Hydrocarbon origin and reservoir forming model of Wuyunting structure in Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin
-
摘要: 近年来,东海盆地西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带武云亭构造油气勘探获得了较好的商业发现,但已钻探的A井与B井流体性质差异较大,A井为气井、B井为油井。通过生物标志化合物对比、碳同位素分析及流体包裹体分析,对武云亭构造油气来源、充注期次及成藏模式进行了分析,结果表明武云亭构造油为正常成熟原油,主要来源于本地宁波19洼平湖组煤系烃源岩;天然气有两种,一种为高成熟天然气,主要来源于东侧主洼宁波27洼平湖组烃源岩,另一种为正常成熟天然气,主要来源于本地次洼宁波19洼烃源岩。包裹体荧光呈现为淡黄色油气包裹体和无色气包裹体,均一温度表明武云亭构造主要经历两期油气充注,时间为2 Ma和现今。武云亭构造油气来源丰富,成藏过程复杂,基于油气来源及成藏特征划分为"双源侧向晚期次生型"和"单源垂向晚期原生型"两种成藏模式。Abstract: In recent years, the oil and gas exploration of the Wuyunting structure in the Pinghu slope belt of Xihu Depression of the East China Sea Basin has reported good commercial discoveries, but the fluid properties of wells A and B that have been drilled are quite different. Well A is a gas reservoir and well B is a reservoir. The hydrocarbon source, filling period and accumulation model of Wuyunting structure were analyzed by biomarker compound comparison, carbon isotope analysis and fluid inclusion analysis. It is believed that the Wuyunting structural oil is a normal mature crude oil, mainly derived from the local Ningbo 19 sub-sag, Pinghu Formation coal-series source rock. The upper part of Pinghu Formation is high-mature natural gas, mainly from the main source of the eastern main shoal of Ningbo 19 sub-sag, Pinghu Formation, and the middle section of Pinghu Formation. It is a normal mature natural gas, mainly derived from local source rocks. The fluorescence of the inclusions is light yellow oil and gas inclusions and colorless gas inclusions. The uniform temperature indicates that the Wuyunting structure mainly undergoes two phases of hydrocarbon charging, 2 Ma and nowadays. The Wuyunting structure is rich in oil and gas resources, and the accumulation process is complex. Based on the hydrocarbon supply mode and the transport system, it is divided into two accumulation models: "dual-source lateral late secondary type" and "single-source vertical transport late native type".
-
Key words:
- Xihu Depression /
- hydrocarbon origin /
- organic inclusion /
- accumulation model
-
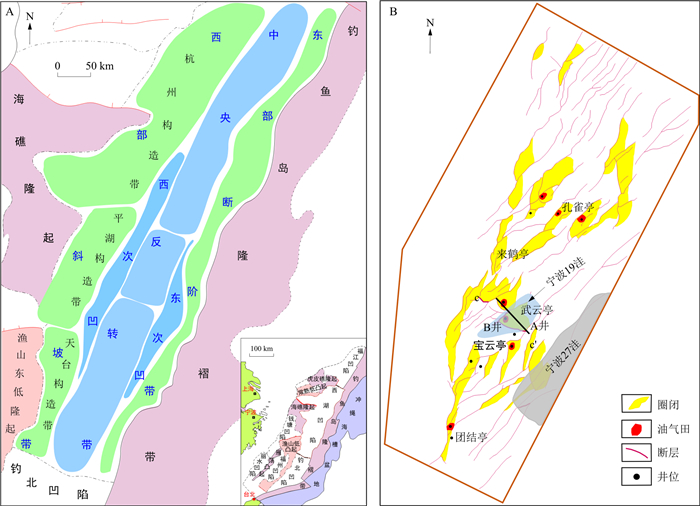
图 1 西湖凹陷构造位置示意图(A)及武云亭构造位置图(B)(据文献[4]修改)
A.西湖凹陷构造区划; B.武云亭构造及断裂
Figure 1. Structural position of Xihu Depression (A) and location map of Wuyunting structure (B)
图 3 武云亭构造天然气成因划分(底图据文献[12])
Ⅰ.煤成气区; Ⅱ.油型气区; Ⅲ.碳同位素系列倒转混合气区; Ⅳ.煤成气和油型气区; Ⅴ.煤成气、油型气和混合气区; Ⅵ.生物气和亚生物气区
Figure 3. Genetic classification of natural gas in Wuyunting structure
图 5 武云亭构造Vandre天然气成熟度计算分布图(底图据文献[15])
Figure 5. Vandre natural gas maturity calculation distribution in Wuyunting structure
图 16 武云亭油气成藏模式(剖面位置见图 1)
Figure 16. Hydrocarbon accumulation model in Wuyunting structure
表 1 武云亭构造天然气组分
Table 1. Natural gas components in Wuyunting structure
井 组段 砂层 组分摩尔分数/% C1 C2 C3 iC4 nC4 iC5 nC5 C6+ N2 CO2 A 平湖组中段 P8 84.40 7.05 2.60 0.54 0.55 0.19 0.14 0.28 0.12 4.13 P10 74.15 12.21 6.72 1.36 1.18 0.27 0.17 0.18 0.44 3.30 B 平湖组中段 P5 76.73 10.98 5.71 1.21 1.06 0.30 0.18 0.02 0.20 3.60 P8 76.30 9.74 6.14 1.83 1.27 0.44 0.24 0.02 0.48 3.53 表 2 武云亭构造天然气碳同位素
Table 2. Natural gas carbon isotope in Wuyunting structure
类型 井 组段 砂层 δ13C/‰ C1 C2 C3 nC4 气藏凝析气 A 平湖组中段 P8 -32.2 -24.9 -24.5 -25.5 P10 -36.9 -27.1 -25.1 -26.7 油藏溶解气 B 平湖组中段 P5 -36.5 -28.5 -25.9 -24.6 气藏凝析气 P8 -39.9 -29.5 -27.3 -26.2 表 3 武云亭构造原油物性
Table 3. Physocal properties of crude oil in Wuyunting structure
原油类型 井 组段 砂层 密度/(g·cm-3) 气油比/(m3·m-3) 凝固点/℃ 运动黏度/(50℃mm2·s-1) 含硫量/% 含蜡量/% 气藏凝析油 A 平湖组中段 P8 0.836 7597 16 1.37 0.06 8.18 P10 0.795 1170 3 2.23 0.047 3.36 油藏黑油 B 平湖组上段 P4 0.869 110 18 4.95 0.078 13.2 P4 0.856 102 18 3.84 0.064 13.7 气藏凝析油 平湖组中段 P5 0.845 273 19 5.68 0.074 12.7 P8 0.775 2039 11 1.25 0.028 5.5 表 4 武云亭构造油-源芳烃成熟度对比
Table 4. Oil-source aromatics maturity comparison in Wuyunting structure
井 组段 砂层 样品类型 4-MDBT/1-MDBT MPI1 计算Rc/% 实测Ro/% A 平湖组中段 P6 泥岩 4.60 0.54 0.72 0.72 P8 油 10.57 1.15 0.96 \ P10 油 8.48 1.01 0.91 \ B 平湖组中段 P8 煤 1.30 0.39 0.65 0.60 P8 泥岩 3.66 0.51 0.70 0.66 平湖组上段 P4 油 12.00 1.09 0.94 \ 平湖组中段 P5 油 8.01 1.03 0.91 \ 注:拟合关系:Rc=0.4×MPI1+0.5 -
[1] 彭伟欣.东海油气勘探成果回顾及开发前景展望[J].海洋石油, 2001, 21(3):1-6. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hysy200103001 [2] 周心怀, 蒋一鸣, 唐贤君.西湖凹陷成盆背景、原型盆地演化及勘探启示[J].中国海上油气, 2019, 31(3):1-10. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghsyq-gc201903001 [3] 姜亮.东海陆架盆地油气资源勘探现状及含油气远景[C]//姜亮.东海陆架盆地油气资源勘探论文集.北京: 石油工业出版社, 2004: 3-8. [4] 蒋一鸣.西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带平湖组碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄及米兰科维奇旋回:对源-汇系统及沉积演化的约束[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6):133-140. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93477A/20196/7100580445.html [5] 叶加仁, 顾惠荣, 贾健谊.东海西湖凹陷油气地质条件及其勘探潜力[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2008, 28(4):111-116. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200804014 [6] 刘金水, 邹玮, 李宁, 等."储保耦合"控藏机制与西湖凹陷大中型油气田勘探实践[J].中国海上油气, 2019, 31(3):11-19. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghsyq-gc201903002 [7] 李宁, 覃军, 江瀚, 等.西湖凹陷T气田油气分布特征与主控因素[J].断块油气田, 2017, 24(3):329-332. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dkyqt201703007 [8] 苏奥, 陈红汉, 王存武, 等.东海盆地西湖凹陷天然气来源探讨[J].地质科技情报, 2014, 33(1):157-162. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201401024 [9] 黄志超, 叶加仁.东海海域油气资源与选区评价[J].地质科技情报, 2010, 29(5):51-55. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201005008 [10] 唐贤君, 蒋一鸣, 张绍亮.平湖斜坡带火山岩层发育构造环境及油气地质意义[J].地质科技情报, 2018, 37(1):27-36. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201801004 [11] 刘道燕.东海陆架盆地烃源岩及其烃类特点[C]//姜亮.东海陆架盆地油气资源勘探论文集.北京: 石油工业出版社, 2004: 181-187. [12] 戴金星.各类烷烃气的鉴别[J].中国科学:化学生命科学地学, 1992, 11(2):185-193. [13] Whiticar M J.Stable isotope geochemistry of coals, humicKerogens and related natural gases[J].International Journal of Coal Geology, 1996, 32(1):191-215. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0166516296000420 [14] Cheng Xiong, Hou Dujie, Zhao Zhe, et al.Sources of natural gases in the Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin:Insights from stable carbon isotopes and confined system pyrolysis[J].Energy & Fuel, 2018, 3(4):126-136. [15] Vandre C, Cramer B, Gerling P, et al.Natural gas formation in the western Nile delta (Eastern Mediterranean):Thermogenic versus microbial[J].Organic Geochemistry, 2007, 38:523-539. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2006.12.006 [16] Ohm S E, Karlsen D A, Austin T J F.Geochemically driven exploration models in uplifted areas:Examples from the Norwegian Barents Sea[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2008, 92(9):1191-1223. doi: 10.1306/06180808028 [17] Prinzhofer A, Vega M A G, Battani A, et al.Gas geochemistry of the Macuspana basin (Mexico):Thermogenic accumulations in sediments impregnated by bacterial gas[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2000, 17:1029-1040. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(00)00033-7 [18] Pallasser R J.Recognising biodegradation in gas/oil accumulations through the δ13C compositions of gas components[J].Organic Geochemistry, 2000, 31:1363-1373. doi: 10.1016/S0146-6380(00)00101-7 [19] Zou Yanrong, Cai Yulan, Zhang Chongchun, et al.Variations of natural gas carbon isotope-type curves and their interpretation:A case study[J].Organic Geochemistry, 2007, 38:1398-1415. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2007.03.002 [20] 钱门辉.西湖凹陷煤系烃源岩生烃特征研究[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2010. [21] 侯读杰, 张林晔.实用油气地球化学图鉴[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2003:159-173. [22] Losh S, Cathles L.Phase fractionation and oil-condensate mass balance in the South Marsh Island Block 208-239 area, offshore Louisiana[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2010, 27(2):467-475. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2009.10.004 [23] 凡元芳.储层沥青的研究进展及存在问题[J].石油地质与工程, 2009, 23(6):35-38. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hnsy200906011 [24] 胡守志, 付晓文, 王廷栋, 等.储层中的沥青沉淀带及其对油气勘探的意义[J].天然气地球科学, 2007, 18(1):99-103. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx200701018 [25] 周心怀, 高顺莉, 高伟中, 等.东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷平北斜坡带海陆过渡型岩性油气藏形成与分布预测[J].中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(2):153-163. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgsykt201902003 -





 下载:
下载: