Prediction of pressure distribution and formation mechanism in low exploration area: A case study of Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin
-
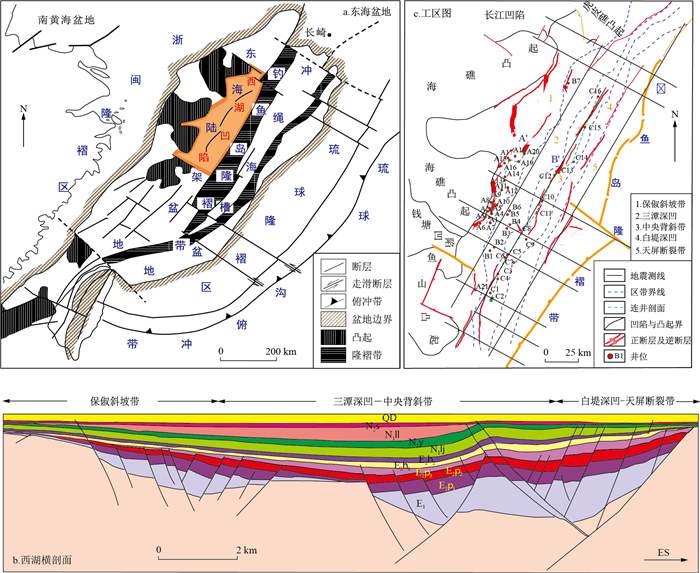
摘要: 基于地震速度谱资料,结合实测钻井压力、测井数据分析结果,从单井-剖面-平面系统预测了东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷的压力分布。研究结果表明:西湖凹陷储层呈现两套压力系统,分别为正常压力系统和超压系统,超压系统主要发育于花港组和平湖组内,层位上由西至东逐渐变新。泥岩亦表现为浅部常压、深部超压,不同的区带有所差异。西湖凹陷超压顶界面分布受深度控制不显著,主要受层位控制,超压顶界面通常位于花港组下段以及平湖组上段。西湖凹陷关键界面超压带覆盖范围、连续性总体较好,且具一定的区域展布方向,在规模较大断层具较明显的差异性。断层对压力的积累起着一定输导、分割和破坏作用。不均衡压实作用和生烃作用是西湖凹陷超压形成的主要机制,但在不同的区带存在较大差异。Abstract: The distribution of pressure was predicted in Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin by combining with the existing measured drilling pressure, log data analysis results and seismic velocity spectrum geophysical data. The results show that there are two sets of pressure systems, normal pressure system and overpressure system in Xihu Depression. The overpressure is mainly developed in Huagang Formation and Pinghu Formation, and the formation gradually changes younger from west to east. Mudstone is also characterized by shallow atmospheric pressure and deep overpressure, but varies in different zones. The interface of overpressure is mainly located in the lower part of Huagang Formation and the upper part of Pinghu Formation. The characteristics of the interface distribution of the overpressure are mainly controlled by the formation, and the depth has little effect on the distribution of the interface. The overpressure zone of the key interface covers a good continuity and has a certain regional distribution direction. There are obvious differences in large scale faults, which play a certain role in transporting, dividing and destroying the accumulation of pressure. Under-compaction and hydrocarbon generation are the main factors that produce overpressure in Xihu Depression, but there are great differences in different areas.
-
Key words:
- overpressure /
- distribution characteristics /
- prediction /
- formation mechanism /
- Xihu Depression
-
表 1 西湖凹陷部分超压钻井统计
Table 1. Statistics of the drilling overpressure formation in Xihu Depression
构造带 区带 井名 深度/m 实测压力/MPa 压力系数 测试点所在层位 保俶斜坡带 平北地区 A11 3 651.66 44.42 1.21 平湖组中段 A11 3 955.00 52.16 1.31 平湖组中段 A12 3 924.82 49.65 1.26 平湖组下段 A12 4 073.00 54.11 1.32 平湖组下段 A12 4 178.50 57.76 1.38 平湖组下段 A16 3 802.89 45.71 1.20 平湖组下段 A17 4 113.00 60.12 1.46 平湖组下段 A18 4 043.00 48.98 1.21 平湖组下段 A19 4 524.30 66.76 1.47 平湖组中段 A19 4 804.90 63.33 1.31 平湖组中段 A13 3 801.60 53.33 1.40 平湖组中段 平中地区 A1 3 789.50 50.50 1.33 平湖组下段 A1 4 148.50 73.82 1.77 平湖组下段 A1 4 278.50 73.50 1.71 平湖组下段 A2 3 379.00 44.22 1.30 平湖组下段 A2 3 494.50 50.61 1.44 平湖组下段 A2 3 574.00 52.59 1.47 平湖组下段 A2 3 619.00 55.54 1.53 平湖组下段 A3 3 327.80 42.07 1.26 平湖组下段 A3 3 397.30 44.17 1.30 平湖组下段 A3 3 429.00 49.66 1.44 平湖组下段 A3 3 501.50 52.74 1.50 平湖组下段 A4 3 678.00 46.50 1.26 平湖组下段 A4 3 695.50 44.66 1.20 平湖组下段 A7 3 765.14 56.49 1.50 平湖组下段 A10 3 780.00 52.51 1.38 平湖组下段 三潭深凹 B2 4 060.15 58.19 1.43 花港组下段 B3 4 142.03 54.41 1.31 花港组下段 B3 3 469.80 51.21 1.47 花港组下段 B4 4 144.76 62.53 1.50 花港组下段 B4 3 964.00 46.41 1.17 花港组下段 B5 4 284.20 53.38 1.24 花港组下段 B5 4 069.60 50.05 1.22 花港组下段 B5 3 962.30 49.20 1.24 花港组下段 B5 3 914.60 47.67 1.21 花港组下段 B6 4 619.50 72.67 1.57 花港组下段 B6 3 981.00 46.24 1.16 花港组下段 中央背斜带 C8 3 925.17 57.36 1.46 花港组下段 C10 3 167.90 44.52 1.40 花港组下段 C10 3 359.70 49.49 1.47 花港组下段 C12 4 182.00 51.43 1.23 花港组下段 C12 4 287.79 52.55 1.22 花港组下段 C12 4 316.00 52.89 1.22 花港组下段 C12 4 390.00 53.75 1.22 花港组下段 C13 4 280.00 53.68 1.25 花港组下段 表 2 西湖凹陷代表井泥岩超压顶界面深度统计
Table 2. Statistics of top interface depth of overpressure of mudstone in Xihu Depression
构造带 区带 井名 深度/m 层位 保俶斜坡带 平北地区 A11 3 450 平湖组上段 A12 3 800 平湖组中段 A14 3 300 平湖组中段 A15 3 550 平湖组上段 A16 3 200 平湖组中段 平中地区 A1 3 300 平湖组上段 A4 3 200 平湖组中段 A6 3 250 平湖组下段 A7 3 150 平湖组上段 A8 2 500 花港组下段 平南地区 A21 3 300 平湖组中段 三潭深凹 B1 2 450 花港组上段 B5 3 100 花港组上段 B6 2 900 花港组上段 B7 3 750 花港组上段 中央背斜带 C1 3 450 平湖组上段 C3 3 100 花港组下段 C5 3 100 平湖组上段 C7 3 100 花港组上段 C8 3 100 花港组上段 C9 3 000 花港组上段 C10 2 850 花港组上段 C13 3 000 花港组上段 表 3 计算压力与钻井实测压力对比
Table 3. Comparison between calculated pressure and measured pressure in drilling
序号 测试深度/m 实测压力/MPa 地震剖面深度/m 计算压力/MPa 相对误差/% 计算点 井号 1 3 028.62 51.13 3 071.08 46.07 -9.90 CDP5090 C1 2 3 359.70 56.88 3 355.82 46.98 -17.40 3 2632.03 26.07 2 630.07 27.35 4.92 4 3 167.90 44.52 3 160.89 44.25 -0.61 5 3 599.05 37.44 3 580.97 35.81 -4.35 CDP1570 A7 6 3 804.00 53.38 3 839.23 53.75 0.68 7 4 280.50 73.53 4 293.02 72.98 -0.75 CDP2610 A10 8 4 148.50 73.82 4 177.38 70.18 -4.93 9 3 797.00 50.59 3 723.23 50.26 -0.65 10 3 229.00 32.17 3 282.37 32.82 2.03 11 2 980.50 29.48 2 964.53 29.65 0.56 12 2 717.75 26.57 2 762.32 27.62 3.96 13 2 315.50 22.82 2 388.00 23.88 4.65 15 2 619.07 26.19 2 655.15 27.88 6.45 CDP6400 C5 16 2 794.82 27.83 2 750.46 28.88 3.77 18 1 950.46 19.46 1 994.79 20.34 4.53 19 2 984.50 29.36 2 948.17 31.43 7.04 20 4 284.20 53.38 4 262.52 53.28 -0.18 CDP2360 B4 21 4 069.60 50.05 4 055.32 50.69 1.28 22 3 962.30 49.20 3 953.78 49.42 0.45 23 3 738.30 39.38 3 754.25 42.55 8.06 -
[1] 郝芳, 邹华耀, 倪建华, 等.沉积盆地超压系统演化与深层油气成藏条件[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2002, 27(5):610-615. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx200205022 [2] 何生, 宋国奇, 王永诗, 等.东营凹陷现今大规模超压系统整体分布特征及主控因素[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2012, 37(5):1029-1042. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201205015 [3] 刘金水.西湖凹陷平湖构造带地层压力特征及与油气分布的关系[J].成都理工大学学报, 2015, 42(1):60-69. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cdlgxyxb201501008 [4] 侯志强, 于浩, 刘云, 等.西湖凹陷M气田区块低孔渗致密砂岩储层高精度三维孔隙压力场地震预测[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2):267-274. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201902032 [5] Liu Y, Jin Y L, Cao Q, et al.Tertiary hydrothermal activity and its effect on reservoir properties in the Xihu Depression, East China Sea[J].Petroleum Science, 2019, 16(2):14-31. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sykx-e201901002 [6] 郑军.西湖凹陷中央背斜带中北部深部优质储层孔隙保存机理[J].地质科技情报, 2016, 35(3):173-179. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201603022 [7] 杨彩虹, 孙鹏, 田超, 等.东海盆地西湖凹陷平湖组异常高压分布及形成机制探讨[J].海洋石油, 2013, 33(3):8-12. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hysy201303002 [8] 张银国.东海西湖凹陷花港组油气地质条件与油气分布规律[J].石油实验地质, 2010, 32(3):223-231. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sysydz201003004 [9] 唐贤君, 蒋一鸣, 张绍亮.平湖斜坡带火山岩层发育构造环境及油气地质意义[J].地质科技情报, 2018, 37(1):27-36. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201801004 [10] 叶加仁, 顾惠荣, 贾建谊.东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷油气成藏动力学[J].天然气工业, 2005, 25(12):5-8. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqgy200512002 [11] Zhang X G, Lin C Y, Muhammad A Z, et al.Paleosalinity and water body type of Eocene Pinghu Formation, Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin[J].Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2017, 158(9):469-478. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=24385c28bcf977a3bd5ed498889d6693 [12] Zhu Y M, Li Y, Zhou J, et al.Geochemical characteristics of Tertiary coal-bearing source rocks in Xihu depression, East China Sea basin[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2012, 35(8):154-165. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=830c5ad4a0a09023a9a880687147c809 [13] 张远兴, 叶加仁, 苏克露, 等.东海西湖凹陷沉降史与构造演化[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2009, 13(2):215-223. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx200902004 [14] Abbas A, Zhu H T, Zeng Z W, et al.Sedimentary facies analysis using sequence stratigraphy and seismic sedimentology in the Paleogene Pinghu Formation, Xihu Depression, East China Sea Shelf Basin[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 93(5):287-297. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c4f773079957bf81a3bc1e34bb973462 [15] 苏奥, 陈红汉.东海盆地西湖凹陷油岩地球化学特征及原油成因来源[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(6):1072-1082. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201506011 [16] 张先平, 张树林, 陈海红, 等.东海西湖凹陷平湖构造带异常压力与油气成藏[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(3):93-97. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200703013 [17] Su A, Chen H H, Chen X, et al.The characteristics of low permeability reservoirs, gas origin, generation and charge in the central and western Xihu Depression, east China sea basin[J].Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2018, 53(5):94-109. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=bce7e8dba10764e343740f3640f1f15e [18] 叶加仁, 韦必则, 周平, 等.东海西湖凹陷地下流体动力场研究[J].中国海上油气, 1999, 13(4):255-259. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=6059146 [19] 张先平, 陈海红, 张树林, 等.东海西湖凹陷温压系统与油气成藏[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2008, 28(2):87-90. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200802013 [20] 彭己君, 张金川, 唐玄, 等.低渗透背景下西湖凹陷致密砂岩气藏的成藏条件[J].地质科技情报, 2015, 34(3):107-112. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201503014 [21] 苏奥, 杜江民, 贺聪, 等.东海盆地西湖凹陷平湖构造带超压系统与油气成藏[J].中南大学学报, 2017, 48(3):742-750. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zngydxxb201703024 [22] 陈子剑.东海西湖凹陷低孔低渗气藏地层孔隙压力研究[D].北京: 中国石油大学, 2017. [23] 徐志星.西湖凹陷异常地层压力特征及其与油气成藏的关系[D].成都: 成都理工大学, 2015. [24] 张国华.西湖凹陷高压形成机制及其对油气成藏的影响[J].中国海上油气, 2013, 25(2):1-8. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghsyq-gc201302002 [25] 范景辉, 杨晓松.岩石波速温度和压力系数的测量方法及应用[J].地球物理学进展, 2002, 17(3):525-532. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxjz200203024 [26] 张卫华, 何生, 郭全.地震资料预测压力方法和展望[J].地球物理学进展, 2005, 20(3):814-817. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxjz200503038 [27] 金业权, 王越之, 李自俊.地震资料预测地层压力的研究[J].石油钻探技术, 2001, 29(3):28-30. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syztjs200103010 [28] 李刚毅.地层压力预测技术及应用研究[D].成都: 成都理工大学, 2009. [29] 赵靖舟, 李军, 徐泽阳.沉积盆地超压成因研究进展[J].沉积学报, 2017, 38(9):973-998. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb201709001 [30] Guo X W, He S, Liu K Y, et al.Oil generation as the dominant overpressure mechanism in the Cenozoic Dongying depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2010, 94(12):1859-1881. doi: 10.1306/05191009179 [31] Tingay M R P, Hillis R R, Swarbrick R E, et al.Origin of overpressure and pore-pressure in the Baram Province, Brunei[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2009, 93(1):51-74. doi: 10.1306/08080808016 [32] Tingay M R P, Morley C K, Laird A, et al.Evidence for overpressure generation by kerogen-to-gas maturation in the norther Malay Basin[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(4):539-672. http://aapgbull.geoscienceworld.org/content/97/4/639 [33] Goulty N R, Ramdhan A M, Jones S J.Chemical compaction of mudrocks in the presence of overpressure[J].Petroleum Geoscience, 2012, 18(4):471-479. doi: 10.1144/petgeo2012-018 [34] Teige G M, Hermanrud C, Wensaal L, et al.The lack of relationship between overpressure and porosity in North Sea and Haltenbanken shales[J].Marine and Petrileum Geology, 1999, 16(4):321-335. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(98)00035-X [35] Hunt J M, Whelan J K, Eglinton L B, et al.Gas generation a major cause of deep Gulf Coast overpressure[J].Oil and Gas Journal, 1994, 92(29):59-63. [36] Luo X R, Vasseur G.Geopressuring mechanism of organic matter cracking:Numerical modelling[J].AAPG Bulletin, 1996, 80(6):856-874. http://aapgbull.geoscienceworld.org/content/80/6/856 [37] 段谟东, 叶加仁, 吴景富, 等.东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷超压成因机制[J].地球科学, 2017, 42(1):119-129. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201701009 -





 下载:
下载: