Characteristics and indication of terrestrial biomarkers of crude oil in different local structures of Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin
-
摘要: 利用地球化学分析手段,对西湖凹陷黄岩构造带、平北地区以及宁波构造带的16个轻质油样品进行了分析。原油中富含反映陆源高等植物输入的生物标志化合物,尤其是源于被子植物、裸子植物及蕨类植物的三环、四环二萜类及其芳构化产物,而反映水生低等植物输入的生物标志化合物含量较低。不同构造带间原油中这些化合物的分布特征具有明显差异,如异海松烷/nC20、异海松烷/(异海松烷+16β(H)扁枝烷)、1,2,5-三甲基萘/1,3,6-三甲基萘、1,7-二甲基菲/(惹烯+1,7-二甲基菲)等。这些差异指示了宁波构造带与平北地区原油裸子植物输入较多,蕨类植物及被子植物输入较少,而黄岩构造带原油蕨类植物输入较多,被子植物与裸子植物较少的特点。研究中利用全油色谱-质谱将原油饱和烃与芳烃组分建立联系,提出(异海松烷+1,7-二甲基菲)/(惹烯+16β(H)扁枝烷)作为反映西湖凹陷轻质原油生源构成的指标,而该参数与全油碳同位素值的正相关关系证明了裸子植物树脂对西湖凹陷轻质油的重要成烃贡献。Abstract: Sixteen light oil samples from Huangyan structural belt, Pingbei area and Ningbo structural belt in Xihu Depression were analyzed by geochemical analysis. The crude oil samples are rich in biomarkers related to the input of terrestrial higher plants, especially the tricyclic and tetracyclic diterpenes and their aromatization compounds derived from angiosperm, gymnosperms, and pteridophytes, while the content of biomarkers reflecting the input of aquatic plants are relatively low. The distribution of these high plant biomarkers between different local structures is obviously different, such as isopimarane/nC20, isopimarane/(isopimarane+16β(H)-phyllocladane), 1, 2, 5-trimethyl naphthalene/1, 3, 6-trimethyl naphthalene, and 1, 7-dimethyl phenanthrene/(retene+1, 7-dimethyl phenanthrene). These differences indicate that there are high contents of gymnosperms input, and low contents of pteridophytes and angiosperms input of crude oil from the Ningbo structural belt as well as the Pingbei area. However, crude oil from the Huangyan structural belt has more pteridophytes input and fewer angiosperms and gymnosperms input. In this study, whole oil gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis was used to develop a relationship between saturated hydrocarbons and aromatic hydrocarbons. The ratio of (isopimarane+1, 7-dimethyl phenanthrene)/(retene+16β(H)-phyllocladane) was proposed as an index to reflect the provenance of organic matter of light oil in Xihu Depression, and the positive correlation between the parameter values and whole oil carbon isotope values proves that the gymnosperms have the most important hydrocarbon-generating contribution to the crude oil in Xihu Depression.
-
Key words:
- diterpenoids /
- biomarkers /
- provenance of organic matter /
- light oil /
- evaporative fractionation
-
图 7 西湖凹陷典型原油芳烃萘系列与菲系列化合物分布特征
a.萘系列质量色谱图,峰侧所标的数字为萘上甲基取代位置;2.2-甲基萘;1.1-甲基萘; 1, 7.1, 7-二甲基萘;1, 2, 5.1, 2, 5-三甲基萘;1, 2, 5, 6 & 1, 2, 3, 5.1, 2, 5, 6+1, 2, 3, 5-四甲基萘;b.菲系列质量色谱图,在峰上标的数字为菲上甲基取代位置,2.2-甲基菲;3.3-甲基菲;9.9-甲基菲; 1.1-甲基菲; 1, 7.1, 7-二甲基菲
Figure 7. Naphthalene and phenanthrene compounds distribution characteristic of typical crude oil samples in Xihu Depression
表 1 原油样品基本信息及物性数据
Table 1. Basic information and physical property data of crude oil samples
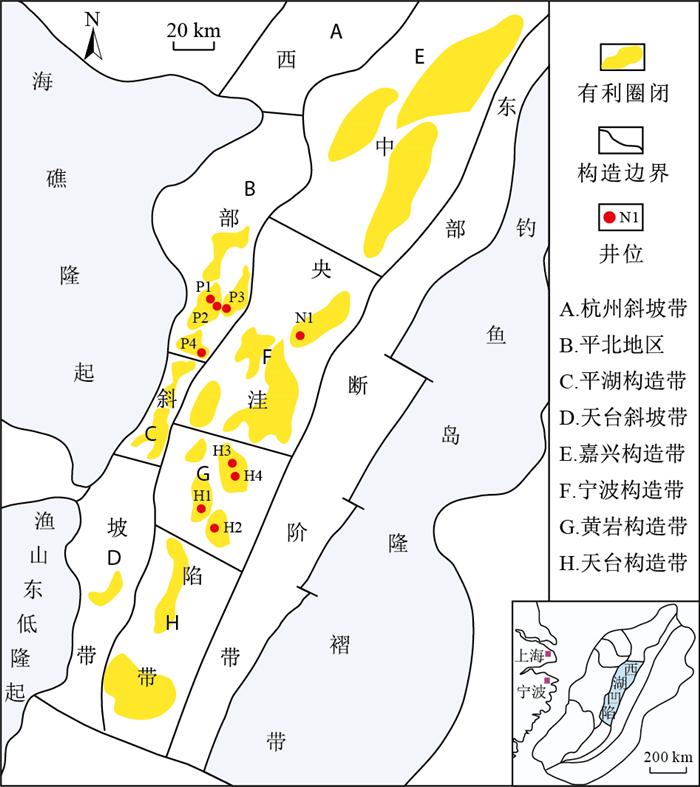
井号 深度/m 层段 构造位置 密度/(g·cm-3) 含蜡量/% 含硫量/% Rc/% H1 2 704.3~2 719.0 E3h上 黄岩构造带 0.79 0.68 0.05 1.34 H1 2 805.8~2 811.3 E3h上 黄岩构造带 0.81 0.33 N.A. 1.37 H1 2 984.5~2 989.5 E3h下 黄岩构造带 0.81 0.41 0.02 1.32 H2 2 512.5~2 519.5 E3h上 黄岩构造带 0.77 1.92 0.05 1.42 H2 3 031.5~3 039.0 E3h下 黄岩构造带 0.80 3.69 0.06 1.29 H3 3 350.0~3 361.0 E3h上 黄岩构造带 0.78 0.79 0.04 1.41 H4 3 416.2~3 437.4 E3h上 黄岩构造带 0.79 1.46 0.01 1.51 P1 4 150.0~4 169.0 E2p下 平北地区 0.84 2.11 0.10 1.57 P2 4 107.5~4 111.0 E2p上 平北地区 0.79 1.62 0.05 1.25 P2 4 186.7~4 202.5 E2p中 平北地区 0.82 3.08 0.07 1.26 P3 4 183.0~4 196.0 E2p上 平北地区 0.82 3.27 0.04 1.29 P3 4 548.7~4 566.2 E2p中 平北地区 0.86 10.54 0.07 1.20 P4 4 359.0~4 382.0 E2p下 平北地区 0.84 8.18 0.06 1.30 P4 4 580.0~4 620.0 E2p中 平北地区 0.80 20.00 0.05 1.24 N1 3 709.0~3 739.0 E3h上 宁波构造带 0.80 5.84 0.08 1.61 N1 3 769.0~3 799.0 E3h上 宁波构造带 0.84 7.75 0.02 1.59 注:Rc=2.432 2×MDI(甲基双金刚烷指数)+0.438 9;MDI=4-MD(甲基双金刚烷)/(1-MD+3-MD+4-MD)[15] 表 2 西湖凹陷原油样品地球化学参数
Table 2. Geochemical parameters of crude oil samples in Xihu Depression
井号 层段 A B C D E F G H I J K H1 E3h上 11.11 1.29 0.16 0.61 0.16 0.32 0.12 0.35 0.87 4.69 2.23 H1 E3h上 8.44 1.26 0.16 0.57 0.15 0.24 0.13 0.34 0.89 5.21 2.30 H1 E3h下 8.82 1.34 0.17 0.63 0.12 0.21 0.14 0.37 0.89 4.15 2.63 H2 E3h上 9.48 0.2 2.12 0.43 0.02 0.22 0.19 0.81 1.11 0.61 0.68 H2 E3h下 7.69 1.64 0.2 0.38 0.02 0.22 0.20 0.74 0.94 0.84 0.71 H3 E3h上 8.19 0.98 0.13 0.67 0.10 N.A. 0.16 0.54 1.02 4.19 2.80 H4 E3h上 8.51 1.08 0.14 0.61 0.16 0.18 0.19 0.66 0.92 3.95 1.85 P1 E2p下 10.16 0.21 0.03 0.76 0.05 N.A. 0.18 0.55 0.96 5.08 6.09 P2 E2p上 6.68 0.95 0.15 0.84 0.63 0.77 0.09 0.30 1.31 9.30 6.58 P2 E2p中 8.15 0.83 0.13 0.83 0.62 N.A. 0.09 0.30 1.30 10.06 6.60 P3 E2p上 7.55 1.46 0.2 0.84 0.46 0.24 0.11 0.33 1.20 8.72 6.50 P3 E2p中 6.79 0.83 0.13 0.74 0.61 0.24 0.11 0.51 1.56 7.23 3.94 P4 E2p下 5.06 1.04 0.14 0.78 0.86 0.48 0.10 0.32 1.28 6.65 4.09 P4 E2p中 5.63 1.04 0.14 0.84 0.54 0.38 0.04 0.15 1.57 7.52 6.51 N1 E3h上 6.94 0.55 0.09 0.98 0.18 0.25 0.08 0.27 0.85 25.09 41.91 N1 E3h上 7.43 0.58 0.09 0.98 0.14 N.A. 0.08 0.27 0.80 31.97 45.67 A.Pr/Ph;B.Pr/nC17;C.Ph/nC18;D.异海松烷/(异海松烷+16β(H)扁枝烷);E.异海松烷/nC20;F.Ts/Tm;G.(1, 2, 5, 6-四甲基萘+1, 2, 3, 5-四甲基萘)/四甲基萘系列;H.1, 2, 5-三甲基萘/1, 3, 6-三甲基萘;I.1-甲基菲/9-甲基菲;J.1, 7-二甲基菲/惹烯;K.(异海松烷+1, 7-二甲基菲)(扁枝烷+惹烯) -
[1] Li S, Yu X, Steel R, et al.Change from tide-influenced deltas in a regression-dominated set of sequences to tide-dominated estuaries in a transgression-dominated sequence set, east China sea shelf Basin[J].Sedimentology, 2018, 65(7):2312-2338. doi: 10.1111/sed.12466 [2] Abbas A, Zhu H, Zeng Z, et al.Sedimentary facies analysis using sequence stratigraphy and seismic sedimentology in the paleogene Pinghu Formation, Xihu depression, east China sea shelf basin[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 93:287-297. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.03.017 [3] 王文娟, 张银国, 张建培.东海盆地西湖凹陷渐新统花港组地震相特征及沉积相分布[J].海相油气地质, 2014, 19(1):64-72. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hxyqdz201401008 [4] Zhu Y, Li Y, Zhou J, et al.Geochemical characteristics of tertiary coal-bearing source rocks in Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2012, 35(1):154-165. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2012.01.005 [5] 苏奥, 陈红汉.东海盆地西湖凹陷油岩地球化学特征及原油成因来源[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(6):136-146. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201506011 [6] 贾健谊, 须雪豪, 孙伯强.东海西湖凹陷原油与天然气的地球化学特征[J].海洋石油, 2000, 20(2):1-7. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK200000739087 [7] Cheng X, Hou D, Zhao Z, et al.Sources of natural gases in the Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin:Insights from stable carbon isotopes and confined system pyrolysis[J].Energy & Fuels, 2019, 33(3):2166-2175. [8] 许婷, 侯读杰, 曹冰.东海盆地西湖凹陷凝析油和轻质油生源母质剖析[J].地球化学, 2015, 44(3):79-90. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqhx201503008 [9] 魏恒飞, 陈践发, 陈晓东, 等.西湖凹陷平湖组滨海型煤系烃源岩发育环境及其控制因素[J].中国地质, 2013, 40(2):131-141. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201302013 [10] 苏奥, 陈红汉, 王存武, 等.东海盆地西湖凹陷天然气来源探讨[J].地质科技情报, 2014, 33(1):157-162. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201401024 [11] 蒋一鸣.西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带平湖组碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄及米兰科维奇旋回:对源-汇系统及沉积演化的约束[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6):133-140. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93477A/20196/7100580445.html [12] 易琦, 邵龙义, 秦兰芝, 等.西湖凹陷平湖构造带花港组沉积环境与聚煤规律[J].煤炭科学技术, 2018, 46(2):78-88. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-MTKJ201802009.htm [13] Zhu X, Chen J, Li W, et al.Hydrocarbon generation potential of paleogene coal and organic rich mudstones in Xihu Depression, East China sea shelf basin, offshore eastern China[J].Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019(184):106450. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092041051930871X [14] 周心怀, 高顺莉, 高伟中, 等.东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷平北斜坡带海陆过渡型岩性油气藏形成与分布预测[J].中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(2):21-32. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgsykt201902003 [15] Chen J, Fu J, Sheng G, et al.Diamondoid hydrocarbon ratios:Novel maturity indices for highly mature crude oils[J].Organic Geochemistry, 1996, 25(3/4):179-190. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0146638096001258 [16] Hakimi M H, Abdullah W H, Shalaby M R.Organic geochemical characteristics of crude oils from the Masila Basin, eastern Yemen[J].Organic Geochemistry, 2011, 42(5):465-476. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2011.03.015 [17] Wu P, Hou D, Gan J, et al.Paleoenvironment and controlling factors of Oligocene source rock in the eastern deep-water area of the Qiongdongnan basin:Evidences from organic geochemistry and palynology[J].Energy & Fuels, 2018, 32(7):7423-7437. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000040440388010_57a9.html [18] 柯友亮, 王华, 甘华军, 等.准噶尔盆地南缘芦草沟组上段油页岩有机地球化学特征及其沉积意义[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3):199-207. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201903021 [19] 李碧, 黄光辉, 徐阳东, 等.塔中台盆区原油正构烷烃摩尔浓度分布特征及意义[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2011, 30(1):97-103. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwysdqhxtb201101014 [20] Meulbroek P, Cathles Ⅲ L, Whelan J.Phase fractionation at south eugene island block 330[J].Organic Geochemistry, 1998, 29(1):223-239. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0146638098001806 [21] Peters K E, Walters C C, Moldowan J M.The biomarker guide[M].: Biomarkers & Isotopes in Petroleum Systems & Earth History Ed, 2005, 2: 490. [22] Ritts B D, Hanson A D, Zinniker D, et al.Lower-middle Jurassic nonmarine source rocks and petroleum systems of the northern Qaidam basin, northwest China[J].AAPG Bulletin, 1999, 83(12):1980-2005. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=4f34450e482723babe2eddf5f2fab618 [23] Noble R A, Alexander R, Kagi R I, et al.Identification of some diterpenoid hydrocarbons in petroleum[J].Organic Geochemistry, 1986, 10(4):825-829. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0146638086800195 [24] 傅宁.东海盆地西湖凹陷煤系烃源岩及凝析油中的二萜化合物[J].中国海上油气:地质, 1994, 8(1):23-30. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400608672 [25] Jiang L, Zhang M.Geochemical characteristics and significances of rearranged hopanes in hydrocarbon source rocks, Songliao Basin, NE China[J].Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2015, 131:138-149. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2015.04.035 [26] Cao Z, Liu G, Xiang B, et al.Geochemical characteristics of crude oil from a tight oil reservoir in the Lucaogou Formation, Jimusar sag, Junggar Basin[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2017, 101(1):39-72. doi: 10.1306/05241614182 [27] 赵帮胜, 李荣西, 王香增, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地延长探区山西组泥页岩沉积地球化学特征及有机质保存条件分析[J].地质科技情报, 2016, 35(6):103-111. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201606015 [28] Moldowan J M, Sundararaman P, Schoell M.Sensitivity of biomarker properties to depositional environment and/or source input in the lower toarcian of sw-germany[J].Organic Geochemistry, 1986, 10(4):915-926. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0146638086800298 [29] Li Z.Geochemical features and source analysis of crude oils from the western slope of bayanhushu sag, hailaer basin[J].Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(4):595-600. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb201204008 [30] Heppenheimer H, Steffens K, Püttman W, et al.Comparison of resinite-related aromatic biomarker distributions in cretaceous-tertiary coals from canada and germany[J].Organic Geochemistry, 1992, 18(3):273-287. doi: 10.1016/0146-6380(92)90069-A [31] Wang R, Sun R, Liu G, et al.A review of the biogeochemical controls on the occurrence and distribution of polycyclic aromatic compounds (PACs) in Coals[J].Earth-Science Reviews, 2017, 171:400-418. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.06.011 [32] Alexander R, Larcher A V, Kagi R I, et al.The use of plant-derived biomarkers for correlation of oils with source rocks in the cooper/eromanga basin system, Australia[J].Appea Journal, 1988, 28(1):310-324. doi: 10.1071/AJ87024 [33] Disnar J R, Harouna M.Biological origin of tetracyclic diterpanes, N-alkanes and other biomarkers found in lower carboniferous gondwana coals (Niger)[J].Organic Geochemistry, 1994, 21(2):143-152. doi: 10.1016/0146-6380(94)90151-1 [34] Philp R P.Geochemical characteristics of oils derived predominantly from terrigenous source materials[J].Geological Society London Special Publications, 1994, 77(1):71-91. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1994.077.01.04 [35] 盛国英, 傅家谟, 刘德汉, 等.富含于泥盆系角质残植煤中的四环二萜烷[J].石油与天然气地质, 1991, 12(2):107-116. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=598337 [36] Noble R A, Alexander R, Kagi R I, et al.Tetracyclic diterpenoid hydrocarbons in some Australian coals, sediments and crude oils[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1985, 49(10):2141-2147. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(85)90072-9 [37] Ellis L, Singh R K, Alexander R, et al.Formation of isohexyl alkylaromatic hydrocarbons from aromatization-rearrangement of terpenoids in the sedimentary environment:A new class of biomarker[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(23):4747-4763. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(96)00281-5 -





 下载:
下载: