolution of the Lower Shihezi Formation in Duguijiahan zone, Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 49-60(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0404 [28] Meng D W, Jia A L, Ji G, et al. Water and gas distribution and its controlling factors of large scale tight sand gas fields: A case study of western Sulige Gas Field, Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2016, 43(4): 663-671. [29] 王伟, 宋渊娟, 黄静, 等. 利用高压压汞实验研究致密砂岩孔喉结构分形特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 22-30. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0402Wang W, Song Y J, Huang J, et al. Fractal characteristics of pore-throat structure in tight sandstones using high-pressure mercury intrusion porosimetry[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 22-30(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0402 [30] 杨华, 钟大康, 姚泾利, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区延长组砂岩储层孔隙成岩类型及其控制因素[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(2): 69-76. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201302011.htmYang H, Zhong D K, Yao J L, et al. Pore genetic types and their controlling factors in sandstone reservoir of Yanchang Formation in Longdong area, Ordos Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(2): 69-76(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201302011.htm [31] Ge X M, Fan Y R, Li J T, et al. Pore structure characterization and classification using multifractal theory: An application in Santanghu Basin of western China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2015, 127: 297-304. [32] Tang X L, Jiang Z X, Li Z, et al. The effect of the variation in material composition on the heterogeneous pore structure of high-maturity shale of the Silurian Longmaxi Formation in the southeastern Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2015, 23: 464-473. -





 下载:
下载: