Application of geostatistical inversion constrained by sequence framework in thin-bedded sandbody prediction
-
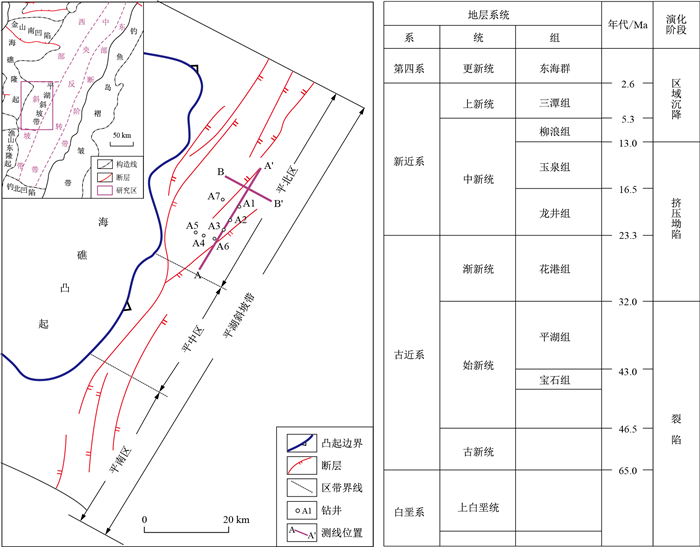
摘要: 西湖凹陷砂岩储层具有砂体厚度薄、砂泥互层发育以及横向变化快的特点,传统的地球物理方法很难精细地刻画砂体空间分布。将层序地层学与地质统计学反演相结合,在建立等时地层格架的基础上,构建相应的地球物理模型,在正确的沉积学理论指导下,对西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带平湖组砂岩储层开展砂体的时空分布预测研究。研究结果表明,平湖组可划分出3个三级层序,下部砂体单层厚度较大,横向连续性好,平面连片发育;中部以泥岩为主,砂体孤立发育,连续性差;上部砂体增多,单层厚度较薄,横向连续性好。结合钻井实际资料分析表明,砂体预测结果垂向分辨率可以达到1~2 m。地质统计学反演有效解决了西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带薄层砂体识别的难题,可为研究区有利储层预测提供重要支撑。Abstract: The spatial distribution of the sand reservoir in Xihu Depression is difficult to predict precisely by using traditional geophysical techniques, owing to the following two main reasons:1)The single-layer thickness of the sand reservoir is thin; and 2)Interbeds of sandstone and mudstone show rapid and frequent lateral lithofaices change.Based on geological data and geophysical techniques, the isochronous sequence stratigraphic framework of the Eocene Pinghu Formation in Pinghu slope belt of Xihu Depression was established.The sandbody distribution within the sequence stratigraphic framework was predicted by using geostatistical inversion.The result shows that Pinghu Formation can be divided into three 3rd-order sequences.The lower sandbody is characterized by large single layer thickness, good lateral continuity, and contiguous plane development.The middle part is composed mainly of mudstone, with the isolated sandbody and poor continuity.The upper part exhibits an increase trend in layer thickness in sandbody with fine lateral continuity.Comparison of the geophysical research with traditional geological research reveals that the vertical resolution of sandbody prediction results obtained by geostatistical inversion could reach a resolution down to 1-2 m.The results indicate that geostatistical inversion is an effective approach to solve the problem on precise lithofacies identification and spatial distribution prediction by using 3D seismic data in Xihu Depression, providing valuable guidance for the favorable reservoir prediction in the future.
-
Key words:
- sequence stratigraphy /
- geostatistical inversion /
- reservoir prediction /
- Xihu Depression
-
图 2 西湖凹陷平湖组单井及地震层序界面划分(剖面位置见图 1)
Figure 2. Drilling and seismic sequence interface of Pinghu Formation in Xihu Depression
图 9 北西向地质统计学反演砂体预测剖面(剖面位置见图 11)
Figure 9. SE-trending sandbody prediction section obtained by implementing geostatistical inversion
图 10 北东方向地质统计学反演砂体预测剖面(剖面位置见图 11)
Figure 10. NE-trending sandbody prediction section obtained by implementing geostatistical inversion
图 12 过A1、A2、A6井砂体预测剖面地质验证(剖面位置见图 11)
Figure 12. Sandbody prediction section for geological verification through wells A1, A2, A4
-
[1] Casey J S, Shuhab D K, Janok P B, et al.Thin-bedded reservoir analogs in an ancient delta using terrestrial laser scanner and high-resolution ground-based hyperspectral cameras[J].Sedimentary Geology, 2016, 342:154-164. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2016.07.004 [2] Wang P W, Jin Z J, Pang Q Q, et al.Characteristics of dual media in tight-sand gas reservoirs and its impact on reservoir quality:A case study of the Jurassic reservoir from the Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin, Northwest China[J].Geological Journal, 2018, 53(6):2558-2568. doi: 10.1002/gj.3091 [3] 柯友亮, 郝杰, 王华, 等.基于叠后地震数据的南堡凹陷高南斜坡带三角洲扇体识别及演化特征[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2):89-100. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201902011 [4] Wang Z G, Gao J H, Lei X L, et al.Application of 3D seismic attributes to optimize the placement of horizontal wells within a tight gas sand reservoir, Ordos Basin, China[J].Geophysics, 2016, 81(3):B77-B86. doi: 10.1190/geo2015-0244.1 [5] Haas A, Dubrule O.Geostatistical inversion:A sequential method for stochastic reservoir modeling constrained by seismic data[J].First Break, 1994, 13(12):561-569. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/283874036_Geostatistical_inversion_a_sequential_method_of_stochastic_reservoir_modeling_constrained_by_seismic_data [6] Dubrule O, Thibaut M, Lamy P, et al.Geostatistical reservoir characterization constrained by 3D seismic data[J].Petroleum Geoscience, 1998, 4(2):121-128. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=CC029759390 [7] Bosch M, Mukerji T, Gonzalez E F.Seismic inversion for reservoir properties combining statistical rock physics and geostatistics:A review[J].Geophysics, 2010, 75(5):165-176. http://scitation.aip.org/getabs/servlet/GetabsServlet?prog=normal&id=GPYSA700007500000575A165000001&idtype=cvips&gifs=Yes [8] Nunes R, Soares A, Azevedo L, et al.Geostatistical seismic inversion with direct sequential simulation and Co-simulation with multi-local distribution functions[J].Mathematical Geosciences, 2017, 49(5):583-601. doi: 10.1007/s11004-016-9651-0 [9] 赵海波, 唐晓花, 李奎周, 等.基于地震岩石物理分析与叠前地质统计学反演技术的齐家地区致密薄储层预测[J].石油物探, 2017, 56(6):83-92. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sywt201706011 [10] 戴婉薇, 范乐元, 胡圣利, 等.基于地质统计学反演和储层分类的相控储层建模方法研究及应用[J].地质科技情报, 2017, 36(1):236-241. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201701031 [11] Johansen T A, Jensen E H, Mavko G, et al.Inverse rock physics modeling for reservoir quality prediction[J].Geophysics, 2013, 78(2):M1-M18. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ab6b37dd35aa031dea22ea312b987bbe [12] 马良涛, 范廷恩, 王宗俊, 等.不确定性反演关键参数的地质含义及正演模型反演研究-以渤海海域W油田为例[J].地球物理学进展, 2017, 32(1):224-230. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQWJ201701031.htm [13] Hemn R, Omid A, Ahmad A.A geostatistical investigation of 3D magnetic inversion results using multi-Gaussian kriging and sequential Gaussian co-simulation[J].Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2018, 154:136-149. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2018.05.003 [14] Xie G L, Shen Y L, Liu S G, et al.Trace and rare earth element (REE) characteristics of mudstones from Eocene Pinghu Formation and Oligocene Huagang Formation in Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin:Implications for provenance, depositional conditions and paleoclimate[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 92(4):20-36. http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=7f2fb359bf88f18a4c9fb3de30ec1d9a [15] 胡明毅, 沈娇, 胡蝶.西湖凹陷平湖构造带平湖组砂岩储层特征及其主控因素[J].石油与天然气地质, 2013, 34(2):185-191. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz201302007 [16] 唐贤君, 蒋一鸣, 张绍亮.平湖斜坡带火山岩层发育构造环境及油气地质意义[J].地质科技情报, 2018, 37(1):27-36. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201801004 [17] 侯国伟, 李帅, 秦兰芝, 等.西湖凹陷西部斜坡带平湖组源-汇体系特征[J].中国海上油气, 2019, 31(3):29-39. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghsyq-gc201903004 [18] 张国华, 张建培.东海陆架盆地构造反转特征及成因机制探讨[J].地学前缘, 2015, 22(1):260-270. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy201501022 [19] 赵丽娜, 陈建文, 张银国, 等.东海西湖凹陷平湖构造带平湖组沉积特征[J].世界地质, 2008, 27(1):42-47. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sjdz200801008 [20] 刘金水, 廖宗廷, 贾健谊, 等.东海陆架盆地地质结构及构造演化[J].上海国土资源, 2003, 24(3):1-6. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=shdz200303001 [21] 蒋一鸣, 周倩羽, 李帅, 等.西湖凹陷西部斜坡带平湖组含煤岩系沉积环境再思考[J].中国煤炭地质, 2016, 28(8):18-25. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgmtdz201608004 [22] 张绍亮, 蒋一鸣.西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带始新统平湖组层序地层[J].海洋地质前沿, 2013, 29(10):8-13. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzdt201310002 [23] 张建培, 徐发, 钟韬, 等.东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷平湖组-花港组层序地层模式及沉积演化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(1):35-41. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201201006 [24] Vail P R, Mitchum R M, Thompson I S.Seismic stratigraphy and global changes of sea level:Part 3.Relative changes of sea level from coastal onlap[J].Bull.Am.Assoc.Petrol.Geol.Mem., 1977, 26(9):1859-1866. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10004120435 [25] 操应长, 姜在兴, 夏斌, 等.利用测井资料识别层序地层界面的几种方法[J].中国石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2003, 27(2):23-26. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sydxxb200302007 [26] 徐强, 姜烨, 董伟良, 等.中国层序地层研究现状和发展方向[J].沉积学报, 2003, 21(1):155-167. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb200301025 [27] Wang G C, Carr T R.Marcellus shale lithofacies prediction by multiclass neural network classification in the appalachian basin[J].Mathematical Geosciences, 2012, 44(8):975-1004. doi: 10.1007/s11004-012-9421-6 [28] Wang X J, Sain K, Satyavani N, et al.Gas hydrates saturation using geostatistical inversion in a fractured reservoir in the Krishna-Godavari basin, offshore eastern India[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 45:224-235. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.04.024 [29] Liu X C, Lu Y C, Lu Y B, et al.The application of geostatistical inversion in shale lithofacies prediction:A case study of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi marine shale in Fuling area in the southeast Sichuan Basin, China[J].Marine Geophysical Research, 2018, 39(3):421-439. doi: 10.1007/s11001-017-9317-4 [30] 范廷恩, 马良涛, 胡光义, 等.基于层序地层学的地质统计学反演[J].地球物理学进展, 2019, 34(1):80-89. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxjz201901011 [31] Larsen A L, Ulvmoen M, Omre H, et al.Bayesian lithology/fluid prediction and simulation on the basis of a Markov-chain prior model[J].Geophysics, 2006, 71(5):R69-R78. doi: 10.1190/1.2245469 [32] Rimstad K, Omre H.Impact of rock-physics depth trends and Markov random fields on hierarchical Bayesian lithology/fluid prediction[J].Geophysics, 2010, 75(4):R93-R108. doi: 10.1190/1.3463475 [33] Ulvmoen M, Omre H.Improved resolution in Bayesian lithology/fluid inversion from prestack seismic data and well observations:Part 1-Methodology[J].Geophysics, 2010, 75(2):R21-R35. http://scitation.aip.org/getabs/servlet/GetabsServlet?prog=normal&id=GPYSA7000075000002000B73000001&idtype=cvips&gifs=Yes [34] 樊鹏军, 马良涛, 王宗俊, 等.地质统计学反演中变差函数地质含义及求取方法探讨[J].地球物理学进展, 2017, 32(6):2444-2450. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxjz201706022 [35] Hong T C, Mrinal K.A new MCMC algorithm for seismic waveform inversion and corresponding uncertainty analysis[J].Geophysical Journal International, 2010, 177(1):14-32. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1111/j.1365-246X.2008.04052.x [36] Boaga J, Vignoli G, Cassiani G.Shear wave profiles from surface wave inversion:The impact of uncertainty on seismic site response analysis[J].Journal of Geophysics & Engineering, 2011, 8(2):162-174. http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/iop/jge/2011/00000008/00000002/art00004 [37] Ren Z Y, Thomas K.Uncertainty and resolution analysis of 2D and 3D inversion models computed from geophysical electromagnetic data[J].Surveys in Geophysics, 2019(5):1-66. -





 下载:
下载: